Records of Natural Products
Year: 2022 Volume: 16 Issue:4 July-August
1) Current Techniques For The Search For Natural Products In Actinobacteria
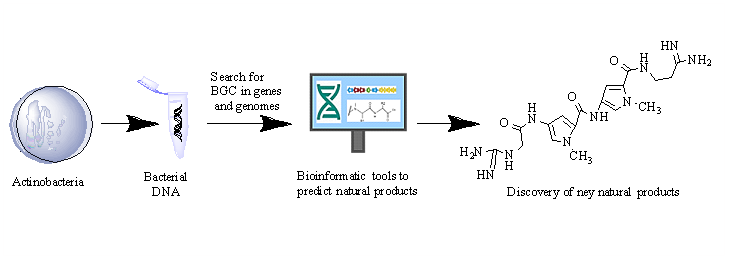
The actinobacteria, also referred to as actinomycetes, have been the most widely used bacteria to produce industrial interest compounds due to their great biosynthetic capacity to generate structural diversity molecules. The actinobacteria with the most significant biosynthetic potential are the genus Streptomyces, Saccharopolyspora, and Micromonospora containing groups of biosynthetic genes such as polyketide synthase systems, non-ribosomal peptide synthase systems, terpenoid systems, ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide systems, among others. This review focuses on genomic mining techniques and current helpful software to search for new natural products in actinobacteria. Currently, molecular techniques have been developed to improve the isolation of natural products, and bioinformatics programs, many are free to access, have been designed to analyze genes and microbial genomes that predict new molecule production. Thanks to these techniques, new natural products of industrial interest have been found in rare actinobacteria such as Nocardia and Rhodococcus.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.286.2107-2132 Keywords Actinobacteria Bioinformatics Genomic mining Natural products DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Honeybee Propolis Phenol, Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester, Attenuates Cisplatin-Induced Kidney Damage – a Multitarget Approach
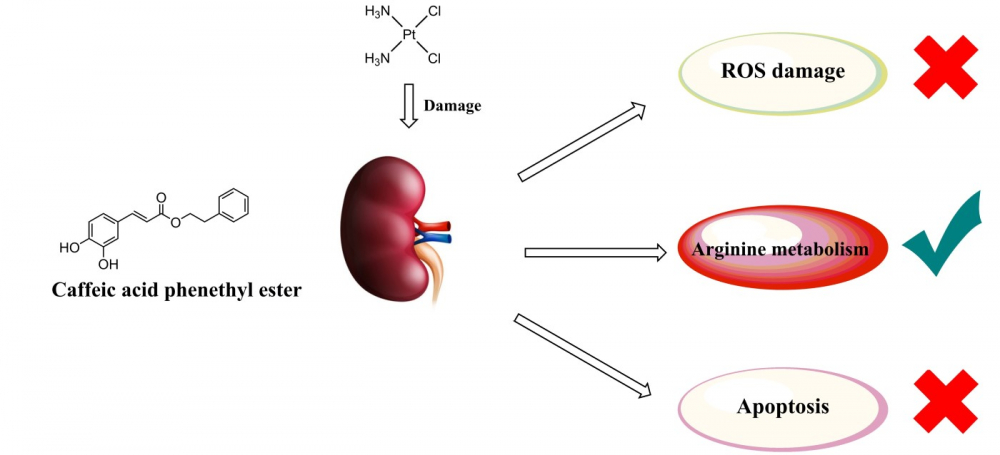
Cisplatin utilization is known to be limited due to numerous side effects, especially to the ones related to kidney tissue injury. The application of antioxidants, as potential supportive drugs, to prevent oxidative cisplatin tissue damage appears intuitive. In this work, we explored the usage of caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) in this respect through the analysis of standard serum biochemical parameters and the ones related to oxidative tissue damage, the changes in arginine metabolism, and apoptosis occurrence that follow cisplatin application in rat kidneys. Additionally, pathohistological analysis and a specific TUNEL staining for the detection of apoptosis was studied. Cisplatin produced marked changes in serum parameters that reflect kidney tissue function, while at the same time produced extensive tissue oxidative damage, increased arginase activity, and depleted reduced glutathione. Moreover, both biochemical and micromorphological analyses indicated significant tubular cell apoptosis. The application of CAPE together with cisplatin prevented the disturbance in serum biochemical and tissue oxidative stress parameters, without affecting arginase activity. Interestingly, CAPE inhibited different enzymes involved in the glutathione metabolism and the apoptotic process. The results of the present study indicate that CAPE could be used as supportive therapy for oncological patients receiving cisplatin since it attenuates the nephrotoxicity of this chemotherapeutic.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.284.2107.2146 Keywords Caffeic acid phenethyl ester kidney cisplatin oxidative damage arginase apoptosis DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) The Limonoids and Other Constituents from the Fruits of Melia azedarach and Their Biological Activity

Eleven chemical constituents, including one new limonoid trichilinin G (1), were identified from the fruit extracts of M. azedarach. The structure of 1 was established by various spectroscopic and mass spectrometric analyses. Among the eleven isolated compounds, trichilinin G (1) and meliatoxin B1 (2) were examined for their antifungal activity against Fusarium oxysporum, Magnaporthe grisea, Phytophthora spp. (PS), and P. capsici (PC). Limonoid 2 showed the best antifungal activity against PS (IC50 = 103.8 µg/mL) and PC (IC50 < 62.5 µg/mL) in a dose-dependent manner. While limonoid 1 exhibited a weak to moderate activity against these Phytophthora species, F. oxysporum and M. grisea were less sensitive to the two compounds tested. The inhibitory effects of trichilinin G on superoxide anion generation and elastase release by human neutrophils were also assessed in cellular model and did not show significant activity.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.277.21.06.2097 Keywords Triterpenoid limonoid trichilinin antifungal anti-inflammatory DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Two New Seco-Abietanoids with Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitory Activity from Cryptomeria japonica D. Don
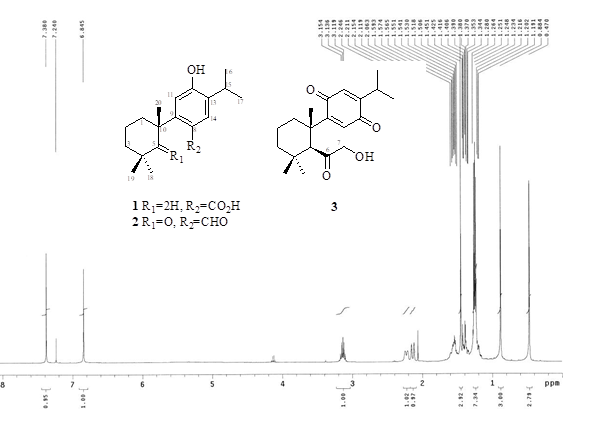
Two new seco-abietanoids, 12-hydroxy-6-nor-5,6-secoabieta-8,11,13-trien-7-oic acid (1) and 7-hydroxy-7,8-secoabieta-8,12-diene-6,11,14-trione (3), together with one known seco-abietanoid, 12-hydroxy-6-nor-5-oxo-5,6-secoabieta-8,11,13-trien-7-al (2), were isolated from the methanol extract of the bark of Cryptomeria japonica. Their structures were elucidated by mean of spectroscopic analysis, as well as on comparison of NMR data with those of known analogues. At a concentration of 50 μM, compounds 1–3 showed inhibitory activity toward xanthine oxidase by 38.2%, 55.9%, and 23.0%, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.289.2106.2121 Keywords Cupressaceae Cryptomeria japonica bark diterpenoid DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Monoester-Type C19-Diterpenoid Alkaloids from Aconitum carmichaelii and Their Cardiotoxicity
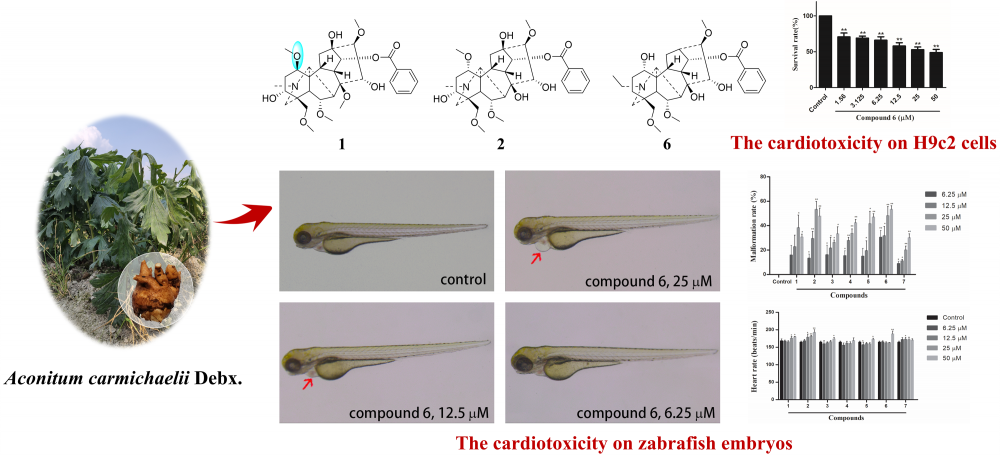
A new (1) and six known (2-7) monoester-type C19-diterpenoid alkaloids were isolated from the lateral roots of Aconitum carmichaelii Debx. Their structures were determined by spectroscopic techniques and calculations of NMR chemical shifts. Compound 1 (1-epi-hokbusine A) was an aconitine-type diterpenoid alkaloid possessing an unusual 1β-methoxy group. According to the main toxicity of the lateral roots of A. carmichaelii, the cardiotoxic effects of the isolates were evaluated using H9c2 rat myocardial cells and zebrafish embryos. The results showed that all the monoester-type C19-diterpenoid alkaloids exhibited cardiotoxicity, and compound 6 was found to be the most toxic compound.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.287.2107.2127 Keywords Aconitum carmichaelii monoester-type C19-diterpenoid alkaloids H9c2 cells zebrafish embryos cardiotoxicity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Essential Oil Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Endemic Achillea lingulata Waldst. & Kit. Compared to Common A. millefolium L.
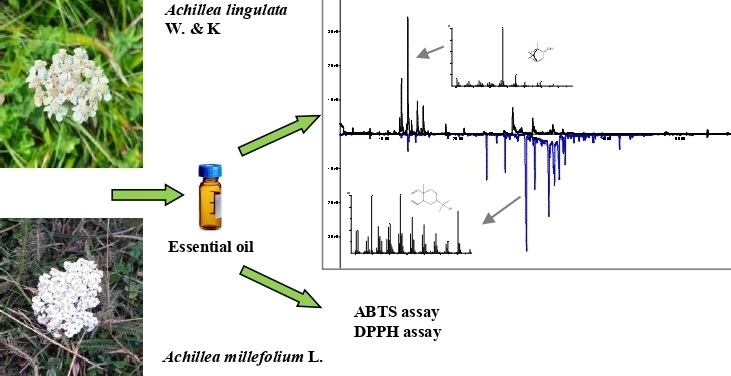
In this study, the chemical composition and antioxidant activity of the hydrodistilled essential oil of Achillea lingulata, an endemic species of the Euro-Mediterranean region, originating from Bosnia and Herzegovina, was investigated for the first time. For comparison, an analysis of the essential oil of the widely distributed Achillea millefolium, which grows together in the same habitat, was made. Ninety-six components were identified in A. lingulata and A. millefolium oils comprising 97.8% and 85.8%, of the total oil, respectively. The oil of A. lingulata was characterized by a high content of oxygenated monoterpenes (76.8%). The main compounds were borneol (30.1%), trans-verbenol (15.5%), 2-tridecanone (12.2%), fragranol (8.3%), and myrtenol (7.9%). In contrast, essential oil of A. millefolium had oxygenated sesquiterpenes (60.8%) as the most abundant compounds, with elemol (32.9%) as the main constituent. In addition, γ-eudesmol (12.9%), caryophyllene oxide (7.7%), trans-caryophyllene (5.7%) and γ-muurolene (4.7%) were present in a significant percentage in A. millefolium oil. Antioxidant activity was tested by three methods, ABTS, DPPH and FRAP, and the obtained results showed low activity of both investigated oils.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.285.2107.2143 Keywords Achillea lingulata Achillea millefolium GC-MS essential oil terpenes antioxidant activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
7) Chemical Constituents and Biological Activity of the Stems of Adinandra hainanensis Hayata
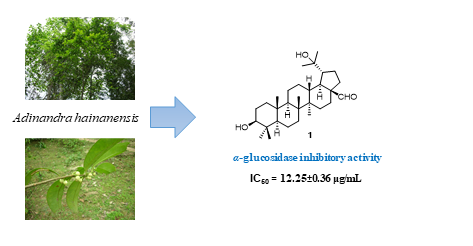
Phytochemical study of Adinandra hainanensis stems led to the isolation of a new triterpene lupan-3β,20-dihydroxy-28-carbaldehyde (1) and eleven known compounds 2-12. The stems of A. hainanensis was rich in lupane-type triterpenes, especially betulinic acid (9) was abundant (around 0.45% w/w). The isolated triterpenes, including new compound 1 showed strong α-glucosidase inhibitory activity with IC50 values ranging of 2.27 ± 0.05 μg/mL to 12.25 ± 0.36 μg/mL. In the cytotoxic evaluation, betulinic acid, the major component, showed good cytotoxic activity against all tested cancer cell lines while new compound 1 was weakly active.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.282.2108.2158 Keywords Adinandra hainanensis lupane triterpene betulinic acid α-glucosidase cytotoxicity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) Two New Bibenzyls from Dendrobium hercoglossum

Two new bibenzyl compounds 3-hydroxy-4, 5, 3′-trimethoxybibenzyl (1) and (R)-4-hydroxy-3, 5, 3′, α-tetramethoxybibenzyl (2), along with twelve known compounds (3−14), were isolated from the stems of Dendrobium hercoglossum Reichb. f. The structures of the new compounds were elucidated on the basis of detailed spectroscopic analysis. The cytotoxic effects of the isolated compounds on two human tumors cell lines (MDA-MB-231 and Hela) were evaluated by the MTT assay.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.291.2109.2198 Keywords Orchidaceae Dendrobium hercoglossum bibenzyl cytotoxicity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.9) Quantitative Analysis and In Silico Molecular Docking Screening for Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor and ADME Prediction of Coumarins and Carbazole Alkaloids from Clausena harmandiana
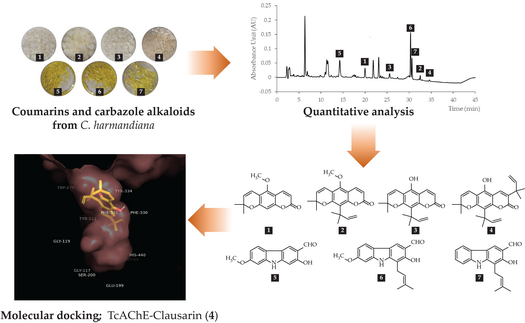
Coumarins and carbazole alkaloids are natural compounds, often with neurological properties, especially as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. In order to screen the candidate anti-acetylcholinesterase agents, in-silico molecular docking was performed aiming to predict the binding mechanism and the results were used to identify pharmacophores of coumarins and carbazole alkaloids from Clausena harmandiana as AChE inhibitory activity. All isolated compounds are xanthoxyletin (1), dentatin (2), nordentatin (3), clausarin (4), 7-methoxymukonal (5), 7-methoxyheptaphylline (6) and heptaphylline (7) displayed the stable binding interactions with Torpedo californica acetylcholinesterase (TcAChE) enzyme via π-π interactions, hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions. All compounds exhibited the interaction with the peripheral anionic site of TcAChE same manner of standard anti-alzheimer drugs. ADME prediction revealed that all compounds met the requirement of drug likeness of Lipinski’s rule of five and had high CNS absorption, excepted 4 should be structure modification to improve CNS penetration. Besides 4, 6 and 7 displayed the highest acetylcholinesterase inhibitor activity among the other compounds. Interestingly, 6 had a high yield (58.01 mg/g extract) from C. harmandiana. It should be a candidate as an anti-acetylcholinesterase inhibitor agent.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.288.2106-2112 Keywords Clausena harmandiana molecular docking coumarins carbazole alkaloids Alzheimer’s disease ADME DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.10) A New Short Chain Acetamide from the Biosphere and Bioactive Glycerolipids Extracted from the Marine Bibalve Codakia orbicularis (Lucinidae).

The marine bivalve Codakia orbicularis, harbors endosymbiotic bacteria located in its gill filaments. Bioassay-guided fractionation of an ethyl acetate extract of the gill tissues led to antibacterial fractions (against Gram positive and negative bacteria). The fraction eluted in AcOEt/ MeOH 90:10 displayed the greatest bioactivity. This fraction was analyzed using usual chromatographic and spectrometric methods and revealed three compounds. The first one (compound 1) was an acetamide isolated for the first time from the biosphere. The other two were mono-glycerolipids (compound 2) and (compound 3) with at the position sn-2 of their glycerol monounsaturated fatty acid chains (respectively C18:1Δ9 and C16:1Δ9). Compounds 2 and 3 showed bacteriostatic activity against two pathogenic Gram-negative bacteria using a disc diffusion assay method. These molecules have been isolated for the first time from a bivalve. Further investigations are currently in progress, so as to understand the role of these bioactive compounds into the regulation of C. orbicularis’ endosymbionts and/or to free-living pathogens.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.295.2108.2194 Keywords Antibacterial activity monoacylglycol ceramide DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.11) Essential Oil from Hedyotis chrysotricha: Chemical Composition, Cytotoxic, Antibacterial Properties and Synergistic Effects with Streptomycin
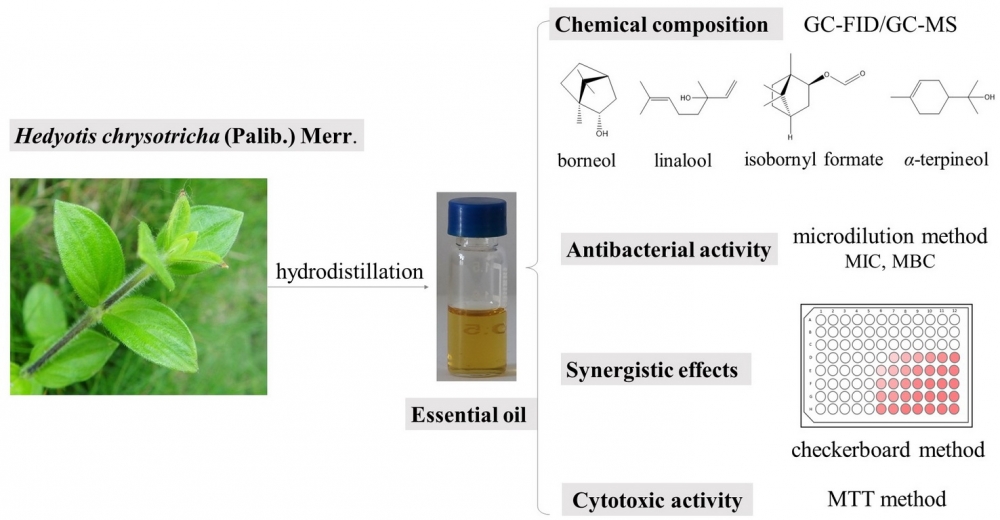
Hedyotis chrysotricha (Palib.) Merr. is a traditional Chinese herb that has been used to treat multiple ailments. In this study, we extracted and characterized the essential oil of H. chrysotricha for the first time and assessed its in vitro cytotoxic, antibacterial activities and the synergistic interaction with Streptomycin. Chemical constituents were determined using GC-FID/MS, which showed 37 components constituted 94.7% of the total oil; borneol (32.7%), linalool (7.5%), isobornyl formate (5.4%) and α-terpineol (4.8%) were the dominant components. The essential oil of H. chrysotricha inhibited strongly the growth of Gram-positive bacteria and possessed a significant cytotoxic activity towards LO2, HepG2 and MCF-7 cells. Besides, the checkerboard assay revealed that the H. chrysotricha essential oil exhibited synergistic potential with Streptomycin. Based on these findings, it can be concluded that the H. chrysotricha essential oil exhibits interesting bioactivities, and could be used as a source of natural antibacterial and anti-tumor compounds.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.279.2108.2168 Keywords Hedyotis chrysotricha (Palib.) Merr essential oil antibacterial activity cytotoxic activity synergistic effects DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.12) Fissistigmol A: A New Polyacetylene alcohol from Fissistigma Minuticalyx

Abstract: A new polyacetylene alcohol, Fissistigmol A (1), along with four known polyacetylene alcohol compounds (2-5) were isolated from the aerial part of Fissistigma minuticalyx (McGr. et W. W. Sm.). Their structures were elucidated based on the spectroscopic evidence, mainly including NMR and induced ECD, and HRESIMS data. In addition, bioactivity assay showed that 1-5 showed notable nitric oxide (NO) inhibitory effects (IC50 < 10 μM) on the model of the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated RAW 264.7 macrophages.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.280.2108.2156 Keywords Polyacetylene alcohol Annonaceae Fissistigma minuticalyx nitric oxide (NO) inhibitory activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.13) Annonaceae Essential Oils: Antimicrobial and Compositions of the Leaves of Uvaria hamiltonii Hook. f. & Thoms. and Fissistigma kwangsiensis Tsiang & P. T. Li
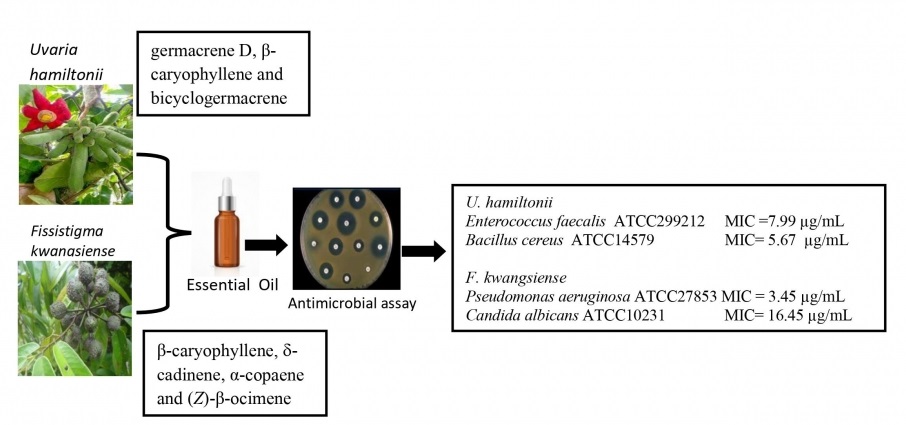
In this study, essential oils hydrodistilled from the leaves of Uvaria hamiltonii Hook. f. & Thoms. and Fissistigma kwangsiensis Tsiang & P. T. Li (Annonaceae) collected in Vietnam were analyzed by gas chromatographic techniques, and screened for the antimicrobial activities. The composition of both essential oils was dominated by sesquiterpenoids (70.0% and 78.7%, respectively). The main constituents of U. hamiltonii were germacrene D (22.9%), β-caryophyllene (21.1%), bicyclogermacrene (11.2%) and caryophyllene oxide (8.6%). The essential oil of F. kwangsiensis also showed abundant sesquiterpenes β-caryophyllene (24.5%), d-cadinene (13.4%) and α-copaene (5.6%), but also included (Z)-β-ocimene (6.7%). The leaf oil of U. hamiltonii demonstrated notable antimicrobial activity against Enterococcus faecalis ATCC299212 with minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) value of 7.99 µg/mL and Bacillus cereus ATCC14579 (MIC 5.67 µg/mL) while F. kwangsiensis showed the most potent activity towards Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC27853 and Candida albicans ATCC10231, with MIC values of 3.45 µg/mL and 16.45 µg/mL, respectively. Both essential oils should be considered for further investigation as renewable “green” antimicrobial agents.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.281.2108-2161 Keywords Antimicrobial activity essential oil composition sesquiterpenes DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.14) A New Iridoid Glycoside Isolated from Valeriana officinalis L.
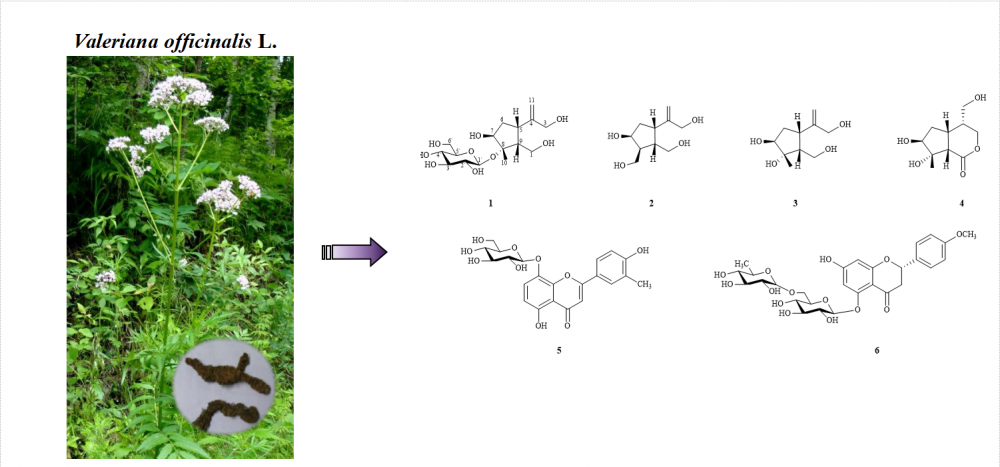
A new iridoid glycoside, (5S,7S,8S,9R)-7- hydroxy-∆4,11-dihyronepeta-1,3-diol-8-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl (1), along with 5 known compounds, dioscoridin A (2), jatamanin J (3), longiflorone (4), apigenin-8-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (5), isosakuranetin-5-O-rutinoside (6), were isolated from the Valeriana officinalis L. Their structures were determined by extensive analysis using various spectroscopic techniques. Moreover, the cytotoxic activity assay toward three human tumor cell (A549, HCT116 and SW620) lines were evaluated by the MTT method in vitro for compounds 1-2, using cisplatin as positive control. Experimental results showed that these compounds displayed weak cytotoxicity in the human cancer cell lines. Notably, compounds 2, 3 and 6 were firstly isolated from this plant, compound 4 was isolated from the genus Valeriana for the first time, compound 5 was isolated for the first time from Valerianaceae family.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.283.2107-2145 Keywords Iridoids Valeriana officinalis L. Valerianaceae cytotoxicity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.15) Insecticidal and Repellent Activities of Volatile Constituents from Litsea dilleniifolia P. Y. Pai et P. H. Huang Against Stored-Product Insects

The volatile oil from leaves of Litsea dilleniifolia P. Y. Pai et P. H. Huang was obtained by hydrodistillation. The qualitative and quantitative analysis of volatile constituents were performed by GC/MS and GC/FID. The volatile oil along with two major components was evaluated for their fumigant, contact toxicity and repellency against stored-product insects, namely Tribolium castaneum and Liposcelis bostrychophila. The volatile oil mainly contained decanal (48.4%), eremanthin (10.4%), zerumbone (10.1%) and estragole (9.2%). In bioassays, L. dilleniifolia volatile oil showed toxicity and repellent activities against T. castaneum and L. bostrychophila. The volatile oil, decanal and estragole at 78.63 nL/cm2 could cause 82-92% repellency against T. castaneum at 4h post-exposure. Among them, decanal (LC50 = 3.90 mg/L air) and estragole (LC50 = 5.33 mg/L air) had significant fumigant toxicity against T. castaneum, and estragole was strongly toxic to L. bostrychophila (LC50 = 0.61 mg/L air). The two components displayed a similar level of toxicity against T. castaneum in contact assays (LD50 = 21.91 and 20.41 µg/adult, respectively). This work indicates that L. dilleniifolia is promising to be developed as botanical insecticides and repellents to control pest damage in warehouses and storage rooms.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.290.2108.2157 Keywords Botanical insecticides Liposcelis bostrychophila repellency Tribolium castaneum the volatile oil toxicity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.16) A New Isoflavan Glucoside from the Roots of Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus

A new isoflavan glucoside, namely astramemside A (1), together with six known compounds (2-7) were obtained from the roots of a traditional Chinese medicine, Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus. Their structures were elucidated by spectroscopic analyses (HRESIMS, UV, IR, 1D and 2D NMR), and the absolute configuration of 1 was determined by combination of chemical transformation and single-crystal X-ray diffraction. Compound 1 showed moderate inhibition on nitric oxide (NO) production induced by lipopolysaccharide in RAW264.7 cells with an IC50 value of 38.98 ± 5.28 uM.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.292.2109.2203 Keywords Astragalus membranaceus var. mongholicus Leguminosae isoflavan glucoside DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.