Records of Natural Products
Year: 2022 Volume: 16 Issue:6 November-December
1) A Review on Medical Plants of Genus Siegesbeckia: Phytochemical and Pharmacological Studies
GGenus Siegesbeckia has been utilized as herbal medicine for treating arthritis, stroke, rash and other diseases for hundreds of years in East Asia. Modern pharmacological researches demonstrated the species of genus Siegesbeckia contains numerous naturally occurring active compounds. Till now, 250 compounds have been separated from Siegesbeckia species, namely 128 diterpenoids, 71 sesquiterpenoids, 14 flavonoids and 37 other compounds. A number of studies showed Siegesbeckia extracts or constituents possessed various therapeutic activities, including anti-inflammation, analgesia, anti-cancer and so on. Some of them have a bright prospect in naturally occurring drug discovery.The information provided by this review is expected to be beneficial for further phytochemical and pharmacological studies of the genus Siegesbeckia.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.317.2201.2332 Keywords Siegesbeckia kirenol diterpenoid anti-inflammation sesquitepenoid DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) A Comprehensive Review on Traditional Uses, Chemical Constituents, and Diverse Pharmacological Importance of the Genus Breynia
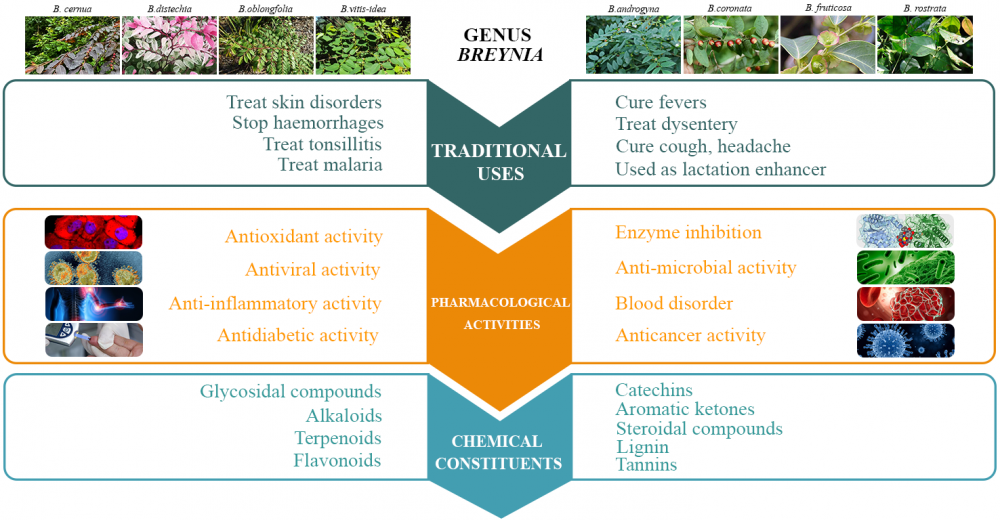
The genus Breynia (family Phyllanthaceae) is widely distributed in Australia, Vietnam, Malaysia, and some regions of India. Traditionally, species of this genus were used to treat various disorders, like skin diseases, pain, cough, tonsillitis, dysentery, and headache. Various studies about this genus are available, but reviews highlighting its pharmacology and phytochemistry are inadequate. This review highlights the pharmacology, phytochemistry, and chemotaxonomic classification of the phytochemicals of ten species of the genus Breynia. About 90 compounds have been isolated from Breynia species, including glycosides, flavonoids, terpenoids, steroids, alkaloids, lignans, phenolic compounds, and catechins. Their structure and presence in each species are presented in tabular form. In pharmacological medicines, the crude extracts and metabolites of the genus Breynia have been found to exhibit diverse biological activity, including, antioxidant, antimicrobial, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antiviral, and activity against various blood disorders. Few isolated compounds show enzyme inhibitory activity (tyrosinase, xanthine oxidase, and elastase inhibition).
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.314.2112.2280 Keywords Breynia Phyllanthaceae chemotaxonomic classification phenolic compounds glycosides pharmacology DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
3) Triterpenes and Saponins from Leaves of Camellia nitidissima, and Cytotoxic Activities Against Bel-7402 and SMMC-7721 Human Liver Cancer Cells
Camellia nitidissima is commonly used for making tea to prevent cancer in China, but its phytochemicals and bioactivity was insufficiently reported. In this work, the total content of saponins from leaves of C. nitidissima was investigated, and the high level of total saponins varied obviously with the augment of leafage. There are 12 triterpenes and saponins, i.e., β-daucosterol (1), α-spinasterol-β-D-glucoside (2), lupeol (3), 17,3β-acetoxy-20-lupanol (4), 3β,6α,13β-trihydroxyolean-7-one (5), oleanolic acid (6), oleanolic acid 3-acetate (7), ginsenoside Rg1 (8), ginsenoside F5 (9), ginsenoside F1 (10), ginsenoside Rd (11), and (3β,6α,12β)-3,6,12-trihydroxydammar-24-en-20-yl-2-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(2→1)-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(2→1)-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside (12) from C. nitidissima leaves were isolated and identified. Specially, five dammarane tetracyclic triterpenoids derived from 20(S)-protopanaxatriols (compounds 8-12) obtained from C. nitidissima were the first reported, and compound 12 is a new dammarane triterpenoid. Based on scratch assay and cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay, compound 12 and the extracts of C. nitidissima leaves showed potential cytotoxic activities against Bel-7402 and SMMC-7721 human liver cancer cells in vitro.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.308.2111.2273 Keywords Camellia nitidissima triterpenes and saponins cytotoxic activities liver cancer DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Antitumor Activity of Ethyl Acetate Extraction of Wikstroemia chamaedaphne: Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis-Inducing Activity in Melanoma Cells
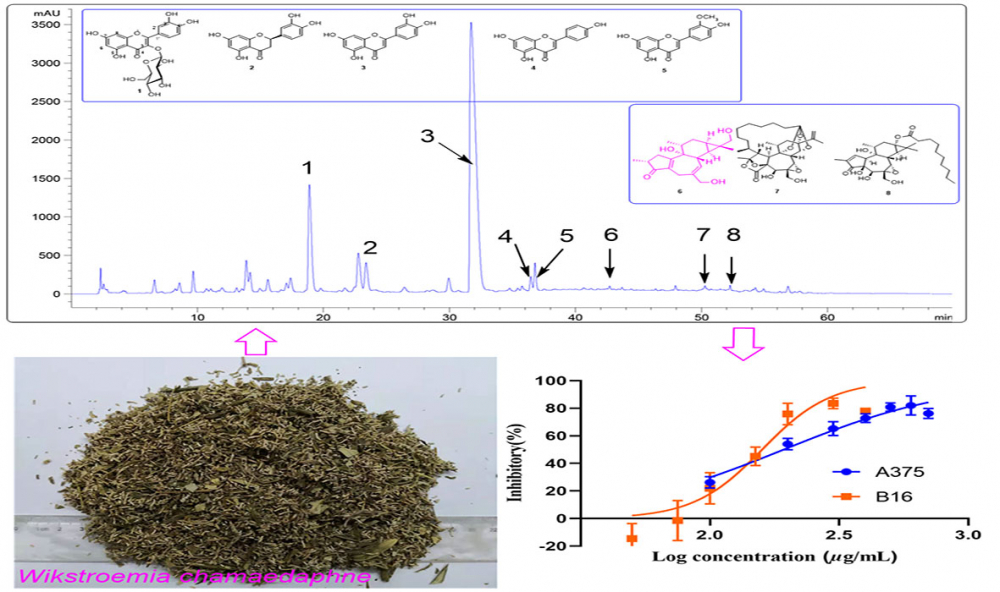
The ethyl acetate extraction (WCE) of Wikstroemia chamaedaphne Meisn on the viability of melanoma cell lines B16 and A375 were evaluated. The WCE exhibited a potent cytotoxic against B16 and A375 with IC50 values of 156.2 and 192.8 µg/mL, respectively. Cell migration was assessed using a wound healing assay. The WCE caused cell cycle arrest in the G0/G1 phase in B16 cells and the S phase in A375 cells, according to cell cycle analysis. Flow cytometric analysis revealed that WCE promoted apoptosis in B16 and A375 cells in a dose-dependent manner. Chemical analysis of WCE resulted in the isolation of a new diterpenoid, wikstchalin A (6) with five known flavonoids (1-5) and two known diterpenoids (7 and 8). Spectroscopic analysis revealed their structures, and CD analysis revealed the absolute configurations of 6. The absolute structure of pimelotide A (7) was firstly confirmed by single-crystal X-ray diffraction. The cytotoxicities of all the compounds (1−8) were evaluated against B16 cell lines. Compound 8 was more active than the positive control, dacarbazine (IC50 300 μM), in terms of cytotoxicity against B16, with an IC50 value of 7.9 μM.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.311.22.02.2343 Keywords Wikstroemia chamaedaphne flavonoid diterpenoid antitumor activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) A Neoprzewaquinone Analogue from Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge

(3R,3′R)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydroneoprzewaquinone A (1), a previously undescribed neoprzewaquinone analogue, was isolated from the root of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. Its absolute configuration was elucidated by comprehensive analyses of spectra including NMR and MS combined with ECD calculations. MTT assay indicated that 1 can inhibit the proliferation of MV-4-11, TMD-8, MOLM-13, and H460 cell lines with IC50 values of 2.21 μM, 2.48 μM, 3.39 μM, and 2.02 μM respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.313.2111.2253 Keywords Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge (3R,3′R)-2,2′,3,3′-tetrahydroneoprzewaquinone A cytotoxic activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) A New Alkaloid from Ormosia hosiei Hemsl. et Wils
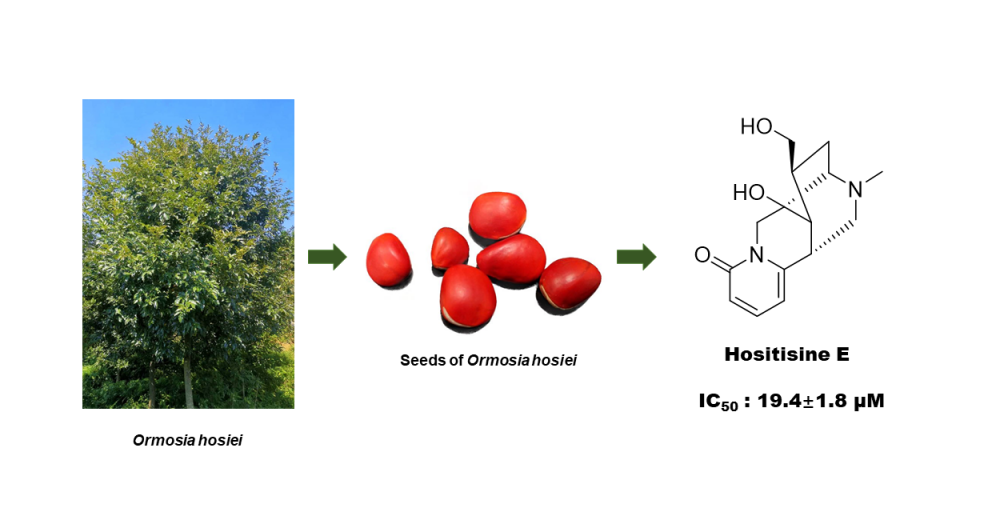
A new alkaloid, hositisine E (1) and nine known compounds (2-10) were isolated from the seeds of Ormosia hosiei Hemsl. et Wils. Compound 1 was identified on the basis of a combination of UV, IR, NMR, CD and HRESIMS data. The structures of the known compounds were determined as isoprunetin (2), biochanin A (3), ononin (4), 4',8-dimethoxy-7-O-β-D-glucopyranosylisoflavone (5), sphaerobioside (6), ambocin (7), rutin (8), kaempferol-3-rutinoside (9) and narcissin (10). In the anti-inflammatory activity assay, compounds 1-3, 7 displayed inhibitory effects against lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin-6 release in RAW264.7 macrophages, exhibiting IC50 values of 19.4 – 58.9 μM.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.316.2201.2340 Keywords Ormosia hosiei cytisine-like alkaloid hositisine flavonoid anti-inflammatory IL-6 DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) New Cyclic Peptides from the Endophytic Aspergillus versicolor 0312 with Their Antimicrobial Activity

This article aims to investigate the chemical constituents of the endophytic Aspergillus versicolor 0312 cultivated in the solid fermentation of rice perlite. Two new cyclic peptide compounds, 7-hydroxyldehydrocyclopeptin (1), 14,31-dimethoxy-penicopeptide A (2) and seven known compounds were isolated from the fermentation. Their structures were characterized by using 1D and 2D NMR techniques and MS spectrometry methods. The antibacterial effects of the isolated compounds were evaluated and the results showed compound 2 exhibited moderate antimicrobial activities against Bacillus subtilis.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.315.2112.2296 Keywords Aspergillus versicolor 0312 endophytic fungi cyclic peptide antimicrobial activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) LC-HRMS Based Approach for Identification and Quantification Analysis of Chemical Constituents of Sea Cucumbers from Aegean Sea - Their Cytotoxic and Antiviral Potentials
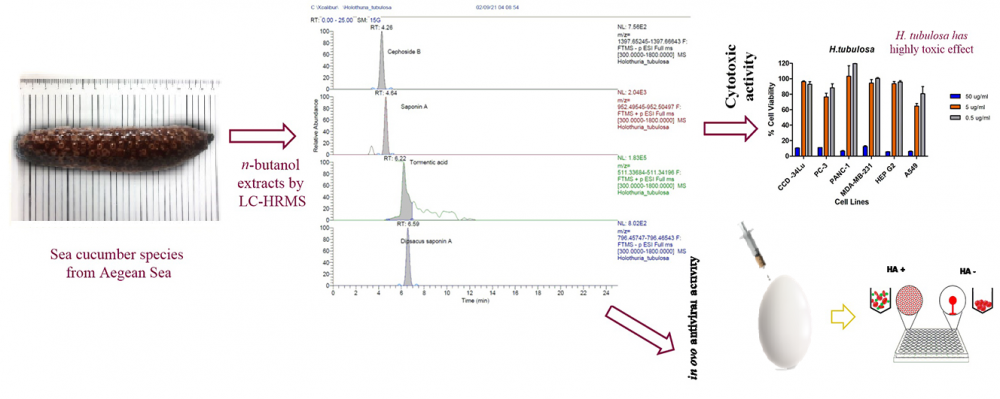
There are nearly 1200 species of sea cucumber in the world's seas. Among these creatures included in the Holothuroidea class, 37 species show distribution in the Mediterranean and Aegean Sea. The purpose of this study is to determine the chemical content and biological potent of five sea cucumber species, Holothuria tubulosa, Holothuria poli, Holothuria mammata, Holothuria sanctori and Stichopus regalis, which were collected from the Aegean Sea. The detailed flavonoid, phenolic and triterpene contents were determined by LC-HR/MS. Cytotoxic activities against several cancer cell lines, MDA-MB-231, PC-3, A-549, PANC-1, HEPG2 and a healthy cell line CCD-34LU were performed by MTT method. Antiviral activities of the samples were measured as virucidal activity against avian coronavirus by in ovo. According to the results of LC-HRMS analysis, H. sanctori, H. poli and S.regalis had the richest chemical content diversity in terms of examined triterpene compounds. Fumaric acid was detected as the most abundant substance in all sea cucumber species. H. tubulosa had a highly toxic effect on all the tested cells. The best cytotoxic activity on A549 cells was seen in H. mammata, H. sanctori and H. poli. H. sanctori also showed a significant toxic effect against PANC-1, MDA-MB-231, HepG2 and A549 cells, whereas the IC50 value in CCD-34LU cells was above 50 μg/ml for this sample. The n-butanol extracts of sea cucumber species reduced hemagglutination (HA) virus titer between 1-fold to 4-fold in log2-based at all tested concentrations. The best inhibited virus HA titer results were found in H. tubulosa at 5 μg/g. According to these results we have obtained, the extracts of sea cucumbers may be used in many fields such as medicine, food, cosmetics in the future. This study is also very important in terms of being a guide for all studies on the use, processing and production of sea cucumbers and detailed isolation and purification studies on sea cucumber species from Turkey.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.323.2202.2349 Keywords Holothuria Stichopus cytotoxicity antiviral activity LC-HRMS avian coronavirus DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.9) Terpenes from the Fresh Stems of Commiphora gileadensis with Antimicrobial Activity
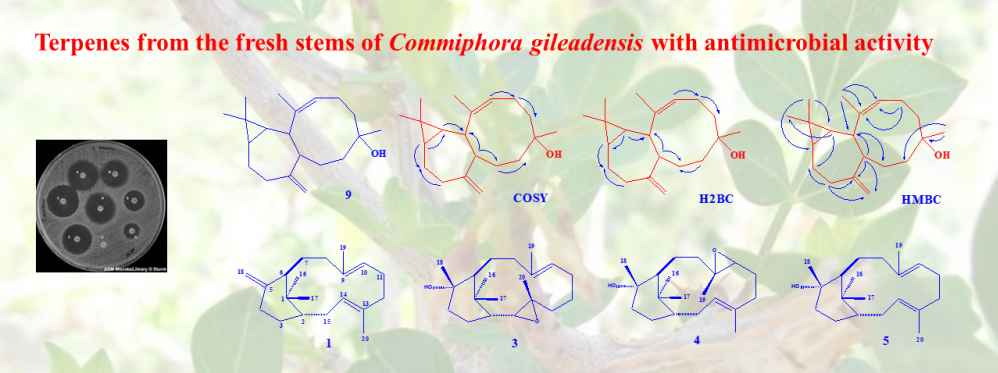
Phytochemical study directed by antimicrobial activity of the fresh Commiphora gileadensis stems CHCl3 extract resulted in the isolation of compounds 1-9. The structures of the isolated compounds were elucidated utilizing various spectroscopic methods including 1D, 2D NMR and HRESIMS. Compounds 1, 3-5 were identified as the ent-verticillane-type diterpenes (1S,3E,7E,11R)-(+)-verticilla-3,7,12(18)-triene (1), (13S,14S)-Ent-13,14-epoxyverticillol (3), (9S,10S)-Ent-9,10-epoxyverticillol (4) and Ent-Verticillol (5) for the first time from Commiphora species. Compound 9 was identified as a diterpene with new skeleton and was given the name “gileadenol”. In addition, four know triterpenes were also identified as friedelin (2), oleanonic aldehyde (6), canyophyllal (7) and urs-12-en-3-one-28-al (8). The three tested ent-verticillane-type diterpenes expressed promising antimicrobial activity especially against K. pneumonia. The new diterpene as well as canyophyllal were less active.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/318.2202.2358 Keywords Commiphora gileadensis antimicrobial ent-verticillane-type diterpenes gileadenol triterpenes DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.10) New Ergostane-type Sterol Produced by an Endophytic Fungus Fusarium phaseoli Isolated from Chisocheton macrophyllus (Meliaceae)
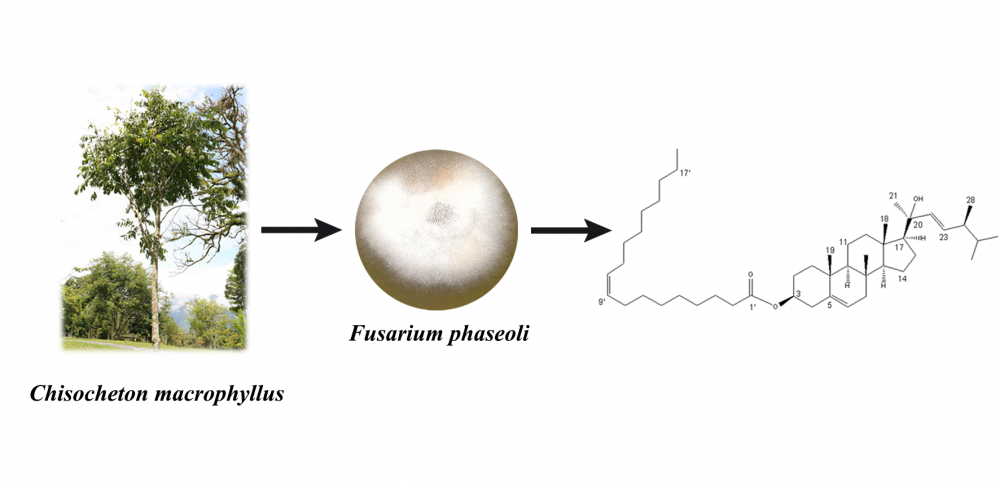
A new ergostane-type sterol, ergost-5,22E-dien-3β-oleate-20-ol (1), along with four known steroids, cerevisterol (2), atroside (3), ergosterol (4), and ergosterol peroxide (5) were isolated from the solid brown rice culture of the endophytic fungus Fusarium phaseoli, derived from the root of Chisocheton macrophyllus. The structures were determined by spectroscopic methods including 2D NMR techniques, MS, and chemical derivatization. Compounds 1-5 were evaluated their antibacterial activities against Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538 and Escherichia coli ATCC 11229, the result showed no activities.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.334.2203.2387 Keywords Fusarium phaseoli Chisocheton macrophyllus Steroid Antibacterial Activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.11) A Novel Nitrogen-containing Glyceride from Fungal Saprobe Tubeufia rubra Reverses MDR of Tumor Cell Lines to Doxorubicin
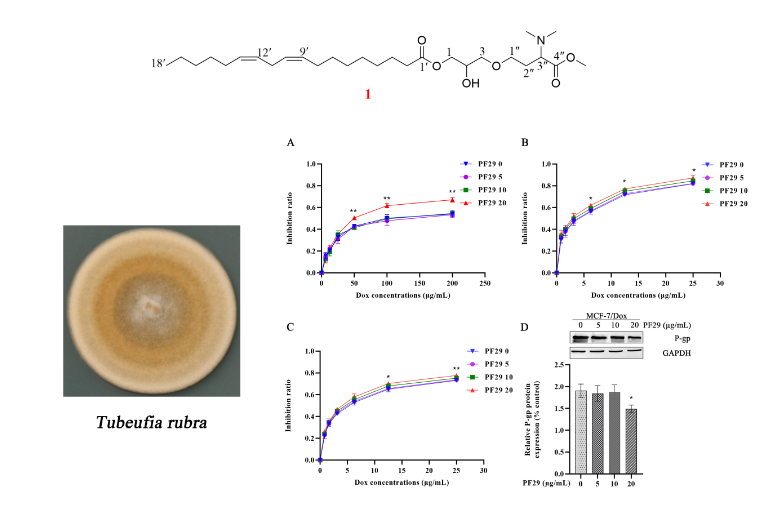
AA chemical investigation of secondary metabolites from the saprobic fungus Tubeufia rubra led to isolation of a novel nitrogen-containing glyceride, Rubracin A (1), and a novel eight-membered cyclic ether carboxylate methyl ester, Rubracin H (2). Together with six known compounds (3-8). The chemical structure of these new compounds were elucidated by 1D and 2D NMR and HR-ESI-MS techniques. Although, there are no observed cytotoxic effects of compound 1 against MCF-7/Dox, A549/Dox, and K562/Dox cells at oncentrations below 25 μg/mL, usage of compound 1 and doxorubicin revealed the MDR reversal via decreased IC50 values than that of sole doxorubicin application in the cell lines. A preliminary Western Blot assay indicated that the MDR reversal of compound 1 was due to suppression of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) expression.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.320.2201.2334 Keywords Rubracin A Tubeufia rubra PF02-2 cytotoxic activity MDR reversal DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.12) A New Indole Glucoside and Other Constituents from the Sea Cucumber-Derived Aspergillus fumigatus M580 and Their Antimicrobial, Cytotoxic, and Inhibitory α-Glucosidase Activities
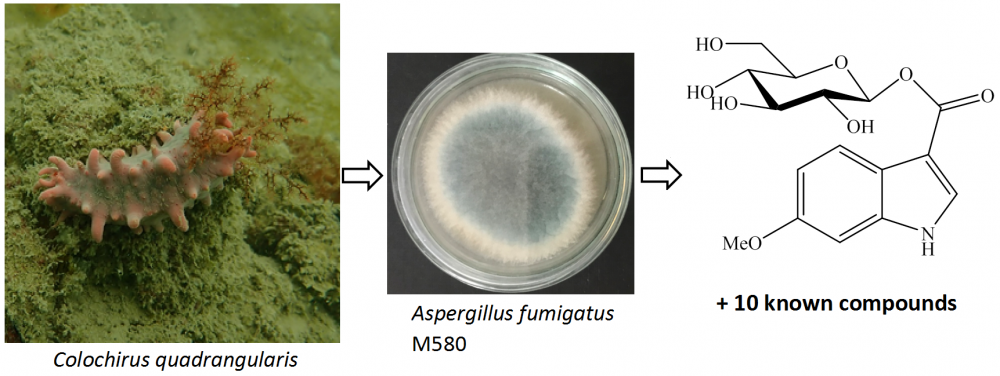
One new indole glucoside, 6-methoxyindole-3-carboxylic acid O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester (1) and ten known alkaloids, fumiquinazoline D (2), fumiquinazoline C (3), fumiquinazoline J (4), bisdethiobis(methylthio)gliotoxin (5), cyclo(L-prolyl-L-tryptophane) (6), tryprostatin B (7), 12,13-dihydroxy-fumitremorgin C (8), 6-methoxyspirotryprostatin B (9), cyclo(L-prolinyl-L-phenylalanine) (10), and cyclo(L-prolinyl-L-valine) (11) were isolated from marine-derived Aspergillus fumigatus M580. Compounds 2, 3, and 7 exhibited significant antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive Enterococcus faecalis with MIC values of 32, 32, and 64 µg/mL, respectively. Compound 4 showed significant cytotoxic activities against Huh7 and HT-29 cancer cell lines with IC50 values of 9.7 ± 0.9 and 10.3 ± 0.9 μM, respectively. Compounds 3 and 10 showed the most α-glucosidase inhibitory activity with inhibitory percentages of 13.6 ± 1.1 and 10.3 ± 0.8 % at the concentration of 100 μg/mL, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.310.2110.2248 Keywords Aspergillus fumigatus indole alkaloid antimicrobial cytotoxic α-glucosidase DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.13) Secondary Metabolites from the Coral-Derived Fungus Aspergillus terreus SCSIO41404 with Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitory Activities
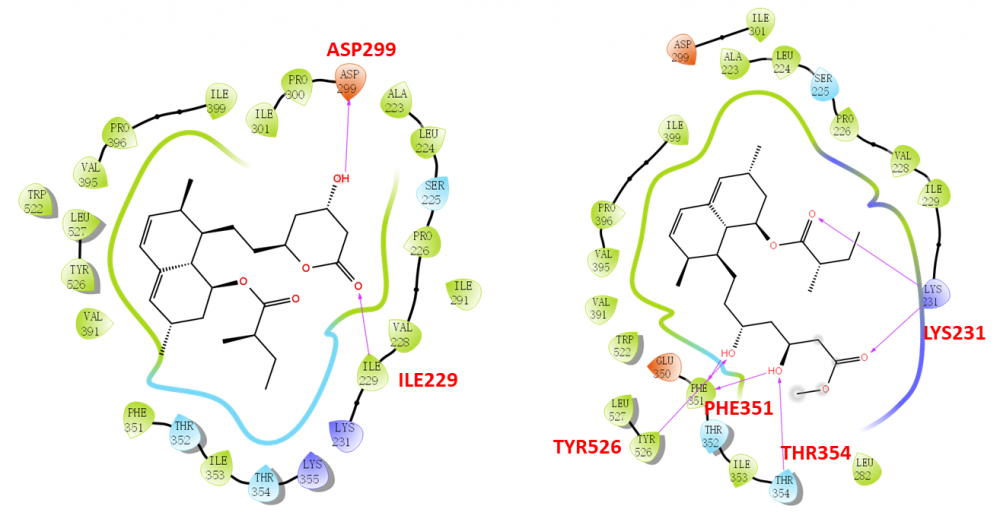
Ten secondary metabolites were isolated from cultures of the marine coral-derived fungus Aspergillus terreus SCSIO41404. The compounds were identified as monacolin K (1), methyl ester of lactone ring-opened monacolin K (2), asperterreusine C (3), 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde (4), 4-hydroxy-3-(3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl) benzaldehyde (5), kojic acid (6), p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid methyl ester (7), o-hydroxyphenylacetic acid methyl ester (8), N-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-acetamide (9), and (S)-methyl 2-acetamido-3-phenylpropanoate (10), by comparing the spectroscopic data with the reported literature values. They were evaluated for their cytotoxic, antibacterial, and enzyme (pancreatic lipase and acetylcholinesterase) inhibitory activities. Monacolin K (1) and its derivative (2) were revealed with obvious pancreatic lipase (PL) inhibitory effects. The in silico molecular docking with PL protein was further performed to understand the binding effects, and it is suggested that the ring opening of the monacolin K facilitates for the PL inhibitory activities.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.312.22.01.2314 Keywords Coral-derived fungus Aspergillus terreus secondary metabolites pancreatic lipase molecular docking DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.14) Degranulation Inhibitors from Petals of Coreopsis grandiflora
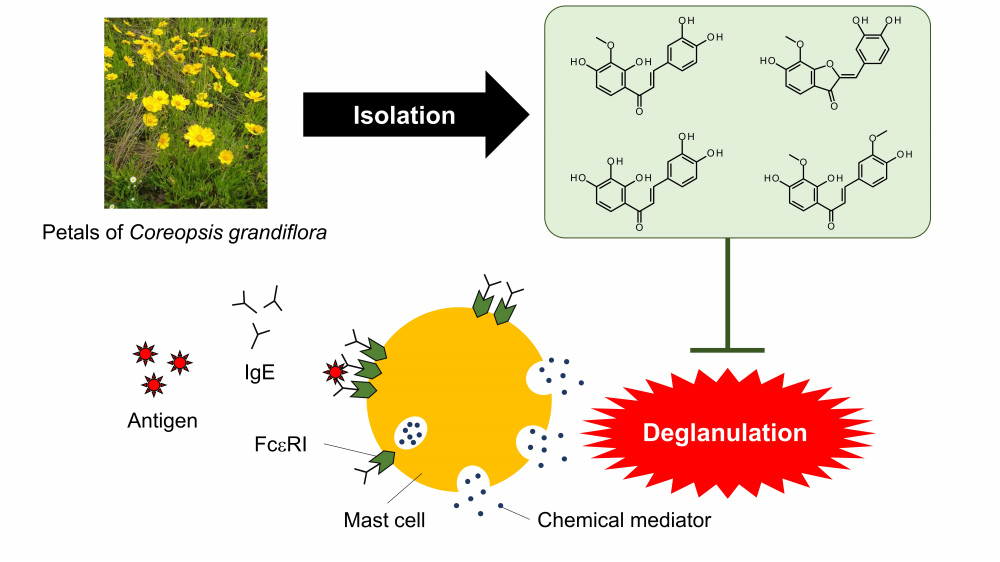
The extracts of petals of Coreopsis grandiflora, a member of the Asteraceae family, were found to inhibit degranulation in RBL-2H3 cells, and lanceoletin, leptosidin, okanin, and 4-methoxylanceoletin were isolated as degranulation inhibitors by liquid-liquid separation and column chromatography. The intensities of the antigen-stimulated degranulation inhibitory activities of the four flavonoids were in the order of leptosidin, okanin, lanceoletin and 4-methoxylanceoletin. Leptosidin, which inhibited antigen-stimulated degranulation most greatly, inhibited calcium ionophore-stimulated degranulation with the same intensity as that of lanceoletin and okanin. As a result of investigation of the structure-activity relationships of the four isolated active compounds for antigen-stimulated degranulation inhibitory activities, it was found the inhibitory activity of lanceoletin, a chalcone, was enhanced by forming a C ring and becoming leptosidin, an aurone. In addition, the three chalcones tended to have greater degranulation inhibitory activity as their molecule polarities increased.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.319.2202.2351 Keywords Degranulation inhibitory activity aurone chalcone Coreopsis grandiflora RBL-2H3 cells DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.15) Three Rare Furan Derivatives Transformed from Secoiridoids were Isolated from the Roots of Gentiana macrophylla
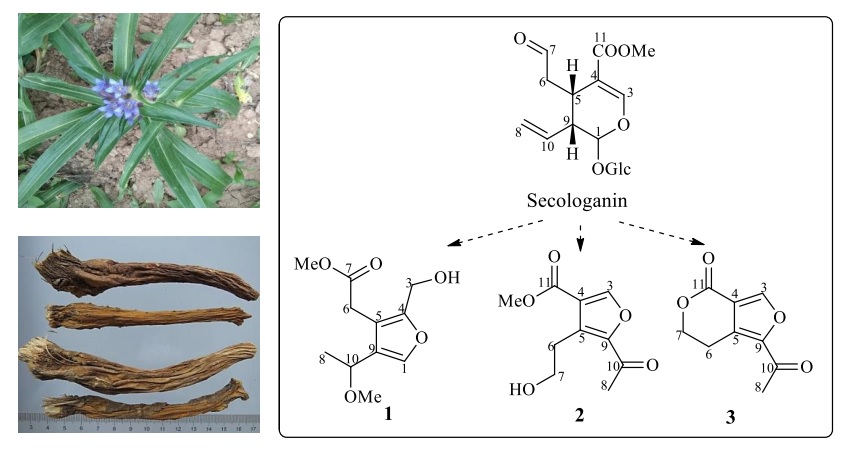
Abstract: Three furan derivatives (1-3) were isolated from the methanol extract of Gentiana macrophylla Pall. (Gentianaceae). Their structures were determined on the basis of spectroscopic analysis including HR-MS, 1D and 2D NMR. Genfurtate (1) was identified as a new compound, while, swertianglide (2) was firstly reported in genus Gentiana, and anglelone (3) was firstly reported in the plant G. Macrophylla. Accordingly, their biosynthesis pathways transformed from secologanin in G. macrophylla was deduced.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.322.2201.2333 Keywords Gentiana macrophylla Gentianaceae furan derivatives structural elucidation biosynthesis secoiridoid glycosides DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.16) Integrated Analysis of Vietnamese Illigera trifoliata ssp. cucullata (Merr.) Kubitzki), Leaf and Stem Essential Oils by GC-FID/GC-MS and 13C NMR

Illigera trifoliata ssp. cucullata (Merr.) Kubitzki (Hernandiaceae) is a liana distributed mainly in the tropical regions of Asia. Nothing is known on the phytochemicals produced by this species. Oil samples have been isolated from leaves, and stems, and analyzed by combination of chromatographic and spectroscopic techniques [GC(FID), GC-MS and 13C NMR]. The compositions of leaf and stem oils were dominated by a-phellandrene (25.8 and 29.2%), a-pinene (26.0 and 9.5%) and b-phellandrene (12.8 and 15.8%), followed by limonene (5.5 and 8.1%) and b-pinene (7.5 and 3.0%). The stem essential oil from Illigera trifoliata ssp. cucullata exhibited antibacterial activity against Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli with MIC values of 4000 μg/mL and IC50 values of 1824,56 ±136 and 2666,66 ±257 μg/mL, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.326.2111.2254 Keywords Illigera trifoliata ssp. cucullata essential oil composition monoterpene hydrocarbons-rich oi α- phellandrene β-phellandrene α-pinene DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.