Records of Natural Products
Year: 2022 Volume: 16 Issue:3 May-June
1) Two New 13-oxomilbemycins from a NTG-Induced Mutation Strain of Streptomyces avermitilis AVE-H39
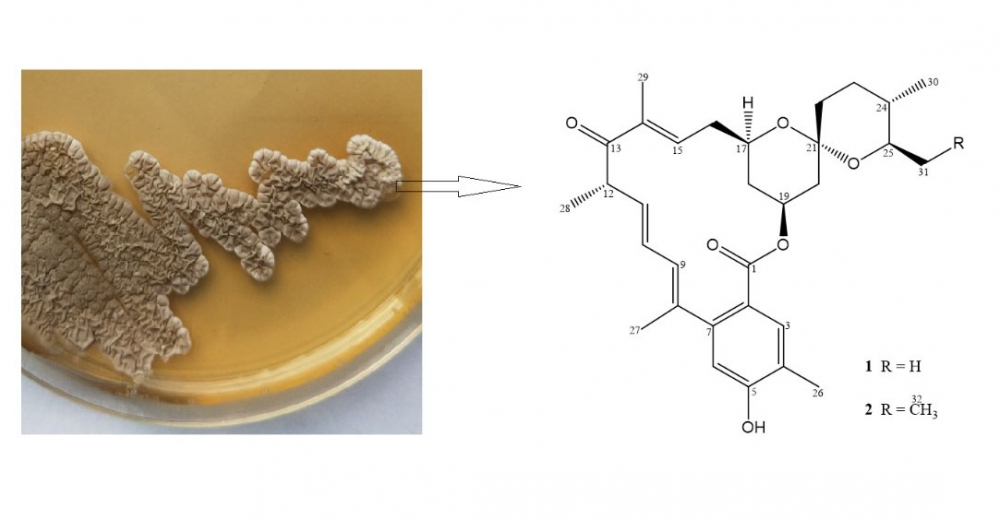
Two new 13-oxomilbemycins, 13-oxomilbemycin β3 (1) and 25-ethyl-13-oxomilbemycin β3 (2), were isolated from the broth of a NTG-induced mutation strain of Streptomyces avermitilis AVE-H39. The structures of 1 and 2 were determined based on MS and extensive NMR analysis. Compounds 1 and 2 possessed moderate nematocidal activity.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.269.2105.2075 Keywords Streptomyces avermitilis AVE-H39 NTG-induced mutation 13-oxomilbemycins nematocidal activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Anti-Obesity and Antihyperlipidemic Effects of Musa cavendishii
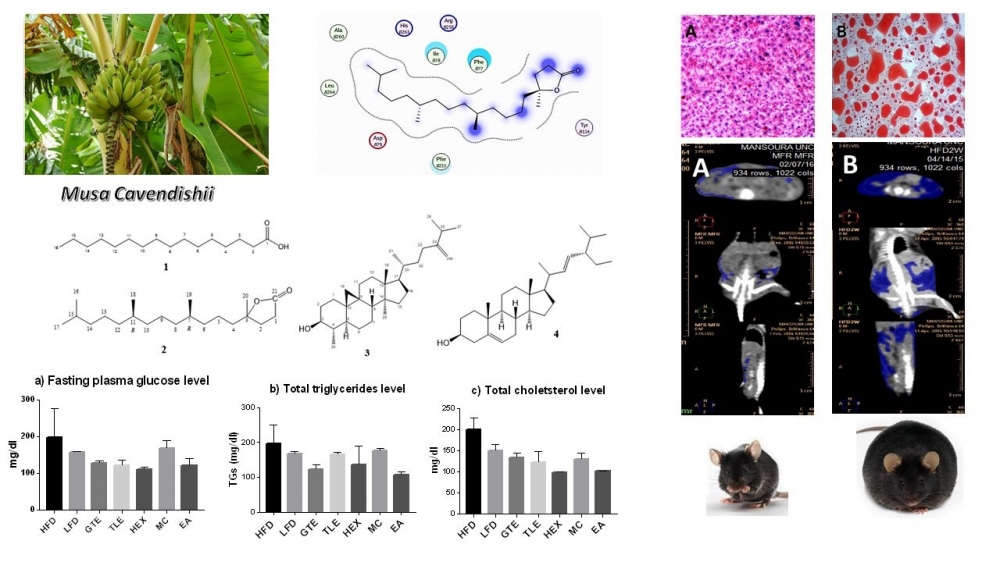
Obesity is a major risk factor in many health problems. This study explored the anti-obesity and antihyperlipidemic effects of Musa cavendishii Lamb. leaves. Doses of 1200 mg/kg of M. cavendishii methanol extract, or 300 mg/kg of fractions, were given to C57BL/6J mice fed with a high-fat diet (HFD) for 7 weeks. The reduction in fat volume was determined using CT scan and histopathological examination of mice livers. The results showed that the n-hexane and the EtOAc fractions reduced the body fat volume to 2.0% and 2.2% respectively, compared to 20.1% in the HFD group. Also, treated groups showed almost normal liver architecture with no fat vacuoles compared to the HFD group. Moreover, the treated groups showed a reduction in the levels of some obesity-related biochemical parameters, including plasma glucose, cholesterol, and triglycerides levels. Chromatographic fractionation of the bioactive n-hexane extract afforded four known compounds viz., palmitic acid (1), 5-methyl-5-(4,8,12-trimethyl-tridecyl)-dihydro-furan-2-one (2), cycloeucalenol (3), and stigmasterol (4). These compounds were in vitro and in silico studied for their pancreatic lipase (PL) inhibition. Compound 2 showed remarkable PL inhibition (89.8%) compared to orlistat (85.0%) at 200 µM, which was in full agreement with the docking scores (-7.19 and -4.05, respectively).
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.275.2103.2001 Keywords musa cavendishii anti-obesity antihyperlipidemic banana leaf anti-adipogenesis pancreatic lipase DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Chemical Composition of Flower Volatiles and Seeds Fatty Acids of Rosa iliensis Chrshan, an Endemic Species from Kazakhstan
Abstract
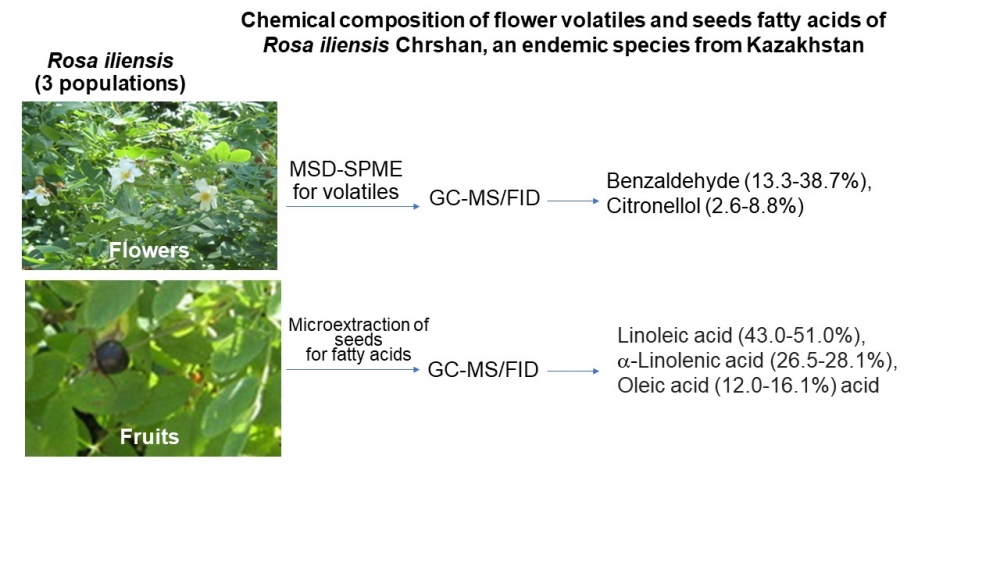
In the present work, the flower volatiles and seed fatty acids compositions of three populations (P-I, P-II, P-III) of Rosa iliensis were investigated for the first time. R. iliensis is a rare, endangered, narrow-endemic species growing in floodplains of the Ili and Sharyn rivers of Almaty region. The flower volatiles have been investigated with the tandem of MSD-SPME and GC-MS/FID techniques. The seed lipids were extracted from the ripe fruits with the microextraction technique. The flower volatiles of R. iliensis three populations were characterized by the abundance of oxygenated monoterpenes with benzaldehyde (13.3-38.7 %) and citronellol (2.6-8.8 %) as the major constituents. There were detected significant differences in floral scents between the populations. The flowers of P-I (from Sharyn River) contain sesquiterpene g-elemene (8.8%), the flowers of P-II (upper reaches of the Ili River) were rich in a-gurjunene (12.8%), while flowers of P-III (lower reaches of the Ili River) contained any sesquiterpenes. Seven fatty acids were determined in the seeds and unsaturated acids were found to be dominant for studied populations. Linoleic (43.0-51.0%), a-linolenic (26.5-28.1%) and oleic (12.0-16.1%) acids were detected as the major constituents. The present study shows that R. iliensis species is rich source of valuable volatiles and fatty acids.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.271.2105.2083 Keywords Rosa iliensis population volatiles fatty acids MSD-SPME GC-MS/FID DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
4) Anti-Inflammatory Components from the Fruits of Amomum aromaticum
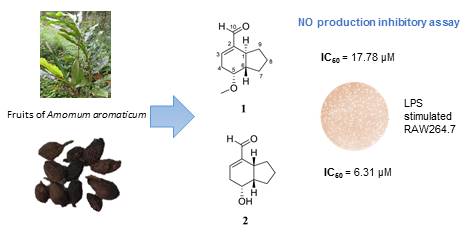
In the course of searching for bioactive components from a Vietnamese spice, the fruits of Amomum aromaticum, a new bicyclic nonane (1) and seven known compounds including 4 monoterpenes (2, 3, 5, 6), one fatty acid (4), and two steroids (7-8) were isolated. Their structures were determined on the basis of spectroscopic analysis. This is the first report of compounds tsaokoin (2), 1β,2α-dihydroxy-p-menth-5-ene (3), oleic acid (4), β-sitosterol (7), and daucosterol (8) in A. aromaticum. To evaluate the anti-inflammatory activities of the isolates, we measured their inhibitory activity against lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in a RAW264.7 murine macrophage model. The new compound rel-(1S,5R,6S)-5-methoxybicyclo[4.3.0]non-2-ene-2-carbaldehyde (1) and tsaokoin (2) showed substantial anti-inflammatory effects, with IC50 values of 17.78 and 6.31 µM, respectively. Thus, A. aromaticum fruits could be a rich source for the discovery of anti-inflammatory agents.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.270.2105.2068 Keywords Amomum aromaticum bicyclic nonane tsaokoin anti-inflammation DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Scopariaine A: A New Alkaloid from Scoparia dulcis with Protective effect on Cardiomyocytes Injury in Vitro
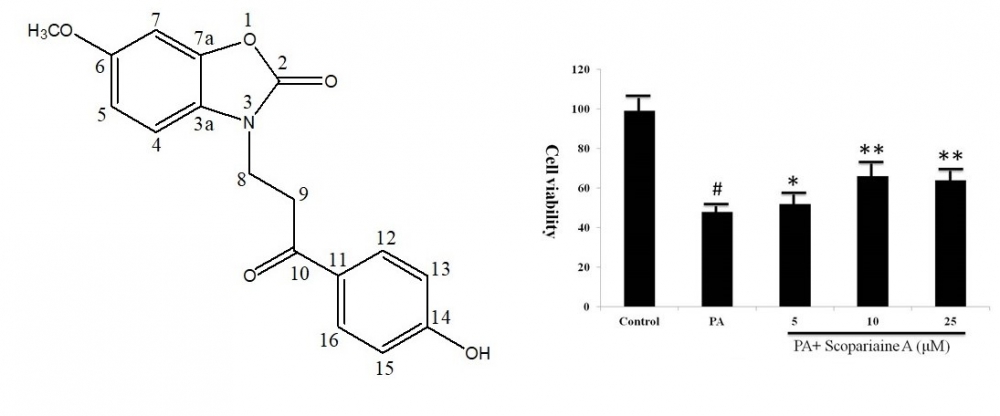
A new alkaloid, named scopariaine A (1), was obtained from the whole plant of Scoparia dulcis L. The new structure was established by various spectroscopic tmethods including 1D (1H-, 13C-NMR), 2D-NMR (HMBC, HSQC) and high resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HR-ESI-MS). Scopariaine A (1) was tested for its protective effect on attenuating palmitate-induced viability at 5, 10 and 25 μM. The results showed that the cell viability was increased in palmitic acid combined with scopariaine A (1) treated H9C2 cells.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.268.2105.2073 Keywords Scoparia dulcis L. scopariaine A alkaloid H9C2 cells DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Constituents of the Flower of Maxillaria tenuifolia and Their Anti-Diabetic Activity
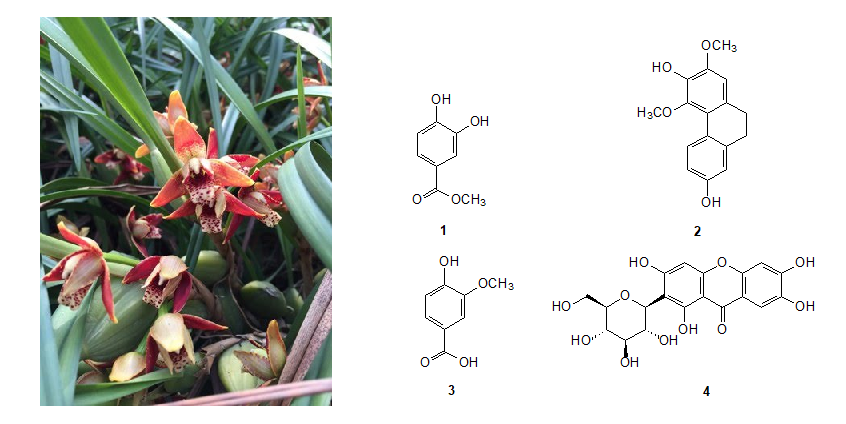
The EtOAc extract of the flower of Maxillaria tenuifolia, which had shown potent α-glucosidase inhibitory, was subjected to activity-guided isolation to yield four compounds, 3,4-dihydroxy benzoic acid methyl ester (1), flavanthridin (2), vanillic acid (3) and mangiferin (4). Their structures were ascertained by comparison of their physical and spectroscopic properties with those reported in the literature. Among them, flavanthridin (2), vanillic acid (3) and mangiferin (4) showed significant α-glucosidase inhibitory activity compared to acarbose at the concentration 1.0 mg/mL. Besides, 3,4-dihydroxy benzoic acid methyl ester (1) and mangiferin (4) also showed more effective in against the peroxidation of linoleic acid in an aqueous system than trolox. These results indicated that the EtOAc extract of M. tenuifolia and the related constituents might have anti-diabetic effect by suppressing carbohydrate disintegration and could prevent damage to organisms by oxidative stress.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.274.2106.2093 Keywords α-glucosidase diabetes maxillaria tenuifolia antioxidative DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) Phenolic Acid Analogues from Balanophora laxiflora Inhibit Proliferation of In Vitro Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells
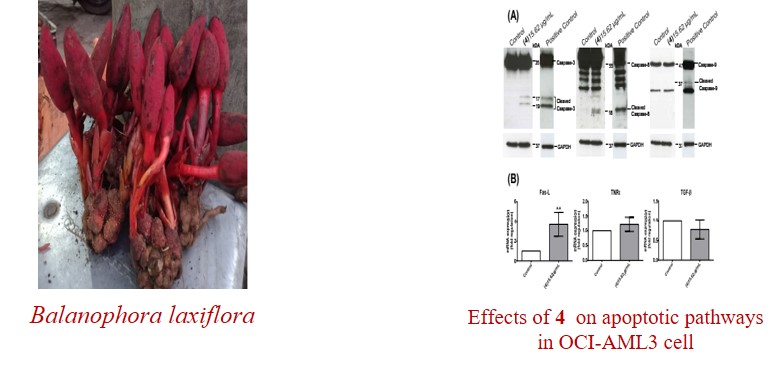
Four phenolic analogues isolated from Balanophora laxiflora; methylgallate (1, MG), 4-hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamaldehyde (2), 3-methoxycinnamic acid (3), and methyl caffeate (4, MC) were shown to have antiproliferative activity on acute myeloid leukemia (OCI-AML3) cells due to impaired cell cycle progression. Three of these compounds (1, 3, and 4) caused increased apoptosis and decreased proliferationin cells. Interestingly, MC (compound 4) significantly decreased the percentage of cells in S phase and G2/M phase, and significantly increased apoptosis in cells at low concentrations. Treatment with these compounds increased Fas ligand production and caspase-8/3, but not caspase-9-dependent, apoptosis. These results suggest that dosing with these compounds decreases proliferation and increases apoptosis in cell lines derived from hematological cancers.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.273.2106.2117 Keywords Balanophora laxiflora hemsl. ex forbes & hemsl phenolic acid analogues antiproliferative activity caspase-8 acute myeloid leukemia cell (OCI-AML) human cancer cell lines DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) A New Diterpenoid with Antitumor Cytotoxicity from Millipede
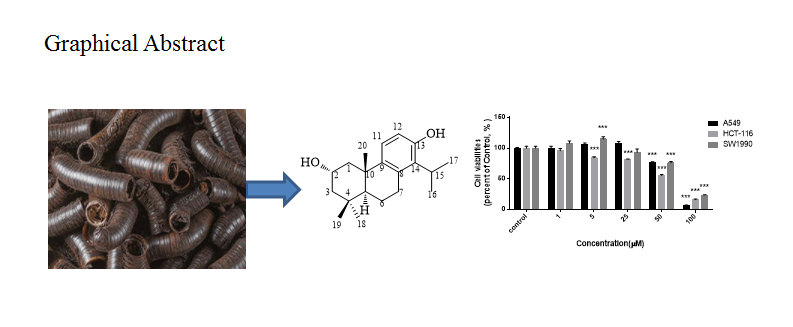
A new diterpenoid, namely millipedine A (10), along with nine known compounds (1–9), were isolated from the methanol extract of Millipede. Their structures were established on the basis of spectroscopic analysis including one and two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy and comparison with previously reported data. New compound showed moderate cytotoxicity against A549, HCT-116, and SW1990 cell lines in MTT assay.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.278.21.07.2135 Keywords Millipede diterpenoid antitumor activities DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.9) A New Organic Acid Derivative from the Fruits of Rosa roxburghii

Phytochemical investigation of the fruits of Rosa roxburghii resulted in the isolation of four organic acid derivatives and three phenylpropanoids, including a new organic acid derivative, Roxbuacidester A (1) and six known compounds (2-7). The structures of all isolates were established by 1D and 2D NMR spectra referring to the literatures, together with HR-MS spectrometric analysis. In addition, compounds 1 and 2 were evaluated for their inhibitory activities on nitric oxide (NO) production stimulated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in a RAW 264.7 cell line. Compounds 1 and 2 showed moderate inhibition of NO production with IC50 values of 46.8 ± 2.3 and 62.5 ± 3.7 μM, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.276.21.07.2138 Keywords Rosaceae Rosa roxburghii organic acid derivative DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.10) Investigation of Pesticidal Activities of Essential Oils Obtained from Vitex Species

Essential oils from renewable plant sources are important considerations for environmentally benign botanical pesticides. In this work, the leaf essential oils of four species of Vitex (Lamiaceae) have been collected from north-central Vietnam, analyzed by gas chromatographic techniques, and screened for mosquito larvicidal activity and molluscicidal activity. Vitex ajugifolia and V. pinnata essential oils were dominated by sesquiterpenoids (97.8% and 95.8%, respectively). In contrast, however, the essential oils of V. trifolia subsp. litoralis showed monoterpenoids to be dominant. The essential oils of V. trifolia subsp. trifolia also showed abundant monoterpenoids (38.4% and 68.0%), but also included (E)-β-caryophyllene (15.8 and 14.5%). Vitex pinnata essential oil showed excellent larvicidal activity against Aedes aegypti and Culex quinquefasciatus. Both V. trifolia litoralis and V. trifolia trifolia demonstrated notable molluscicidal activities against Gyraulus convexiusculus and Pomacea canaliculata. The research results suggest that essential oils of Vitex species might have potential to be used as natural pesticides.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.266.21.06.2108 Keywords mosquito larvicidal molluscicidal chemical composition botanical pesticide DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.