Records of Natural Products
Year: 2024 Volume: 18 Issue:2 March-April
1) Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Activities of Tradescantia spathacea
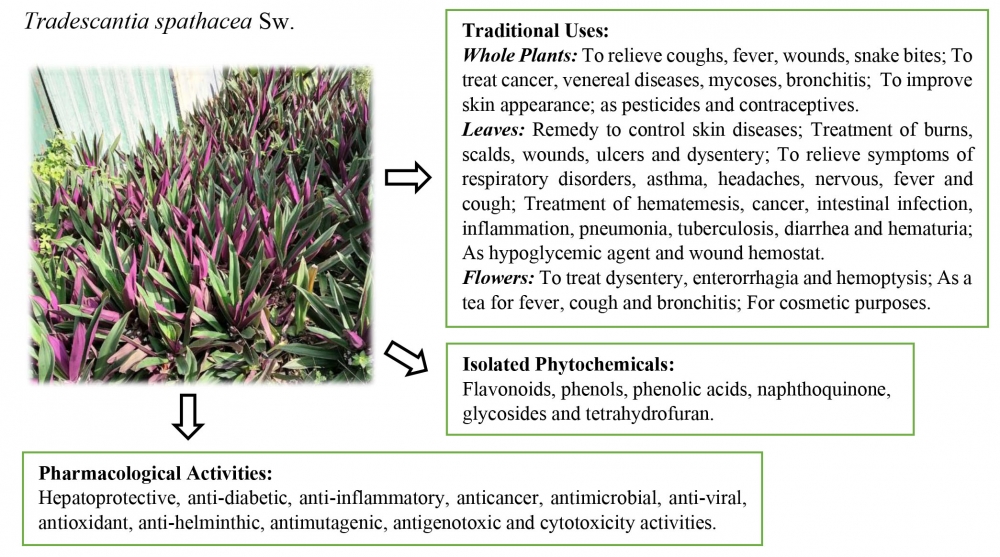
Tradescantia spathacea has been traditionally employes for treating various conditions, including coughs, fevers, wounds, inflammation, and oxidative-related diseases. This paper presents a comprehensive review of its traditional uses, alongside an examination of phytochemical and pharmacological studies aimed at validating ethnopharmacological practices. A systematic search across electronic databases using relevant keywords yielded 845 articles, of which 70 articles were reviewed. T. spathacea exhibits a broad spectrum of pharmacological activities, as evidenced by in vivo studies demonstrating hepatoprotective, anti-diabetic, anti-inflammatory and anticancer effects. In vitro studies further support its medicinal properties, including antimicrobial, anti-viral, antioxidant, anti-helminthic, antimutagenic, antigenotoxic and cytotoxic activities. While these modern pharmacological properties substantiate traditional uses, further research is essential to validate them and develop safe and effective therapeutic formulations. Further investigations should focus on bioassay-guided isolation of bioactive compounds, extensive pharmacological, clinical, and toxicological studies, incorporating adequate data replication, proper standardization and control groups, and the selection of reasonable doses or concentrations of extracts and controls.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.436.2311.2983 Keywords Commelinaceae Tradescantia spathacea traditional uses phytochemistry pharmacological properties DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Whole Genome Expression Analysis Identifies Multiple Targeted Integrative Effects of Polyphenol-Rich Propolis on HER-2-Positive Breast Cancer Cell Line
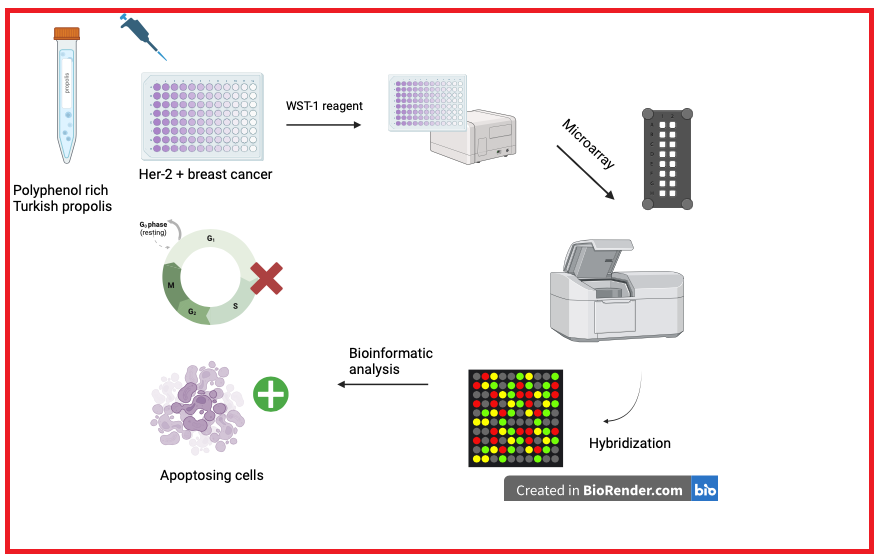
Natural products have been focused by researchers due to their important anticarcinogenic characteristics in the treatment of cancer with the slightest side effects possible. Propolis is one of the most prominent candidates among these natural products in terms of its anticancer features. In this study we aim to research the effects of Anatolian propolis on ER/PR-, HER-2/neu+ human breast cancer cell line SK-BR-3 with intent to clarify the molecular mechanism propolis in HER+ breast cancers in overview of whole genomic expression for the first time via a microarray experiment. Afterwards, microarray data was validated via real time PCR with the selected genes. After performing bioinformatic analysis via GeneSpring Software and String analysis, a 50 µg/mL dose of propolis affected several pathways of HER-2 positive breast cancer cells including cell cycle, DNA repair and apoptosis especially at 48th hour exposure. In contrast, after exposure to 50 µg/mL dose of propolis, up-regulated genes were detected at diverse pathways such as immune response, cell migration regulation, organization of cell-cell adhesion, etc. For this reason, we proposed that polyphenol-rich propolis can be used in the treatment of HER-2 positive breast cancer with characteristics of less toxic than the current treatment methods
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.437.23.10.2947 Keywords Breast cancer HER-2 microarray flavonoids bioinformatics DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Two New Furanones Isolated from Coptis deltoidea Rhizome
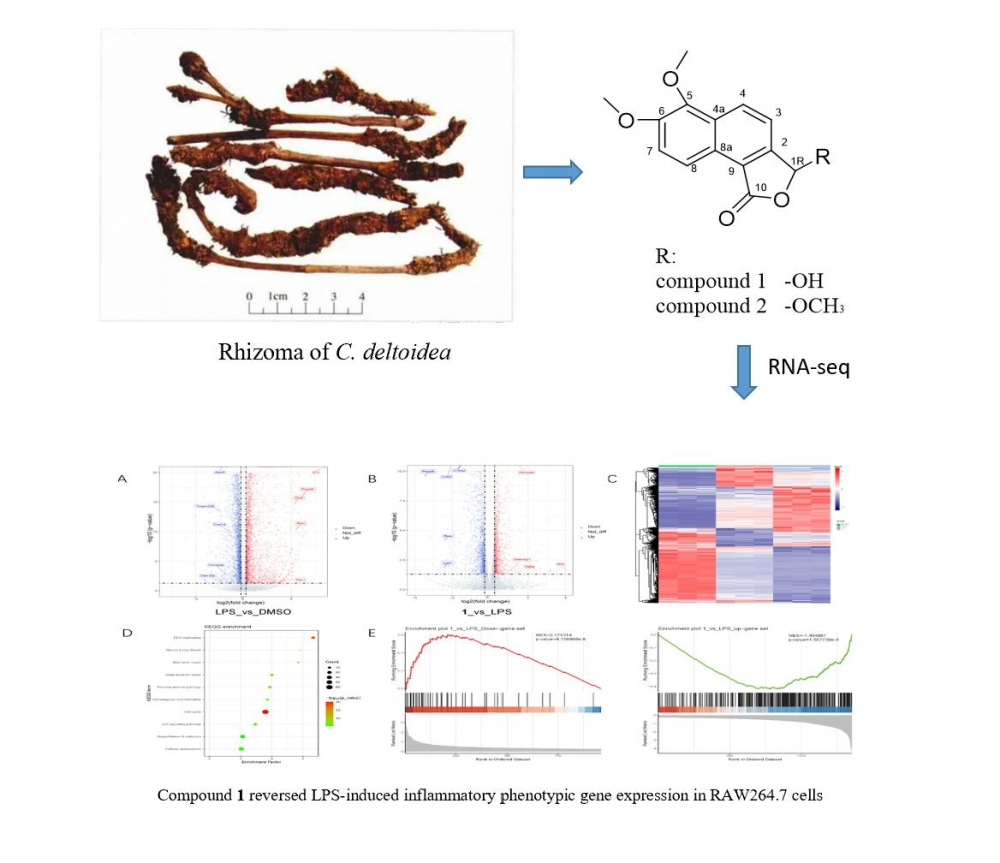
Two undescribed furanones (1-2) were isolated from Coptis deltoidea rhizome. HRESIMS, NMR and ECD calculations were used to ascertain their structures. Based on the inflammation cell model of RAW264.7 macrophage which induced by lipopolysaccharides (LPS), RNA-Seq was used to reveal the biological activity of 1. According to the findings, 1 dramatically changed the genes expression profile of the inflammatory cell model produced by LPS in RAW264.7 cells which indicated that it had potential anti-inflammatory activitiy.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.442.2310.2941 Keywords Structural elucidation RNA-Seq RAW264.7 anti-inflammatory DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Chemical Composition, Antioxidant Potential and Antibacterial Activity of Pistacia atlantica Desf. Essential Oil Leaves, with A Focus on Variations in The Main Trunk Diameter
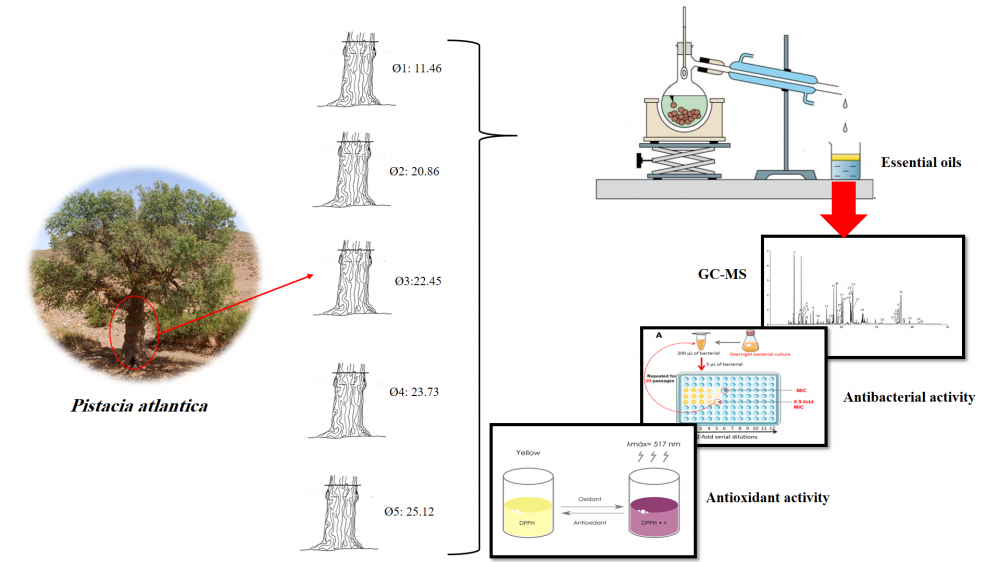
The aim of the present study is to assess the chemical compounds, antibacterial potential, and antioxidant qualities of essential oils as extracted from dried leaves of five Pistacia atlantica of different trunk diameters from Rommani (a rural area in the west of Morocco). The DPPH and FRAP methods are used to measure antioxidant activity. Essential oils have been tested on Acinetobacter baumannii, Escherichia coli, Enterobacter cloacae, Klebsiella pneumonia, Staphylococcus aureus, and Staphylococcus epidermidis. The essential oils were analysed using gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (GC/MS) analysis. The obtained results show that the tree's diameter, which is proportional to its age, was related to the original components. Terpinen-4-ol (19.00%–22.33%) with a diameter greater than or equal to 23.73 cm and α-Pinene (18.49%–37.51%), smaller than or equal to 22.45cm, are the two primary components. The findings of the DPPH and FRAP tests indicate that the IC50 values range from 8.70 ± 0.02 mg/mL to 11.46 ± 0.01 mg/mL and the EC50 values range from 8.27 ± 0.04 mg/mL to 12.76 ± 0.16 mg/mL, respectively. The interval of the zone of inhibition [8.77 ± 1.48 mm – 12.07 ± 2.51 mm], according to the results of antibacterial activity testing, shows that MIC and MBC vary between 4 and 10 µL/mL.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.447.2311.2984 Keywords P. atlantica DPPH chemical compounds antibacterial activity secondary metabolites biological activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Identification of Diverse Sesquiterpenoids from Eupatorium adenophorum
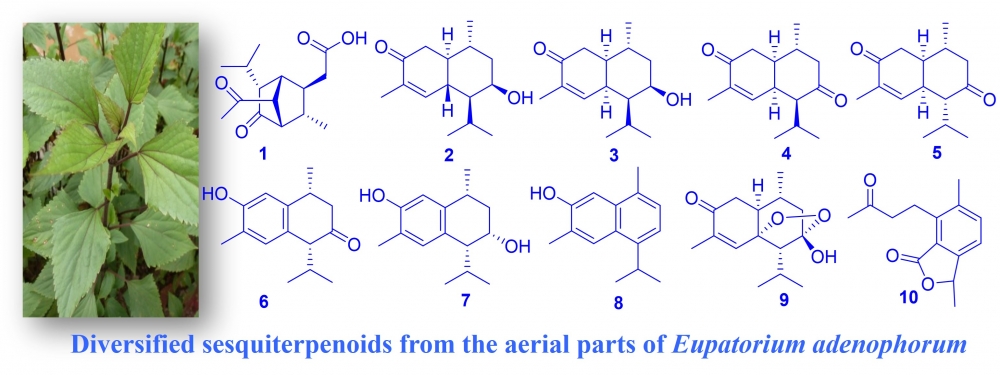
Ten sesquiterpenoids (1-10), including two new compounds 1 and 2, were isolated with the use of several chromatographic methods from the above-ground tissues of Eupatorium adenophorum Spreng. Comprehensive spectroscopic studies, such as single-crystal X-ray diffraction, 1D, 2D-NMR, and HRMS, were used to characterize their structures. The cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory actions and properties of the new compounds 1 and 2 were examined and briefly discussed.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.445.2401.3018 Keywords Chemical structures compositae sesquiterpenoids eupatorium adenophorum DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) A New Diphenyl Ether Derivative from an Endolichenic Fungus Preussia africana
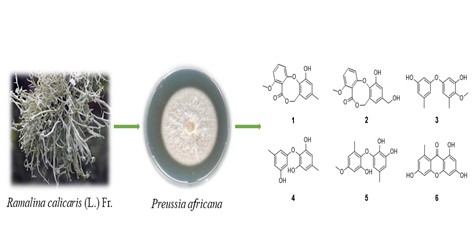
A new diphenyl ether derivative, namely barceloneic lactone D (1), along with five known compounds (2-6) were isolated from the solid cultures of an endolichenic fungus, Preussia africana. The structure of new compound was elucidated by HR-ESI-MS, 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy. All the isolates were evaluated for their antifungal activities. All compounds showed definite inhibitory activities with inhibition rate ranging from 9.2% to 79.2%.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.446-2401.3027 Keywords Preussia africana diphenyl ether antifungal DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) Alchemilla pseudocartalinica Juz: Phytochemical Screening by UPLC-MS/MS, Molecular Docking, Anti-oxidant, Anti-diabetic, Anti-glaucoma, and Anti-Alzheimer Effects
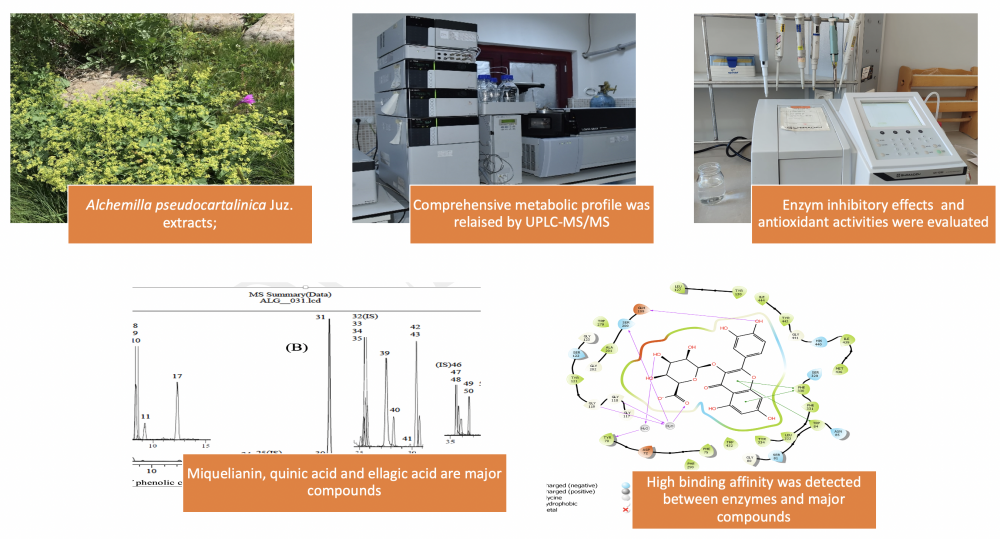
Alchemilla species (Rosaceae) are popularly known as ‘Lady’s Mantle, Lion’s claw’ and are used for medicinal purposes as diuretic, laxative, tonic, and wound healing agents. Bioactivities and phenolic content of Alchemilla pseudocartalinica Juz. species have yet to be investigated. Our research focused on assessing the antioxidant characteristics of A. pseudocartalinica methanol (MEAP) and water extracts (WEAP), as well as their inhibitory effects on acetylcholinesterase (AChE), α-glycosidase (α-gly), and human carbonic anhydrase II (hCA II) enzymes. Additionally, we conducted chemical characterization using UPLC-MS/MS and investigated the correlation between major phenolic compounds and enzymes through molecular docking analysis. To assess the antioxidant activities of the MEAP and WEAP, six test systems were employed, including DPPH, ABTS, DMPD, FRAP, CUPRAC, and Fe3+ reducing assays. The outcome showed that the methanol extract of the plant generally has stronger antioxidant activity. In addition, UPLC-MS/MS analysis indicated, miquelianin (44.095 mg/g), quinic acid (17.054 mg/g), and ellagic acid (6.492 mg/g) were significant in the methanol extract. A molecular docking study revealed a significant affinity for binding between the hCAII enzyme and quinic acid, miquelianin, and AChE/α-gly enzymes. A. pseudocatalinica methanol and water extracts have high antioxidant activity and good inhibition effect against AChE, α-glycosidase, and hCA II enzymes.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.448.2312.2993 Keywords Alchemilla antioxidant activity enzyme inhibition UPLC-MS/MS molecular docking DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) A New Butoxy Substituted Indolediketopiperazine from the Marine Derived Fungus Aspergillus sp. 66may
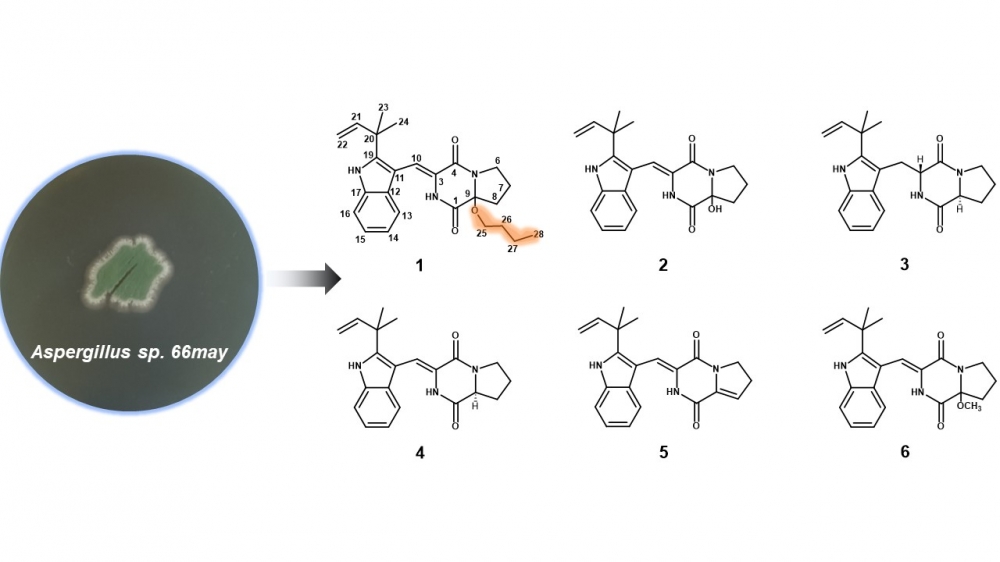
A new butoxy substituted indolediketopiperazine (1), together with five known indolediketopiperazines (2−6), which are derivatives of brevianamides, were isolated from the marine derived fungus Aspergillus sp. 66may. Careful analysis and comparison of the HRESIMS, as well as 1D and 2D NMR datasets, identified the structures of the isolated compounds. The subsequent antibacterial and anti-inflammatory activities showed that compound 4 possessed antimicrobial bioactivities against Bacillus subtilis ATCC 39620 with minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) value of 64 μg/mL. Compounds 1, 2, 4 exhibited potential inhibitory activities against NO production with IC50 value of 28.2, 21.3, 23.6 μM, respectively. It seems that butoxy substitution at C-9 in brevianamides have little effects on their antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory bioactivities.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.450.2401.3022 Keywords Diketopiperazines brevianamide antibacterial activity anti-inflammatory DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.9) A New olefin Derivative from Ficus esquiroliana Levl.
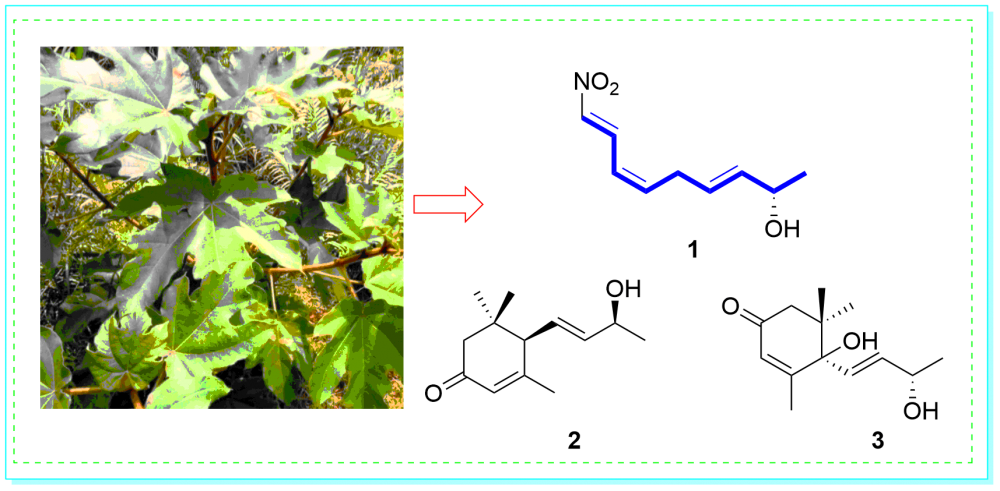
A new olefins derivative, ficuole A (1) and two known compounds (2−3) were obtained from the ethyl acetate extract of the Ficus esquiroliana Levl. The structures were elucidated using comprehensive spectroscopic methods, and the absolute configurations were defined by comparing the observed optical rotation with the standard values. All compounds were tested for α-glucosidase inhibitory activities. Compounds 1 and 3 against α-glucosidase with the IC50 values of 876.5 and 934.6 μM, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.2310.2932 Keywords Ficus esquiroliana Levl olefins derivative α-glucosidase activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.10) Currephila A, a New Chromanol Derivative from the Endophytic Fungus Curreya pityophila
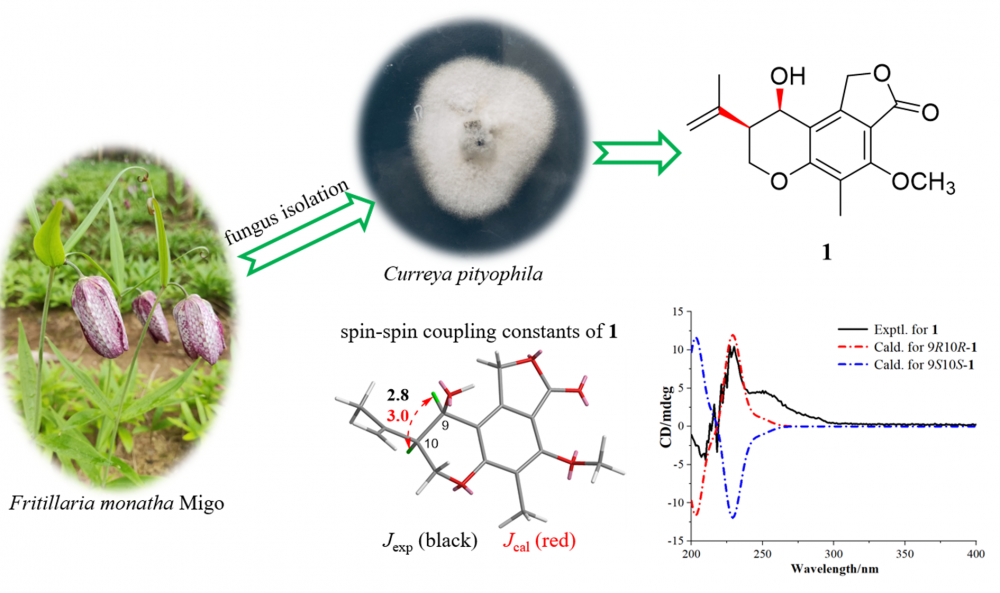
A previously undescribed chromanol derivative, named currephila A (1), was isolated from the endophytic fungus Curreya pityophila, along with two known compounds (2 and 3). Their structures were elucidated based on spectroscopic methods, electronic circular dichroism, and spin−spin coupling constants. The cytotoxic activities of compounds 1 and 2 against human breast adenocarcinoma MCF-7 cells were evaluated.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.443.2312.2999 Keywords Curreya pityophila endophytic fungus secondary metabolite chromanol DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.11) Phytosteroids from Roots of Psammosilene tunicoides W.C.Wu et C.Y.Wu
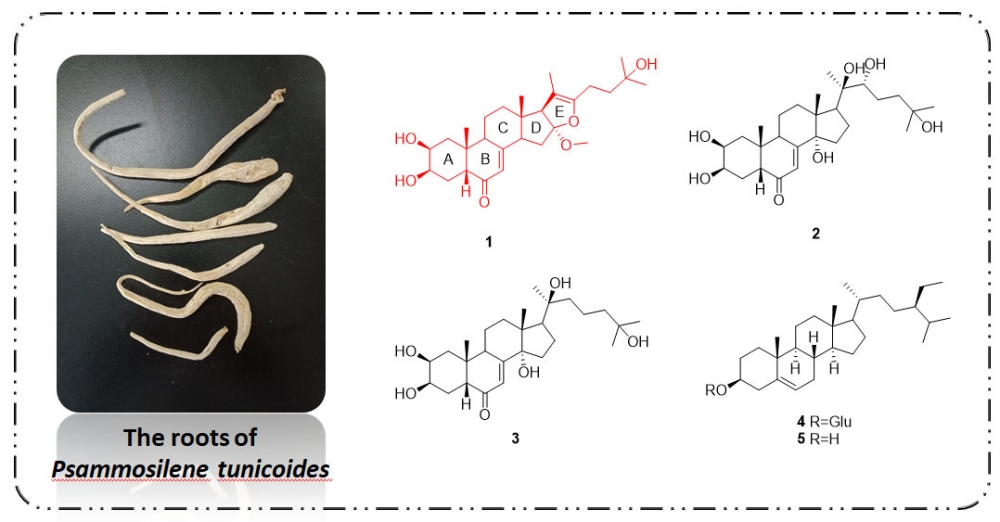
To explore structurally and pharmacologically interesting secondary metabolites from Psammosilene tunicoides, a crude extract of this plant was investigated, leading to the isolation of a new phytoecdysteroid, furoecdysterone (1) and four known phytosteroid compounds, ecdysterone (2), 22-deoxyecdysterone (3), β-sitosteryl d-glucoside (4), and b-sitosterol (5). Their structures were identified based on a detailed analysis of NMR spectra and MS data. Those compounds, except for 2, showed moderate NO inhibition activities on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced release in RAW 264.7 cells.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.444.2312.2991 Keywords Psammosilene tunicoides phytoecdysteroid nitric oxide inhibition activity RAW 264.7 cells DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.12) A New Prenylated Coumarin from the Roots of Toddalia asiatica
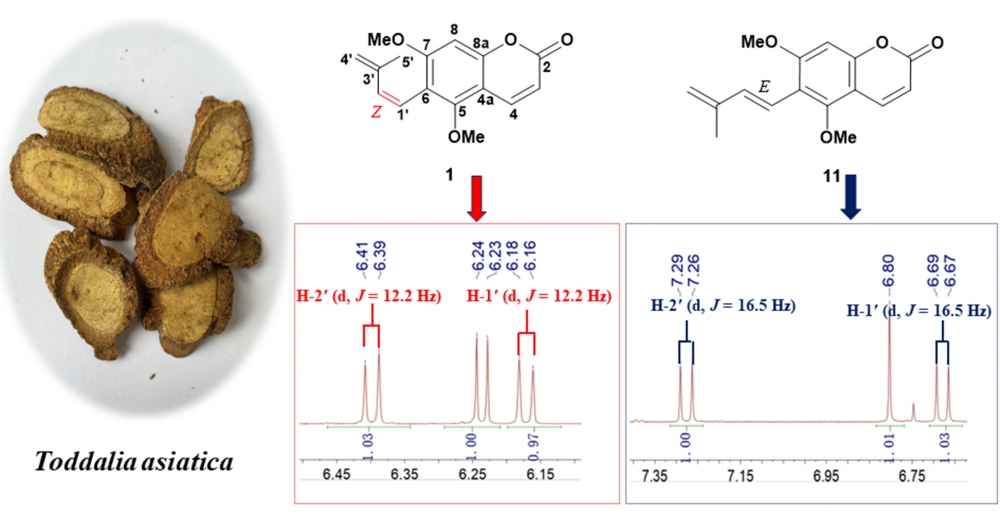 A new prenylated coumarin, 5, 7-dimethoxy-6-[(Z)-3'-methylbutan-1',3'-d-ienyl] coumarin (1), along with ten known compounds (2-11), was obtained from the roots of Toddalia asiatica (Linn.) Lam. Their structures were determined based on 1 D and 2 D NMR spectroscopy as well as high-resolution mass spectrometry. Notably, the structure of (3S, 4R)-3,4-epoxypimpinellin was revised as its cis-epimer, compounds (2-7) were isolated from this genus for the first time. The cytotoxic activities of the isolated compounds 1-11 were evaluated against SW480, A549, MDA-MB-231, HepG 2, HEp-2, SGC7901 cancer cell lines. Compound 10 exhibited weak cytotoxicity against HEP 2 with IC50 value of 75.19 ± 1.17 µM.
DOI
http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.449.2401.3015
Keywords
Toddalia asiatica
coumarins
chemical constituents
cytotoxic activity
DETAILS
PDF OF ARTICLE
© 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
A new prenylated coumarin, 5, 7-dimethoxy-6-[(Z)-3'-methylbutan-1',3'-d-ienyl] coumarin (1), along with ten known compounds (2-11), was obtained from the roots of Toddalia asiatica (Linn.) Lam. Their structures were determined based on 1 D and 2 D NMR spectroscopy as well as high-resolution mass spectrometry. Notably, the structure of (3S, 4R)-3,4-epoxypimpinellin was revised as its cis-epimer, compounds (2-7) were isolated from this genus for the first time. The cytotoxic activities of the isolated compounds 1-11 were evaluated against SW480, A549, MDA-MB-231, HepG 2, HEp-2, SGC7901 cancer cell lines. Compound 10 exhibited weak cytotoxicity against HEP 2 with IC50 value of 75.19 ± 1.17 µM.
DOI
http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.449.2401.3015
Keywords
Toddalia asiatica
coumarins
chemical constituents
cytotoxic activity
DETAILS
PDF OF ARTICLE
© 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.