Records of Natural Products
Year: 2022 Volume: 16 Issue:5 September-October
1) A New Iridoid Glycoside from Wine-Processed Corni fructus
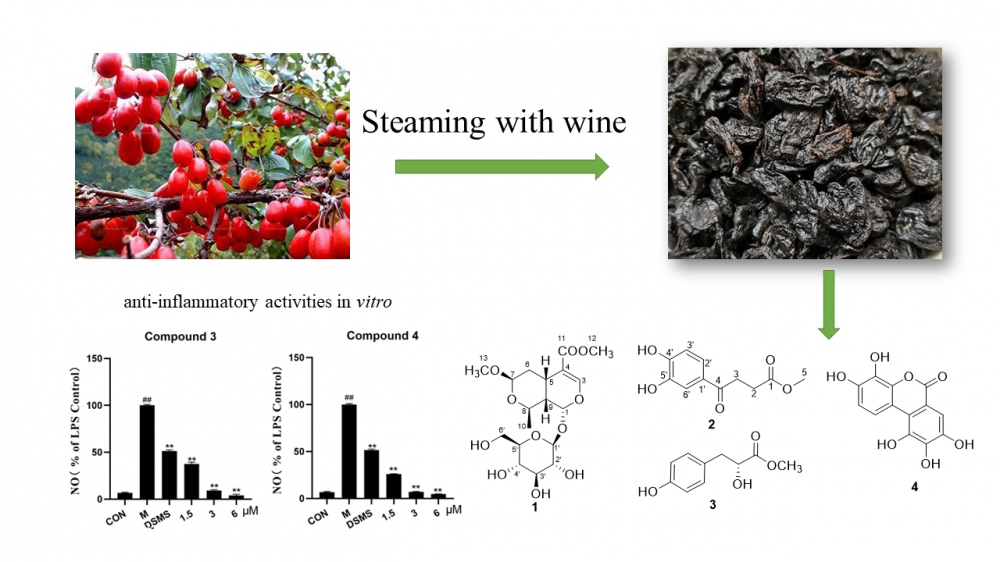
A new iridoid glycoside, cornusglucoside I (1), and a new natural product methyl 4-(3′,4′-dihydroxyphenyl)-4-oxobutanoate (2), together with two known isolated compounds (3-4) were obtained from the 30% ethanol extract of the wine-processed Corni fructus. Their structures were clarified by spectroscopic analysis and literature data. The absolute configuration of 1 was elucidated by ECD calculation. By evaluating the NO production induced by LPS in RAW 264.7 cells to assess the anti-inflammatory activities of isolated compounds. Among the tested compounds, compounds 3 and 4 exhibited stronger anti-inflammatory activity than the positive drug dexamethasone (6 μM), which may be potential anti-inflammatory drugs.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.300.21.10.2232 Keywords Iridoid glycoside wine-processed Corni fructus anti-inflammatory activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
2) Secondary Metabolites with Tyrosinase and Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitory Activities from Leonuri Fructus
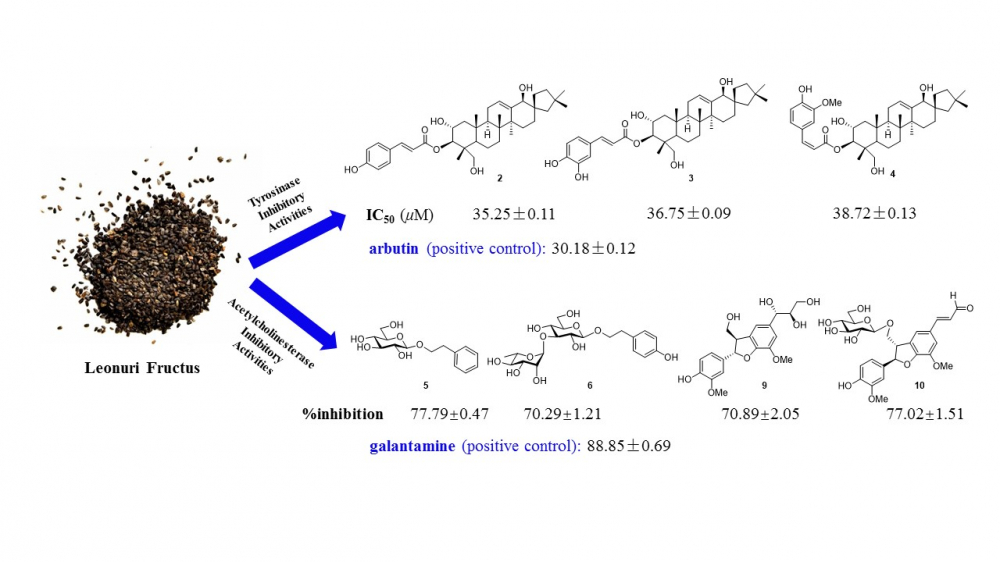
Fourteen secondary metabolites, including one cinnamate derivative (1), three spirocyclic nortriterpenoids (2–4), three phenylethanoid glycosides (5–7), four lignans (8–11) and three phenolic compounds (12–14) were isolated from the EtOH extract of Leonuri Fructus. Their structures were elucidated on the basis of 1D NMR, 2D NMR and HR-ESI-MS data analysis. All isolates were tested for their antioxidant, tyrosinase and acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activities. Most of them showed moderate antioxidant activities. Compounds 2–4 exhibited obvious inhibitory activities against mushroom tyrosinase at 25 μM, with %inhibition values of 49.36 ±2.69%, 43.43 ± 3.35%, 51.69 ± 2.81%, respectively, with arbutin used as the positive control (51.90 ± 2.57%). Compounds 3, 5–6 and 9–10 exhibited significant inhibitory activities against acetylcholinesterase, similar to the positive control, galantamine
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.297.2110.2223 Keywords Leonuri Fructus Leonurus japonicus nortriterpenoid phenylethanoid glycoside tyrosinase acetylcholinesterase DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) A New Iridoid Glucoside from the Stems of Myoporum bontioides (Sieb.et Zucc.) A. Gray
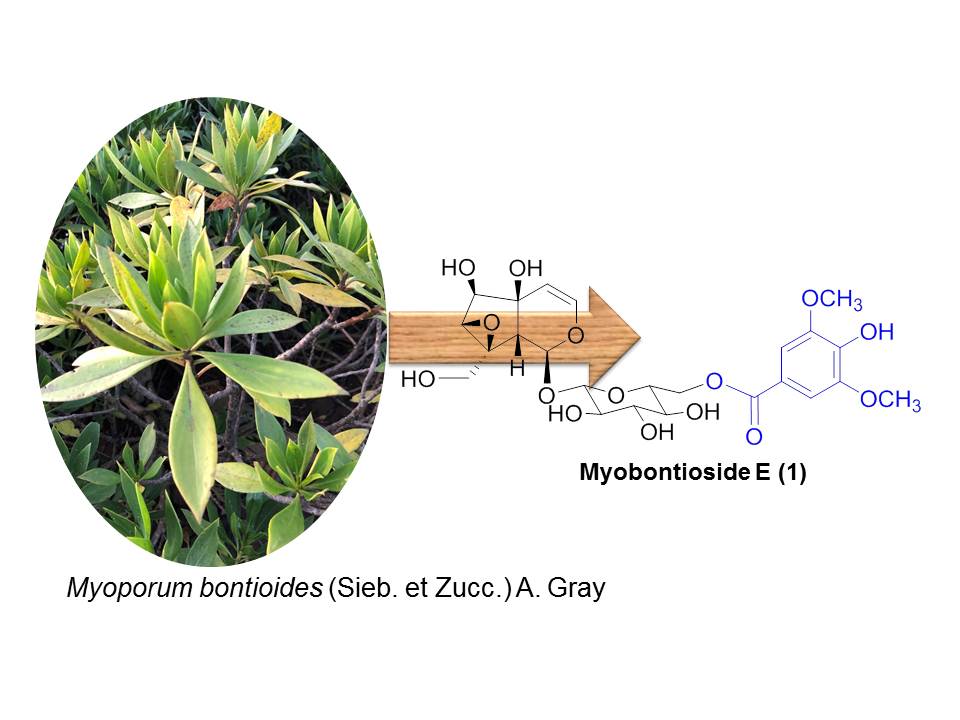
A phytochemical investigation of the stems of Myoporum bontioides (Sieb. et Zucc.) A. Gray, a semi-mangrove plant distributed along coastlines of north-eastern Vietnam and some Asian countries led to the isolation of a new iridoid glucoside (1), named myobontioside E, together with fourteen known compounds (2-15). Their structures were elucidated by means of HR ESI-MS, 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy as well as comparison with the data reported in the literature. The cytotoxic effects on 8505C, MKN7, HT29, and T24 cell lines were assessed using SRB assay. Only iridoid 2 exhibited weak cytotoxicity against all tested cell lines with IC50 values ranging from 60.19 to 69.14 µM.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.296.2108.2191 Keywords Myoporum bontioides Myoporaceae iridoid glucoside dammarane saponin cytotoxicity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Improved Anti-Atopic Dermatitis Effect of H. macrophylla through the Generation of Hydrangenol by Microwave Processing

The compounds hydrangenol and hydrangenol 8-O-glucoside are abundant in Hydrangea macrophylla. This study investigated the effects of hydrangenol and hydrangenol 8-O-glucoside derived from H. macrophylla on atopic dermatitis (AD). Compared with hydrangenol 8-O-glucoside, hydrangenol resulted in more potent inhibition of interleukin 4 (IL-4) gene expression and β-hexosaminidase release, as well as more potent inhibition of the phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6). Ultra High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UHPLC), the concentrations of hydrangenol were found to be lower than the concentration of hydrangenol 8-O-glucoside in H. macrophylla extracts. To increase the hydrangenol content of H. macrophylla extract, component conversion methods were studied. Conclusion, microwave processing was found to be the optimal method for deglycosylation.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.298.21.10.2250 Keywords Hydrangea macrophylla hydrangenol hydrangenol 8-O-glucoside atopic dermatitis microwave irradiation DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Bronchodilator Phenylpropanoid Glycosides from the Seeds of Prunus mahaleb L.
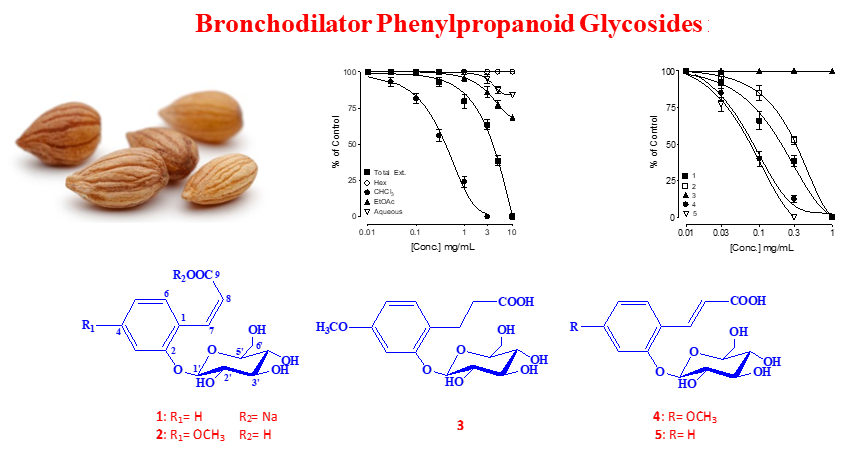
Prunus mahaleb seeds were selected for phytochemical study directed by ex-vivo bronchodilator effect based on the traditional use for the treatment of respiratory problems. From the active chloroform fraction, five known phenylpropanoid glycosides: cis-melilotoside sodium salt (1), cis-methoxy-melilotoside (2), 3-(2-O-b-D-glucopyranosyl-4-methoxyphenyl) propanoic acid (3), trans-methoxy-melilotoside (4) and trans-melilotoside (5) were identified for the first time from genus Prunus. Chemical structure of the compounds elucidated by spectroscopic techniques such as 1D, 2D NMR and HR-ESI/MS. Compounds 1, 2, 4, 5 showed promising bronchodilator effects against carbamylcholine (CCh) induced bronchospasm in isolated Guinea-pig trachea while 2 was found completely inactive. The mechanism(s) of action was studied using both CCh, low K+ (25 mM) and high K+ (80 mM)-mediated contractions and compound 2 was found distinctly more potent and efficacious against CCh compared to both types of K+-mediated contractions where partial efficacy was observed, hence showed dual inhibition of cholinergic receptors followed by Ca2+ channels. The anticholinergic and Ca2+ inhibitory activities of compound 2 were further confirmed when it deflected CCh concentration response curves (CRCs) without suppression, whereas its higher doses shifted Ca2+ CRCs similar to verapamil. The bronchodilator effect proved to be mediated via dual anticholinergic and Ca2+ channels blocking effects.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.303.2111.2270 Keywords Prunus mahaleb L seeds bronchodilator phenylpropanoid glycosides anticholinergic calcium channel blocker DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Cytotoxic Diterpenoids from Scoparia dulcis
A new scopadulane-type diterpenoid (1) and one known labdane-type diterpenoid (2) have been isolated from the whole plants of a traditional medicinal plant, Scoparia dulcis. Their structures were established mainly by spectroscopic methods, and the absolute configuration of compound 1 has been determined by quantum chemical calculation of the electronic circular dichroism (ECD) spectrum and comparison with the experimental one. The cytotoxicity of 1 and 2 against two breast cancer cell lines (MCF-7 and MDA-MB231) and a cervical cancer cell line (Hela) were tested, and only compound 2 displayed inhibitory activities against these cells with IC50 values ranging from 8.1 to 45.2 mM, while compound 1 were inactive. In addition, compound 2 also showed in vitro anti-tumor activity against MCF-7, MDA-MB231, and Hela cells in a concentration-dependent manner.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.304..2111.2266 Keywords Scoparia dulcis Scrophulariaceae scopadulane diterpenoid labdane diterpenoid cytotoxicity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) A New Alkaloid from the Endophytic Fungus of Crocus sativus L., Aspergillus fumigatus Y0107
A new alkaloid (compound 1), together with 8 known alkaloids (compounds 2-9), were isolated from Aspergillus fumigatus Y0107 extracts from the lateral buds of Crocus sativus Linn (saffron). The structure of compound 1 was elucidated with NMR spectroscopy, High-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HR-ESI-MS) and compared with its analogues in the literatures. The antibacterial activities of the crude ethyl acetate (EA) extract (CEE) and isolated compounds (compounds 1, 2, 6, 8) were evaluated against plant pathogenic bacteria. Compound 2 and the CEE demonstrated moderate inhibitory activity with MICs of 100 μg/mL against Erwinia sp.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.307.2110.2235 Keywords Crocus sativus L. endophytic fungus Aspergillus fumigatus Y0107 alkaloids plant pathogenic bacteria DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) A New Benzophenone Derivative from the Endophyte Shiraia sp. BYJB-1

A new benzophenone derivative, shiraone A (1), along with seven known compounds, linchenxantone (2), 4-hydroxymellein (3), hypocrellin A (4), hypocrellin B (5), 9,11-dehydroergosterol peroxide (6), ergosteroal peroxide (7), and lactariolide I (8), were isolated from the cultures of Shiraia sp. BYJB-1, a fungus from the leaves of the medicinal plant Selaginella delicatula. The structures of these compounds were established via extensive spectroscopic techniques, including 1D/2D NMR, HRESIMS and through comparison with data reported in the literatures. In addition, the cytotoxic activities and antibacterial activities of compounds 1-8 were evaluated, and compounds 6 and 7 exhibited moderate cytotoxic activities against SMMC7721 cell line with IC50 values of 25.9 and 45.8 μM respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.306.2111.2265 Keywords Endophytic fungus Shiraia sp. benzophenone cytotoxic activity antibacterial activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.9) Essential Oils of Lauraceae: Constituents and Antimicrobial Activity of Dehaasia cuneata (Blume) Blume and Caryodaphnopsis tonkinensis (Lecomte) Airy-Shaw from Vietnam
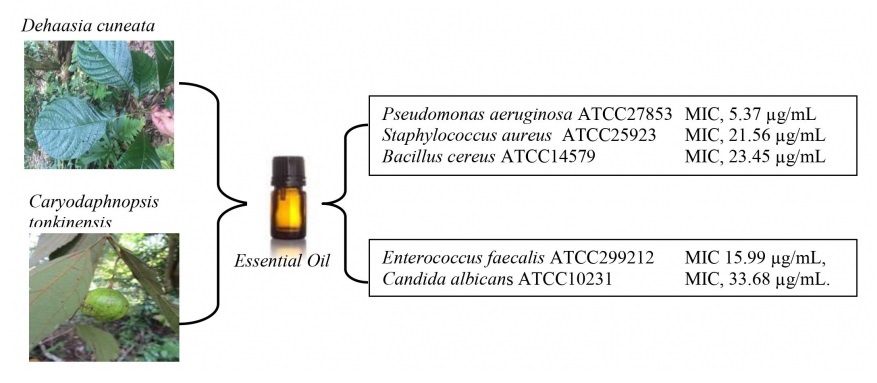
The herbs, Dehaasia cuneata (Blume) Blume and Caryodaphnopsis tonkinensis (Lecomte) Airy-Shaw (Lauraceae) were used ethnomedically for the treatment of malaria, inflammation and amelioration of microbial infections. We report herein the chemical constituents and antimicrobial activity of the leaf essential oils of D. cuneata and C. tonkinensis from Vietnam. The technique of gas chromatography (GC) and gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (GC/MS) was used to analyze the oil samples while the microdilution assay was employed to determine the antimicrobial efficacy. The main constituents of D. cuneata were α-pinene (49.0%), camphene (19.5%), β-pinene (15.6%) and limonene (7.5%), while α-pinene (26.8%), β-pinene (23.0%) and bicyclogermacrene (8.5%). The leaf oil of D. cuneata displayed potent antimicrobial activity against Gram-negative bacteria, Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC27853 with minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) value of 5.37 µg/mL; and Gram-positive microorganisms of Staphylococcus aureus ATCC25923 (MIC, 21.56 µg/mL and Bacillus cereus ATCC14579 (MIC, 23.45 µg/mL). The leaf oil of C. tonkinensis exhibited good antibacterial activity towards Enterococcus faecalis ATCC299212 with MIC value of 15.99 µg/mL, and anti-candidal action against Candida albicans ATCC10231 with MIC value of 33.68 µg/mL. the chemical constituents and antimicrobial activity of the essential oils were being reported for the first time.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.301.2110.2240 Keywords Antimicrobial activity essential oil composition terpenes DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.10) Sesquiterpenoids and Diterpenoids from the Flowers of Nicotiana tabacum L. and Their Antifungal Activity
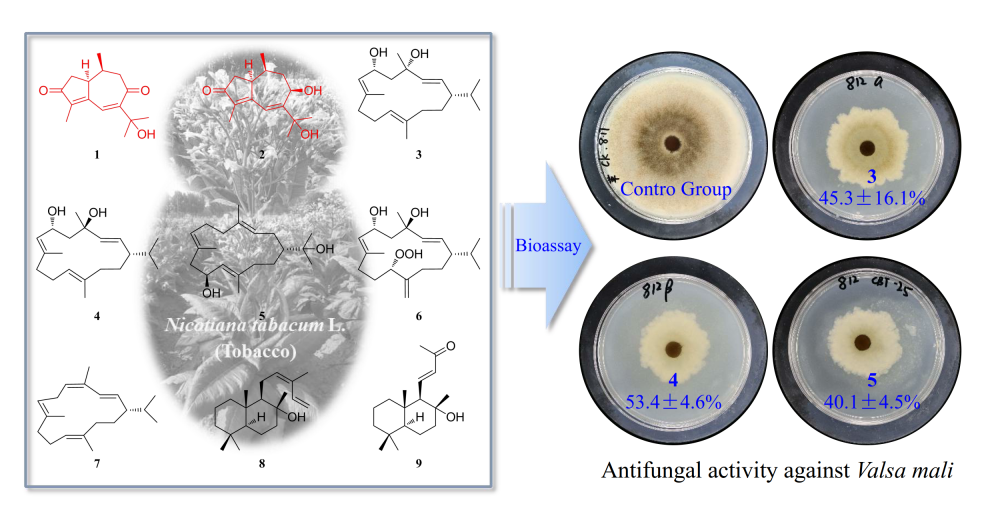
Two new guaiane-type sesquiterpenoids, nicotiasesquiterpenes A (1) and B (2), and seven known cembrane-type diterpenoids (3−9), were isolated from glandular trichome secretions of fresh flowers of Nicotiana tabacum L. These new chemical structures were established by extensive analyses of HRESIMS and 1D and 2D NMR data, while the other structures were elucidated by comparison of 1D NMR data with those reported in the literature. All of the isolated compounds were tested for their antiphytopathogenic fungal activity against Valsa mali var. mali, Alternaria porri, and Botrytis cinerea at a concentration of 10 µg/mL. Compounds 3, 4, and 5 exhibited medium antifungal effects against Valsa mali var. mali, with inhibitory rates of 45.3±16.1, 53.4± 4.6, and 40.1±4.5%, respectively, while the other compounds showed only insignificant activities.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.293.2109.2211 Keywords Nicotiana tabacum Valsa mali var. mali Alternaria porri Botrytis cinerea antifungal activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.11) Cytotoxic Drimane-type Sesquiterpenoids from the Fungus Aspergillus flavipes 297
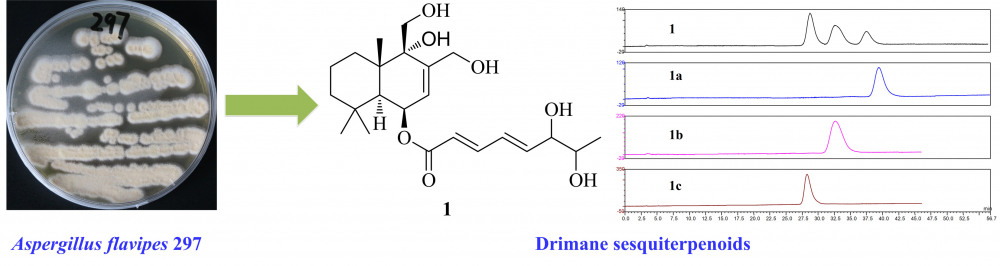
Chemical investigation of the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus flavipes 297 led to the isolation and identification of three drimane-type sesquiterpenoids, asperflavinoid A (1) and (6-strobilactone-B) esters of (E,E)-6,7-dihydroxy-2,4-octadienoic acids (2 and 3). Asperflavinoid A (1) was characterized as unseparated diastereomers and its chemical structure was determined by spectroscopic analysis of NMR and MS data. In the cytotoxic assay, compound 1 showed promising inhibitory effects on HepG2 and MKN-45 cell lines.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.294.2109.2194 Keywords Aspergillus flavipes natural products drimane sesquiterpenoids cytotoxicity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.12) Secondary Metabolites from Thraustochytrium aureum and their Biological Activity
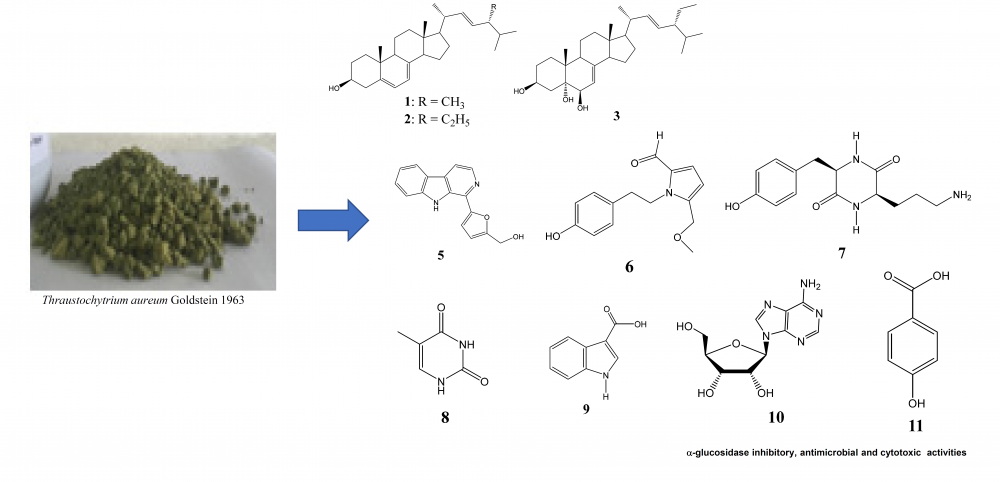
Phytochemical investigation of Thraustochytrium aureum led to the isolation of eleven compounds including ergosterol (1), 7-dehydroporiferasterol (2), (22E,24R)-ethylcholesta-7,22-dien-3β,5α,6β-triol (3), poriferasterol glucoside (4), perlolyrine (5), pyrrolezanthine-6-methyl ether (6), 3-(3-aminopropyl)-6-[(4-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]-2,5-piperazinedione (7), 5-methyluracil (8), 1H-indole-3-carboxylic acid (9), adenosine (10), and p-hydroxybenzoic acid (11). Screening for α-glucosidase inhibitory, antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities of the extracts and isolated compounds were carried out. The n-hexane extract was the most active, which showed strong α-glucosidase inhibitory activity with IC50 of 48.22 μg/mL, inhibition against E. faecalis, S. aureus and C. albicans microorganism strains with MIC values of 128, 64 and 64 μg/mL, respectively. Compound 6 have shown to be the most active among isolated compounds, which inhibited α-glucosidase with IC50 value of 7.96 μg/mL; E. faecalis and C. albicans microorganism strains with MIC values of 64 and 16 μg/mL and inhibited the growth of A549, HepG2, MCF7 and LNCaP cancer cell lines with IC50 values of 62.26, 41.03, 57.21 and 43.23 μg/mL, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.299.21.10.2236 Keywords Thraustochytrium aureum alkaloid steroid microalga α-glucosidase DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.13) A New ent-Atisane Diterpenoid from the Stems of Euphorbia royleana
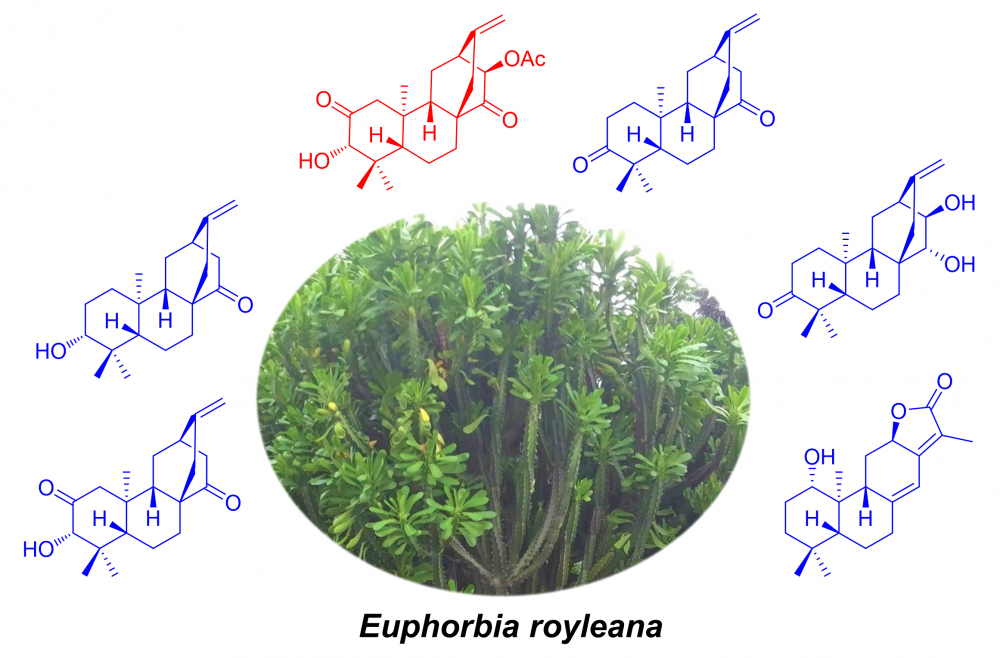
A new ent-atisane diterpenoid, named euphrosanoid A (1), along with five known analogues (2-6) were isolated from the stems of Euphorbia royleana. The structure of new compound 1 was determined by extensive spectroscopic data, especially 1D and 2D NMR experiments, and the absolute configuration of 1 was determined by comparison of experimental and calculated electronic circular dichroism (ECD) data. All isolated compounds were evaluated for their cytotoxic activities, and compounds 1 and 5 showed weak cytotoxicities against HCT-15 cancer cells with IC50 values of 62.98 ± 6.27 and 44.35 ± 3.66 uM, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.302.2111.2287 Keywords Euphorbia royleana cytotoxic activity ent-atisane diterpenoid DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.14) Composition and Antimicrobial Activity of Essential Oils from Leaves, Twigs and Ripe Fruits of Magnolia grandis

The leaves, twigs and ripe fruits of Magnolia grandis (Hu & W.C.Cheng) V.S.Kumar, growing wild in Ha Giang Province of Vietnam, were hydrodistilled to obtain essential oils which had the respective average yields of 0.09%, 0.25% and 0.62% (v/w), calculated on a dry weight basis. The oils were analyzed using gas chromatography-flame ionization detector (GC-FID) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Major components of these three oil samples were: α-pinene (11.8%), linalool (15.4%) and (E)-β-caryophyllene (10.7%) (leaf oil); α-pinene (42.8%) and β-pinene (23.7%) (twig oil); α-pinene (52.2%) (ripe fruit oil). The essential oils from leaves showed stronger inhibitory effects on the seven tested microorganism strains than those from twigs and ripe fruits. To our best knowledge, this is the first time that information on essential oils of M. grandis leaves, twigs and ripe fruits is reported.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.305.2112.2299 Keywords Magnolia grandis antimicrobial activity essential oil composition α-pinene DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.15) A New Eremophilanolide from the Fresh Roots of Rehmannia glutinosa
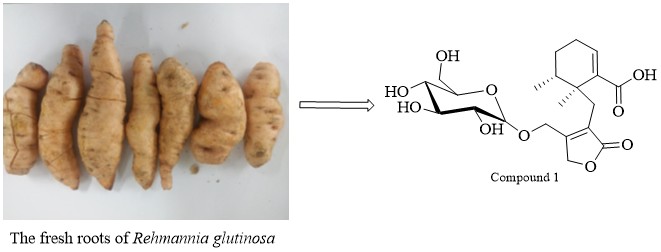
A new eremophilanolide, serratifolide F (1), and six known compounds were isolated from the fresh roots of Rehmannia glutinosa. Their structures were characterized by analysis of NMR, CD, HRESIMS, and comparison of the data in previous literatures. The protective effects against lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated damage on normal rat kidney tubule epithelioid (NRK-52e) cells of the compounds were evaluated using MTT assay and real time cellular analysis (RTCA). The results showed that compound 3 exhibited renoprotective activity with EC50 value of 45.1 μM.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.309.2111.2258 Keywords Scrophulariacea Rehmannia glutinosa eremophilanolide glycosides renoprotective activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2022 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.