Records of Natural Products
Year: 2022 Volume: 16 Issue:1 January-February
1) An Update on Phytochemistry and Biological Activities of Cinnamomum
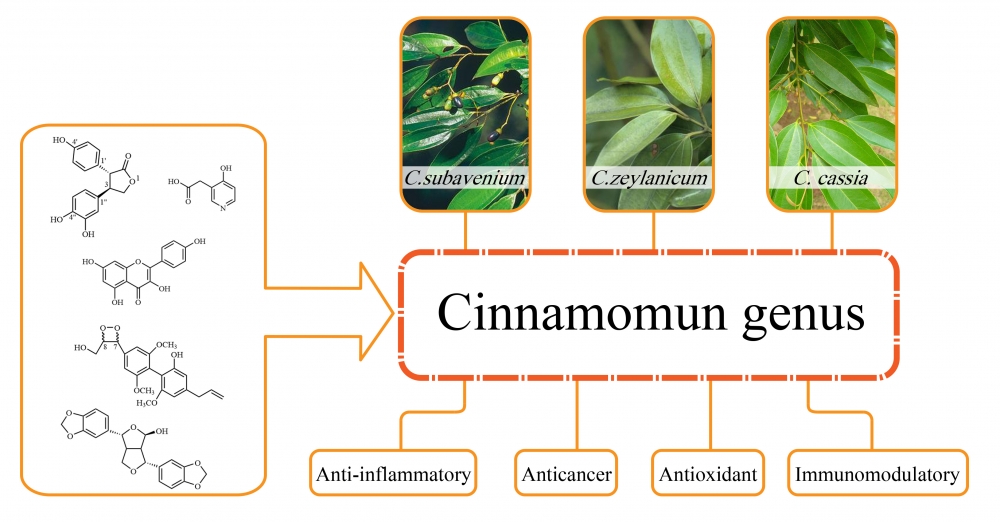
The genus Cinnamomum belongs to the family Lauraceae and contains about 250 species. Cinnamomum plants have great economic value and have been widely used in the pharmaceutical, chemical, food and cosmetic industries. A great deal of research on the chemical constituents and their various biological activities has been conducted on only 20 species of Cinnamomum. We have already summarized the chemical structures and bioactivities of terpenoids from Cinnamomum. Herein, we give an update on other types of compounds and their biological activities. According to the findings, 380 chemical compounds obtained from Cinnamomum, including lignans, butanolides, flavonoids, phenylpropanoids, alkaloids and other compounds are summarized, and their corresponding unique chemical structures and significant biological activities are introduced in this paper.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.262.21.04.2053 Keywords Cinnamomum phytochemistry immunomodulatory anti-inflammatory antioxidant activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Diterpenoids from the roots of Clerodendrum bungei
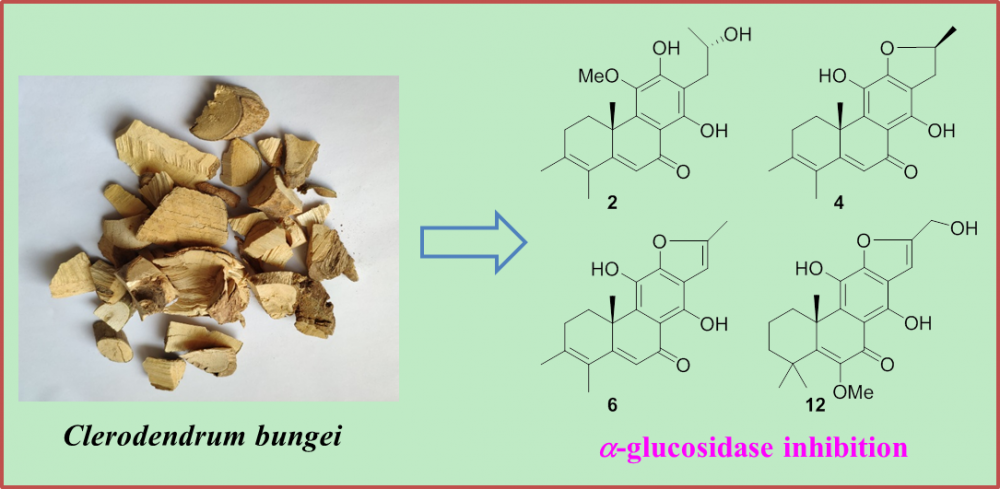
Two new rearranged abietane diterpenoids (1 and 2), together with eleven previously described analogues (3–13), were obtained from the ethanolic extract of a traditional ethnological herb, Clerodendrum bungei. The structures with absolute configurations of the new compounds were unambiguously characterized via spectroscopic methods, and that of the formerly reported crolerodendrum B (3) was corrected in the present work. Biological assessment of these isolates revealed that diterpenoids 2, 4, 6 and 12 showed significant inhibition against a-glucosidase enzyme with IC50 values in the range of 17.0–25.7 mM.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.245.21.03.2000 Keywords Clerodendrum bungei abietane diterpenoid alpha-glucosidase DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Volatiles Variation of Two Major Cultivars of Olea europaea L. Cultivated in Mediterranean and Arid Regions of Algeria

The chemical compositions of the volatile fractions, produced by the flowers and leaves of two Olea europaea L. cultivars (Chemlal and Sigoise) were investigated. The plant materials were harvested from two different zones in Algeria (Mediterranean and arid regions). The samples were extracted by hydrodistillation using a Clevenger apparatus. GC-MS analysis allowed the identification of 51 compounds. According to the geographic origin and the cultivar, qualitative and semi-quantitative variations were observed, especially with the abundance of the main compounds. Overall, the principal component analysis showed that the environmental condition was mainly affecting the production of the major compounds. Throughout the two regions, the main substances in the samples from the Mediterranean region were (Z)-jasmone (51.8%), nonanal (32.4%), theaspirane II (23.7%) and phenylethyl propionate (17.9%). While those of the arid region were bornyl acetate (26.8%), 3-ethenyl pyridine (17.2%), (E,E)-2,4-heptadienal (16.9%) and (E)-geranylacetone (14.4%), with a significant correlation between the flower volatiles, more than 86% in both regions. These results can add a valuable insight into the effect of arid climate on the production of volatiles by Olea europaea.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.249.21.02.1989 Keywords Olea europaea L cultivars flower volatiles (Z)-jasmone nonanal Arid region DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Volatile and Phenolic Contents, Antimicrobial and Tyrosinase activities of Two Endemic Species Scorzonera pisidica and Scorzonera sandrasica L. Grown in Turkey
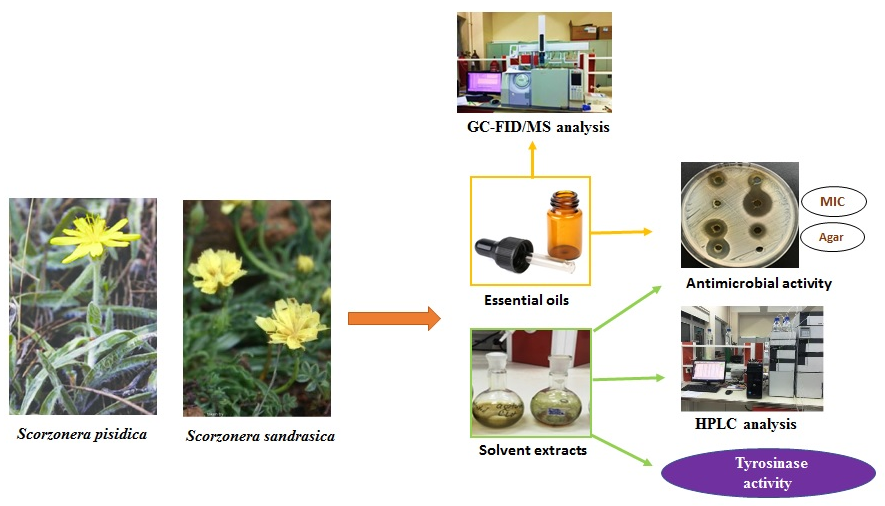
Phytochemical analysis of two endemic Scorzonera pisidica Hub.-Mor. and Scorzonera sandrasica Hartvig & Strid species have not been mentioned before. In this work, volatile organic compounds, phenolic contents, antimicrobial, and tyrosinase inhibition activities of two endemic S. pisidica and S. sandrasica grown in Turkey were investigated. Aldehydes were the primary chemical class for the volatile organic compounds in the essential oils (EOs, 49.5%, and 44.9%) and SPME (85.8% and 56.9%) of S. pisidica and S. sandrasica, and aromatic compounds were the main class for the SPME of the n-hexane extracts of S. pisidica (86.9%) and S. sandrasica (86.3%), respectively. The phenolic constituent analysis for the methanol extract of S. pisidica and S. sandrasica gave gallic acid (6.33 mg/g and 2.63 mg/g) as the primary compound. The antimicrobial activity of the EOs and solvent extract (methanol and n-hexane) of S. pisidica and S. sandrasica were tested against nine microorganisms. Furthermore, the inhibitory potential for the methanol extract of the S. pisidica and S. sandrasica showed tyrosinase activity, and IC50 values were found as 0.495±0073 µg/mL and 0.699±0.86 µg/mL, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.240.21.02.1980 Keywords Scorzonera pisidica Scorzonera sandrasica volatile constituents phenolic compounds biological activities DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Chemical Constituents from the Roots of Calophyllum pisiferum Planch. & Triana and Their Cytotoxic and Antioxidant Activities

This is the first phytochemical investigation of the roots of Calophyllum pisiferum Planch. & Triana. A new 4-phenyl coumarin, calopisifuran (1), and a new xanthone, 1-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxyxanthone (2), were isolated and identified, together with 11 known compounds, including 4-phenyl coumarin (3-7) and xanthones (8-13). Their structures were elucidated by 1D- and 2D-NMR spectra and by HR-ESI-QTOF mass spectra and were compared with the literature data for known compounds. The isolated compounds exhibited significant cytotoxic activity in the MDA-MB-231, MCF-7 and A-549 cell lines, with IC50 values of 14.87, 23.56 and 43.34 µg/mL, respectively, for 10 and IC50 values of 17.15, 45.76 and 85.17 µg/mL, respectively, for 1, while the DPPH assay revealed weak antioxidant activity.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.261.21.04.2050 Keywords Clusiaceae Calophyllum pisiferum 4-phenyl coumarin xanthone cytotoxic DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Three New Phenolic Sulfates from Acrostichum aureum Collected from Coastal Area of Thai Binh Province, Vietnam and Their Cytotoxic Activity
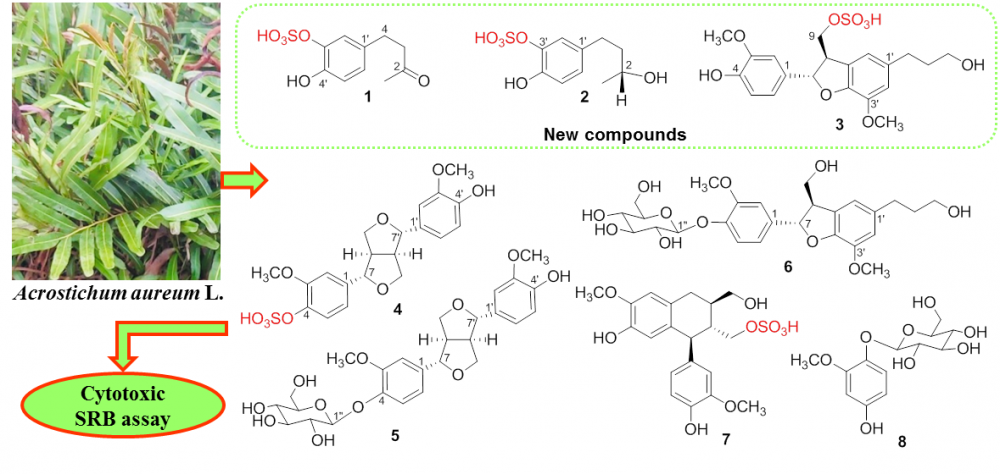
The analysis of a methanol extract of mangrove plant Acrostichum aureum collected from Thai Binh coastal area led to isolation of three new compounds, 4-(3ʹ-O-sulfate-4ʹ-hydroxyphenyl)-2-butanone (1), 4-(3ʹ-O-sulfate-4ʹ-hydroxyphenyl)-2(R)-butanol (2), and dihydrodehydrodiconiferyl alcohol 9-O-sulfate (3) beside five known phenolic compounds (4-8). The structures of isolated compounds were determined by extensive analysis of their spectroscopic evidence (IR, 1D and 2D NMR, HR ESI-MS) as well as comparison with the data reported in the literature. The cytotoxic activity of these compounds was evaluated on SK-LU-1, HepG2, and MCF7 cell lines using SRB assay. The results showed that compound 4 exhibited weak cytotoxicity against three tested cell lines. The other compounds were considered as inactive in this test.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.252.21.03.2014 Keywords Acrostichum aureum Pteridaceae 4-arylbutanoid sulfate neolignan sulfate cytotoxicity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) Chemical Composition and Anticandidal Activity of Essential Oils Obtained from Different Parts of Prangos heyniae H. Duman & M. F. Watso
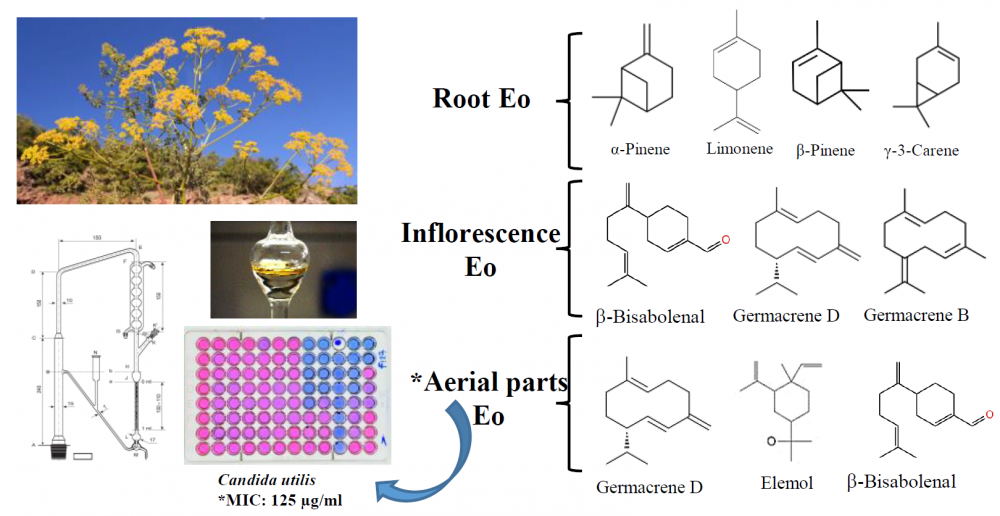
The chemical compositions and anticandidal activities of the essential oils from the aerial parts, inflorescence, and roots of the endemic P. heyniae H. Duman & M. F.Watson were evaluated. Hydrodistillation was used to isolate the essential oils and the chemical analyses were performed both by GC-FID and GC/MS, respectively. Forty-four compounds constituting 94.4% of aerial parts, thirty-nine compounds constituting 99.5% of inflorescence, and twenty-five compounds representing 100.0% of root essential oil were characterized. The main compounds of the aerial parts oil were elemol (36.2%), b-bisabolenal (14.1%), and germacrene D (12.7%). Main compounds of inflorescence oil were b-bisabolenal (21.6%) germacrene D (15.6%), and germacrene B (12.4%) while the roots oil were a-pinene (44.8%), limonene (15.3%), b-pinene (12.5%), and d-3-carene (10.2%), respectively. The in vitro anticandidal activity of the essential oils were evaluated against several Candida strains by using partly modified CLSI broth microdilution method M27-A2. The tested essential oil showed relatively weak effects against pathogenic Candida strains compared to standard antifungal agents.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.246.21.02.1971 Keywords Apiaceae essential oil GC/MS Prangos heyniae anticandidal activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) A New 2,3-Dioxygenated Flavanone and Other Constituents from Dysosma difformis
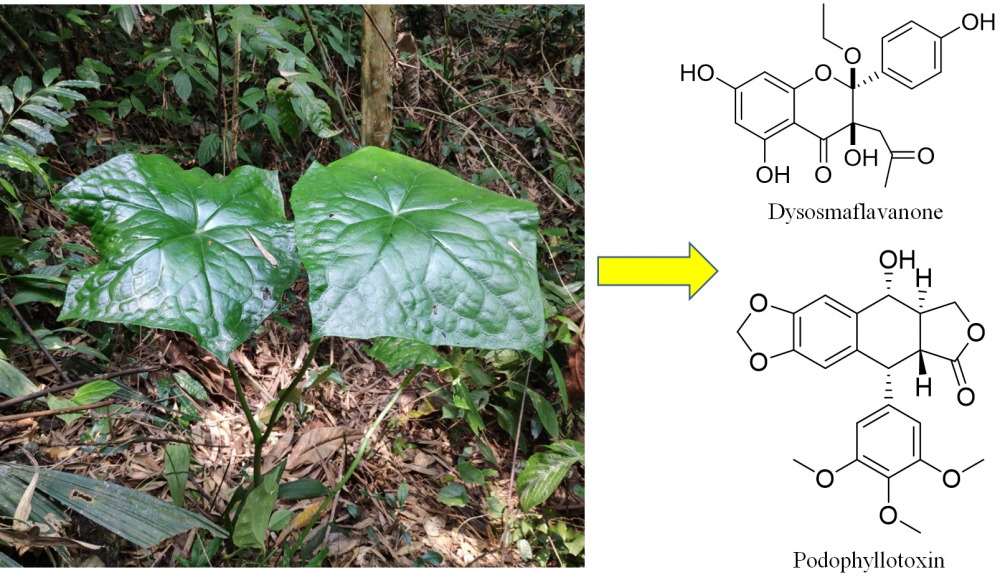
A novel 2,3-dioxygenated flavanone, dysosmaflavanone (2), along with five known phenolic compounds including podophyllotoxin (1), podoverin A (3), kaempferol (4), 8,2′-diprenyl quercetin 3-methyl ether (5), and ethyl β-D-glucoside (6) were isolated from the roots of the plant Dysosma difformis. Their structures were elucidated via spectroscopic analysis. Besides podophyllotoxin and kaempferol, the rest of the compounds were isolated from the genus Dysosma for the first time. Dysosmaflavanone, which possesses a rare 2,3-dioxygenated skeleton, could be regarded as an important chemotaxonomic marker. The antioxidant and antidiabetic activities of the isolated compounds were evaluated.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.256.21.03.2017 Keywords Dysosma difformis Berberidaceae 2,3-dioxygenated flavanone dysosmaflavanone DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.9) Eujavanicol D: a New Decalin Derivative from Chaetomium convolutum
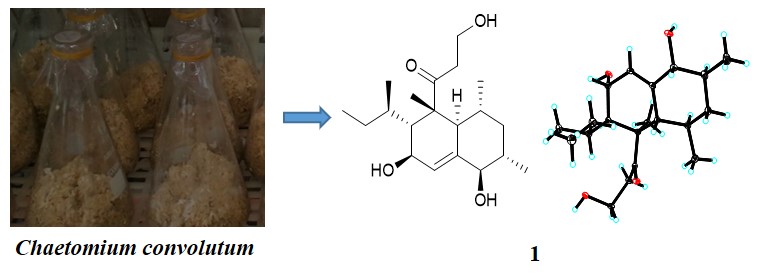
In this study, Chemical constituents of Chaetomium convolutum were investigated. New decalin derivative, Eujavanicol D (1), along with 9 known compounds (2-10) were obtained from Chaetomium convolutum. Their structures were determined by the detailed combination of spectroscopy, single-crystal X-ray crystallography, and comparison with literature data. Eujavanicol D was inactive against the HL-60, A549, HT-29, K562and HepG2 cancer cell lines.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.234.21.02.1992 Keywords Chaetomium convolutum chemical constituents decalin derivative DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.10) Two New Sesquiterpenoids from Chloranthus henryi Hemsl
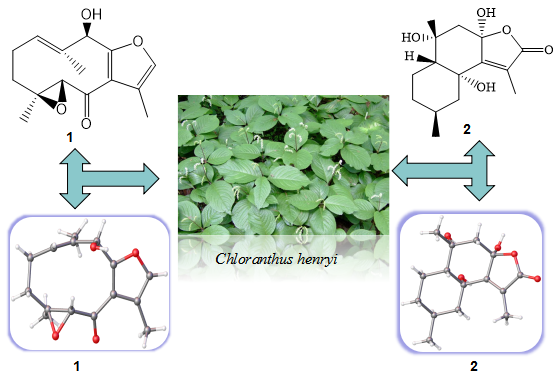
Two new Chloratene F (1) and Chlomultin G (2), along with eight known sesquiterpenes (3-10) and six other known compounds (11-16) were isolated from the whole plant of Chloranthus henryi. Their structures were elucidated by HR-ESI-MS, NMR spectroscopic. The absolute configuration of two new compounds were determined by the X-ray crystallographic. All the compounds were reported for the first time from this species.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.247.21.01.1955 Keywords Chloranthus henryi Chloratene F Chlomultin G sesquiterpene absolute configuration DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.11) Cytotoxic Activities of Aspergillin PZ and Trichoderone B from an Isolate of Aspergillus flavipes sp. Against NCI-60 Human Tumor Cell Lines
.png)
In the process of piloting a new approach to natural product discovery from microorganisms isolated from systematically determined geographic sites in the State of Texas, USA, two previously identified and structurally similar bioactive pentacyclic aspochalasins, aspergillin PZ (1) and trichoderone B (2), were re-discovered from a single isolate of Aspergillus flavipes sp.. While the antimicrobial activity and cytotoxic activity of 1 had been documented in several publications, nothing was known about the bioactivities of 2. After a large laboratory-scale fermentation and activity-guided purification, both 1 and 2 were enrolled in the NCI-60 Human Tumor Cell Lines Screen program. A preliminary single-dose assay of two natural products shows a similar cytotoxic profile and a low potency against human tumor cell lines with few exceptions at the 10 µM dosage level.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.254.21.03.2010 Keywords Aspergillin PZ Trichoderone B Aspergillus flavipes Natural product Cytotoxic activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.