Records of Natural Products
Year: 2023 Volume: 17 Issue:3 May-June
1) Triterpenoids and Pharmacological Activities from Kadsura (Schisandraceae) were Gathered from 1987 to 2022
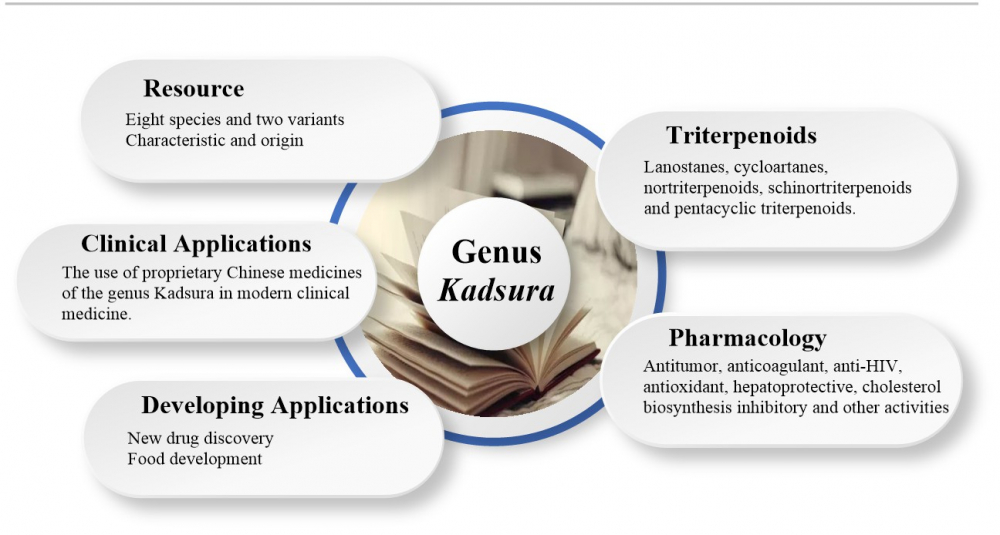
The genus Kadsura is a commonly used herb in Chinese folklore, with sedative, hypnotic and beneficial effects, mainly for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, insomnia and other conditions. Modern pharmacological studies have shown that triterpenoids are one of the main components to possess these medicinal effects. In addition, triterpenoids in genus Kadsura also exhibited anti-tumor, cholesterol synthesis inhibition, anti-HIV, antioxidant and hepatoprotective activities. At present, there are few literatures reported on the triterpenoids in this genus. Therefore, the purpose of this paper is to review the triterpenoids in the genus Kadsura and their pharmacological activities, introduce the research progress on their germplasm resources, clinical applications and developmental applications, and provide references for further research and development of the plant resources of this genus.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.373.2209.2588 Keywords Kadsura triterpenoids pharmacological activities clinical applications developing applications DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) Research Progress on the Chemical Components and Pharmacological Activities of Gesneriaceae
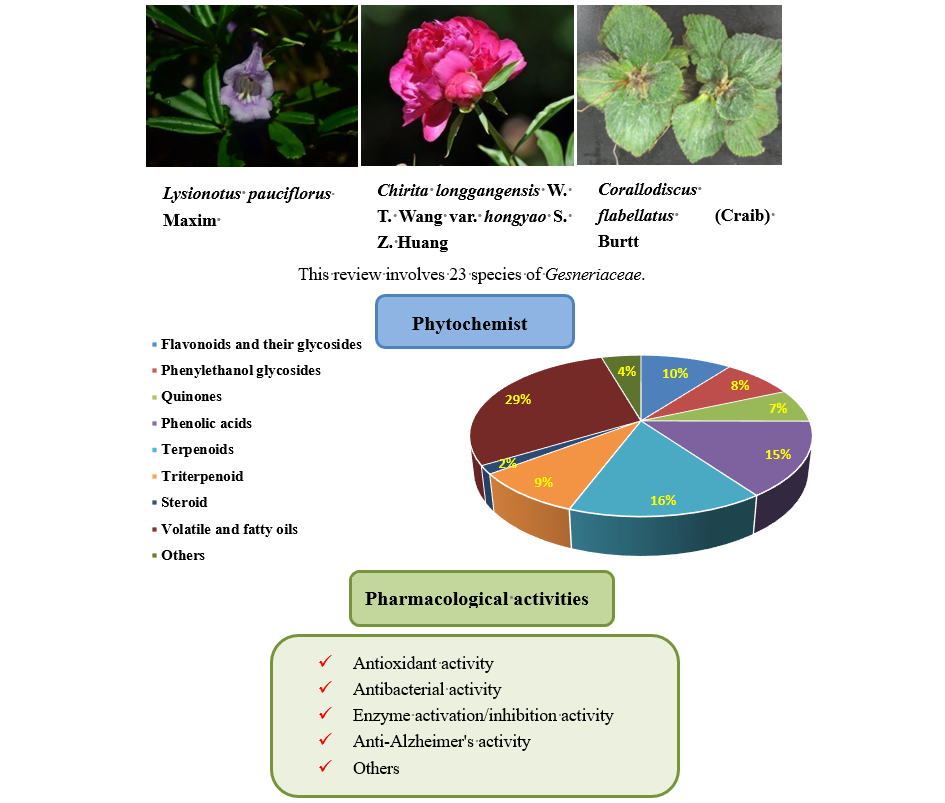
The chemical components of the family Gesneriaceae are complex and diverse. The compounds isolated from the plants of this family mainly include flavonoids, phenylethanoid glycosides, terpenoids, anthraquinones, organic carboxylic acids, and steroids. Gesneriaceae have a wide range of pharmacological activities, including antioxidant, antibacterial, anti-tumor, enzyme inhibition and activation, cytotoxicity, and anti-Alzheimer activities. In this study, the chemical components and pharmacological activities of Gesneriaceae in recent years were summarized to provide a reference for future studies.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.372.22.05.2470 Keywords Gesneriaceae chemical components flavonoids phenylethanosides pharmacological activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) Comparative Analyses on Chemical Constituents and Biological Activities of Laserpitium siler L. from Serbia
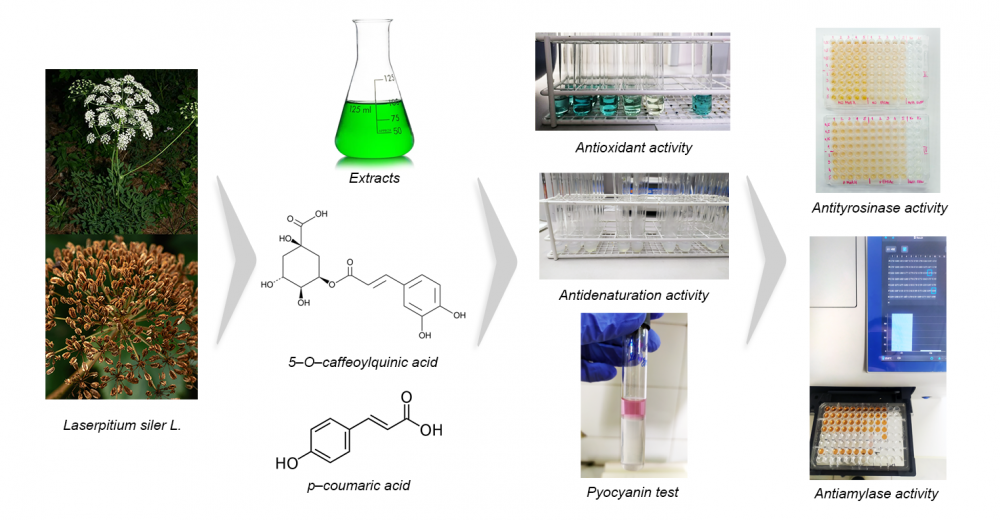
The traditional European medicinal plant Laserpitium siler L. was studied for the first time for the chemical composition and in vitro biological potential of extracts from fruits and aerial parts. Eight extracts were subjected to spectrophotometric detection and LC-MS quantification of phenolics. The bioactivity assessment comprised antioxidant, antimicrobial, anti-denaturation, acetylcholinesterase, tyrosinase, α-amylase, and α-glucosidase inhibition assays. The spectrophotometric analyses showed that the alcoholic extracts contained the most phenolic acids and coumarins. Among the twenty quantified compounds in the methanolic extracts, chlorogenic acid (29.098 mg/kg in the fruits; 47.438 mg/kg in the aerial parts) and p-coumaric acid (7.468 mg/kg in the fruits; 9.482 mg/kg in the aerial parts) were the most abundant. The DPPH/ABTS/BBT tests showed the strongest antioxidant effect of the methanolic extract of the aerial parts. The results of the microdilution assay referred to stronger antibacterial than antifungal activity, with the essential oil being as effective as the antibiotics used. The extracts expressed promising activity against P. aeruginosa PAO1 biofilm formation and pyocyanin synthesis. The prevention of BSA denaturation by the ethanolic extracts was comparable to diclofenac (91.08%-fruits, 95.08%-aerial parts, and 95.60%-diclofenac). IC50 values showed greater enzyme inhibitory potential of aerial parts and the highest reduction of α-glucosidase activity.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.364.2207.2528 Keywords Laserpitium siler phenolics LC-MS antioxidant antimicrobial enzyme inhibitory activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Anti-inflammatory Continents from the Heartwood of Dalbergia melanoxylon
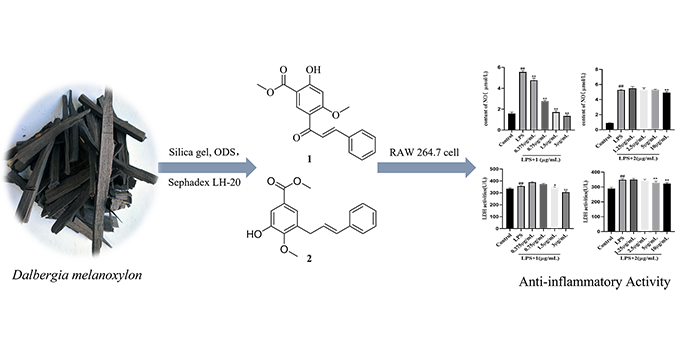
A new chalcone compound, methyl 5-cinnamoyl-2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzoate (1), and a new cinnamylphenol compound, methyl 3-cinnamyl-5-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzoate (2) together with four known compounds (3-6) were obtained from the CH2Cl2 soluble fraction of Dalbergia melanoxylon. Their structures were elucidated by comprehensive spectral measurements, single crystal X-ray diffraction and literature data. According to the determination results of compound 1 and 2 on RAW 264.7 cell viability, the IC50 values of compounds 1-2 were 4.11 and 113.99 μg/mL, respectively. Compared with LPS model group, compound 1 and 2 could significantly reduce the release of NO in the concentration rages of 0.375~3.0 μg/mL and 10 μg/mL (P<0.01), and significantly inhibit the secretion of LDH with 1.5~3 μg/mL and 5~10 μg/mL.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.366.2208.2560 Keywords Dalbergia melanoxylon chalcone cinnamylphenol anti-inflammatory activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) Diterpenoids from the Seeds of Euphorbia Lathyris and their Cytotoxic Acitivity
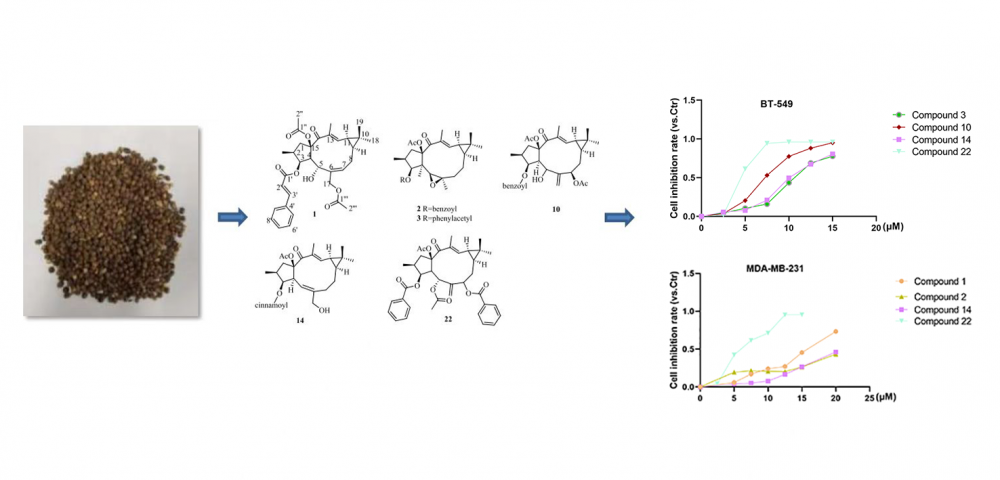
A new lathyrane-type diterpenoid, named euphorbia factor L35 (1), along with twenty-two known analogues (2-23) were isolated from the seeds of Euphorbia lathyris. Their structures were elucidated by using 1D- and 2D-NMR spectra and HRESIMS analysis. The cytotoxic effects of the isolated compounds against BT-549 and MDA-MB-231 cancer cells lines were evaluated by the SRB assay. Compounds 3, 10, 14, and 22 were found to exhibit considerable cytotoxic activities against BT-549 cells, with IC50 values ranging from 4.7 to 10.1 μM. Compounds 1, 2, 14 and 22 were able to inhibit the MDA-MB-231 cells growth with IC50 values of 5.7 to 21.3 μM, while other compounds showed no obvious inhibitory effects.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.365.2205.2459 Keywords Euphorbia lathyris; lathyrane-type diterpenes; cytotoxic activity. DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Analysis of Phenolic Compounds by LC-HRMS and Determination of Antioxidant and Enzyme Inhibitory Properties of Verbascum speciousum Schrad
Studies have shown an inverse correlation among age-related illnesses like coronary heart disease and cancer and intake of fruit and vegetable. Given the probable health benefits of natural antioxidants from plants, research on them has increased. Verbascum L is a large genus of Scrophulariaceae family and 323species distributed worldwide. Since Verbascum L. species are plants that grown in many regions of the Turkiye and used in folk medicine, it is important to evaluate the biological activity of these species. In this study antioxidant properties of Verbascum speciosum Schrad. were investigated. The antioxidant capacities of water and ethanol-based extracts obtained from air parts were evaluated with Fe3+ reducing, CUPRAC, FRAP, DPPH‧ and ABTS•+ scavenging antioxidant methods. Extracts were examined to determine their AChE, α-glycosidase and α-amylase enzyme inhibitions also. This investigation could be a basis for further phytochemical investigations of Verbascum speciosum Schrad.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.370.2210.2598 Keywords Verbascum speciosum antioxidant activity reducing power radical scavenging enzyme inhibition DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) Isolation of Undescribed Biflavonoid from Potamogeton pusillus L. and Antidiabetic Activity Properties
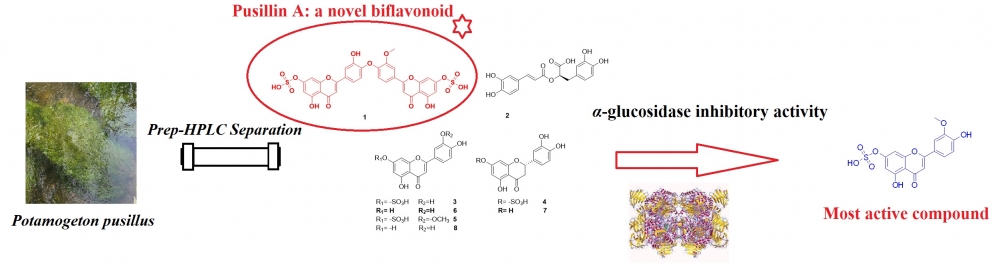
A phytochemical study on the Potamogeton pusillus L. led to the isolation and identification of a novel biflavonoid, pusillin A (1) with known seven compounds, including rosmarinic acid (2), luteolin-7-O-sulfate (3), eriodictyol-7-sulfate (4), chrysoeriol-7-sulfate (5), eriodictyol (5), luteolin (7) and chrysoeriol (8). Their structures were elucidated based on spectrometric analysis, including LC-MS/MS and NMR. All compounds were screened for in vitro antidiabetic activity using the spectrophotometric method. Sulfated flavones (1, 3, 4, and 5) exhibited prominent α-glucosidase inhibitory activity, and compounds 2, 6, 7, and 8 showed moderate inhibitory activities. All isolates were reported for the first time from the plant material.
8) Chemical Constituents from The Leaves and Twigs of Magnolia Decidua
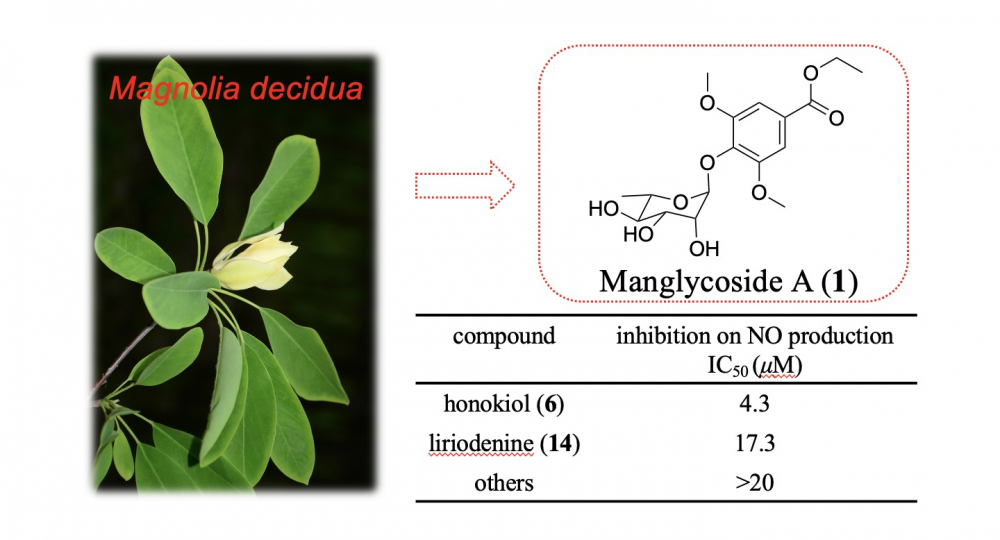
A previously undescribed phenolic glycoside (manglycoside A, 1), as well as 16 identified compounds (2–17), were isolated from the leaves and twigs of the 'vulnerable' plant Magnolia decidua (Magnoliaceae). Comprehensive spectroscopicinvestigation and chemical transformations revealed the structure of the previously unknown compound 1. Among the isolates, honokiol (6) and liriodenine (14) were discovered to exhibit anti-inflammatory activities in LPS-induced RAW 264.7cells via reducing nitric oxide (NO) formation, with IC50 values of 4.3 and 17.3 μM, correspondingly.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.376.2207.2525 Keywords Magnoliaceae Magnolia decidua phenolic glycoside aMnglycoside A anti-inflammatory DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.9) A New Sesquiterpene and Two Nitro-containing Phenylpropionic Acid Derivatives from the Fungus Aspergillus terreus LPFH-1
Chemical study of the fungal strain Aspergillus terreus LPFH-1 led to the isolation of 8 compounds (1-8), including a new acyclic sesquiterpenoid (1) and two new natural products (2 and 3). Their structures were determined by extensive analyses of the spectroscopic data including 1D (1H and 13C NMR) and 2D NMR (1H-1H COSY, HSQC, HMBC, NOESY) data. Compounds 2 and 3 were nitro-containing phenylpropionic acid derivatives, whose absolute configuration was determined by comparing their specific rotations with those of synthetic products. The known compounds were identified as 4-hydroxy-3-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)benzaldehyde (4), ethyl 2,4-dihydroxy-5,6-dimethylbenzoate (5), terretonin D (6), asperterpene K (7), and asterrelenin (8).
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.375.2211.2623 Keywords Aspergillus terreus marine-derived fungus new sesquiterpenes phenylpropionic acid DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
10) A Previously Undescribed Cleistanthane-Type Diterpenoid from Peniophora incarnate

A newly discovered cleistanthane-type diterpenoid named incarnatin A (1) was isolated from Peniophora incarnate, an endophytic fungus obtained from the roots of Ligusticum chuanxiong. Its absolute configuration was unambiguously elucidated by spectroscopic means including HRMS and NMR combined with ECD calculations. Transcriptome sequencing indicated that 1 could inhibit angiogenesis.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.374.2210.2619 Keywords Peniophora incarnate Cleistanthane-Type diterpenoid Incarnatin A Structural elucidation Transcriptome sequencing Angiogenesis DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.11) Eupalinolide N, a Previously Undescribed Sesquiterpene Lactone with Anti-inflammatory Activity from Eupatorium lindleyanum

A previously undescribed sesquiterpene lactone, named eupalinolide N (1), was isolated from traditional Chinese medicine “Ye-Ma-Zhui” (Eupatorium lindleyanum) by ethanol reflux extraction, reduced pressure concentration, macroporous resin column chromatography, and C18 reversed-phase chromatography. Its structure was elucidated by a comprehensive interpretation of spectroscopy evidence as well as ECD calculations. 1 showed anti-inflammatory activity by inhibiting the gene expressions of pro-inflammatory factors including IL-1β, TNFα COX-2, and iNOS at the concentration of 7.5 μM, as well as attenuating the excretion of NO, IL-6, and TNF-α in Raw 264.7 macrophages at the concentration of 15 μM.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.368.2206.2499 Keywords Eupatorium lindleyanum sesquiterpene lactone spectroscopic analyses anti-inflammatory activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.12) Essential Oil of Satureja montana L. from Herzegovina: Assessment of Composition, Antispasmodic, and Antidiarrheal Effects
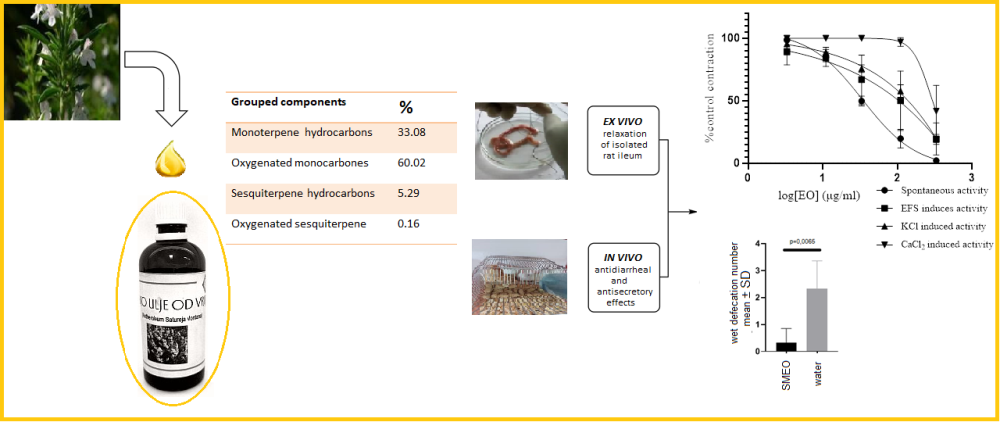
Satureja montana L. (SM) has a long traditional use as a spice and a medicine for various gastrointestinal disorders, including painful spasms and diarrhea. Contrary to conventional drugs, administration of SM and its extracts are considered safe. Previous studies have shown that the essential oils (EOs) of SM from different areas are rich in monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, diterpens, and phenolic compounds, including flavonoids, tannins, and acids with great composition variability. Determination of composition of EO from Herzegovinian SM done by gas chromatography-flame ionization detection and gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC-FID and GC/MS, respectively) revealed carvacrol as a primary substance followed by γ-terpinene, p-cymene, and β-caryophyllene. Ex vivo spasmolitic activity caused by EO was evident in different types of isolated rat ileum function with the most potent effect on spontaneous activity followed by electrical field stimulation and KCl- and CaCl2-induced activity. SMEO produced in vivo antidiarreal activity on castor oil-induced diarrhea in young rats and showed the potential to cause a decrese water content in the feces of adult Wistar rats.This study indicates that effects of SM on the intestinum could be mediated through combination of Kv channel activation and Ca channel blockade, but additional mechanisms might be involved. The results of this study corroborate the traditional use of SM as antispasmodic, antidiarrheal, and antisecretory agents.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.358.2207.2522 Keywords Satureja montana antispasmodic antidiarrheal DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.13) Anti-inflammatory Benzofurans from the Heartwood of Dalbergia cochinchinensis Pierre ex Laness

A new benzofuran, Cochinfuran A (1), and four known benzofurans (2-5) were isolated from the heartwood of Dalbergia cochinchinensis Pierre ex Laness. The chemical structure of the new benzofuran was determined based on broad NMR and mass spectrometry evaluation. Bioactivity assays showed that the compounds 1-3 and 5 were found as anti-inflammatory agents with IC50 values 49.01 ± 1.54, 1368.93 ± 0.98, 67.48 ± 0.92 and 77.91 ± 1.53 μM, respectively. They could reduce the production of NO (P<0.001) with 3.52~7.04, 1.96~7.84, 1.85~7.40 and 0.98~3.93 μM and restrained LDH (P<0.01) with 3.52~7.04, 3.93~7.84, 3.70~7.40 and 0.98~3.93 μM in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages, respectively, the compound 4 (IC50 218.20 ± 3.39 μM) showed no anti-inflammatory activity.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.371.2210.2594 Keywords Dalbergia cochinchinensis Pierre benzofurans anti-inflammatory activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.14) A New Triterpenoid Saponin Isolated from Zornia diphylla
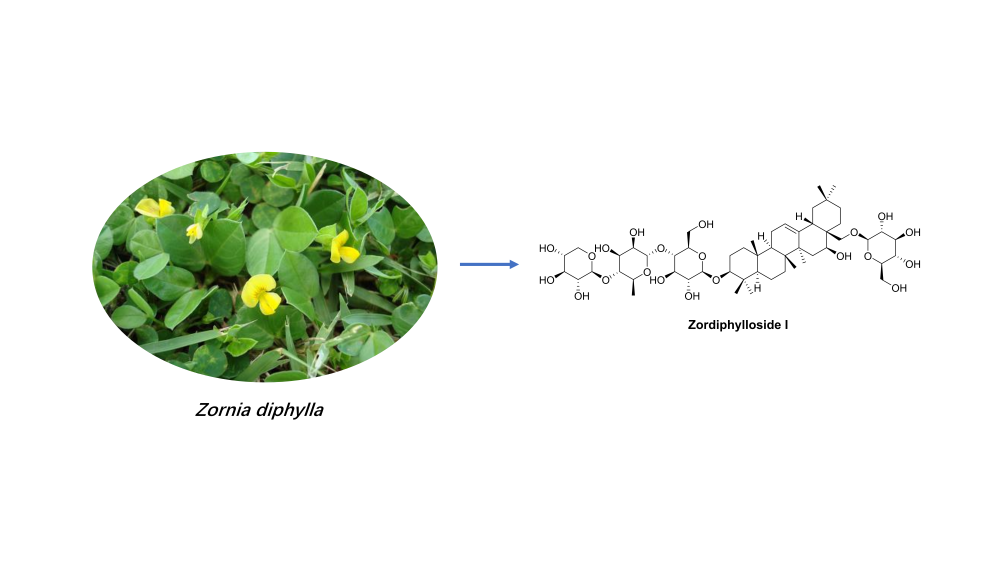
Phytochemical investigation on the aerial parts of Zornia diphylla resulted in the isolation and identification of one undescribed triterpenoid saponin, zordiphylloside I (1), together with 25 known compounds. Their structures were elucidated by comprehensive spectroscopic methods, including 1D and 2D NMR and MS. Notably, 24 compounds were isolated from this plant for the first time. Zordiphylloside I showed moderate cytotoxicity against human breast carcinoma cell line (MCF-7) and human prostate cancer cell line (LNCaP), with IC50 values of 26.52 and 45.37 µM, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.383.2301.2666 Keywords Triterpenoid saponin Zornia diphylla Fabaceae cytotoxicity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.15) Phenolic Bisabolanes from the Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sp. MEA11

In our work, the deep sea sediment-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. MEA11 was examined for secondary metabolites. Chromatographic separations resulted in the identification of a new phenolic bisabolane (1) and seven known analogs (3-7 and 8a, 8b). The structures were determined by 1H, 13C NMR, and MS data. The known compounds were identified to be 11,12-dihydroxysydonic acid (2), hydroxysydonic acid (3), aspergoterpenin B (4), engyodontiumone J (5), sydowic acid (6), penicipyran A (7), 1-hydroxyboivinianic acid (8). The NMR data of 7 in methanol-d4 were reported for the first time. Compounds 6-8 exhibited inhibitory effect against α-glucosidase with IC50 values of 176, 89, 232 uM, which were more active than the positive control acabose.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.377.2202.2454 Keywords Phenolic bisabolanes Aspergillus sp. DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.16) Two New Sesquiterpenoids from Kalimeris shimadae
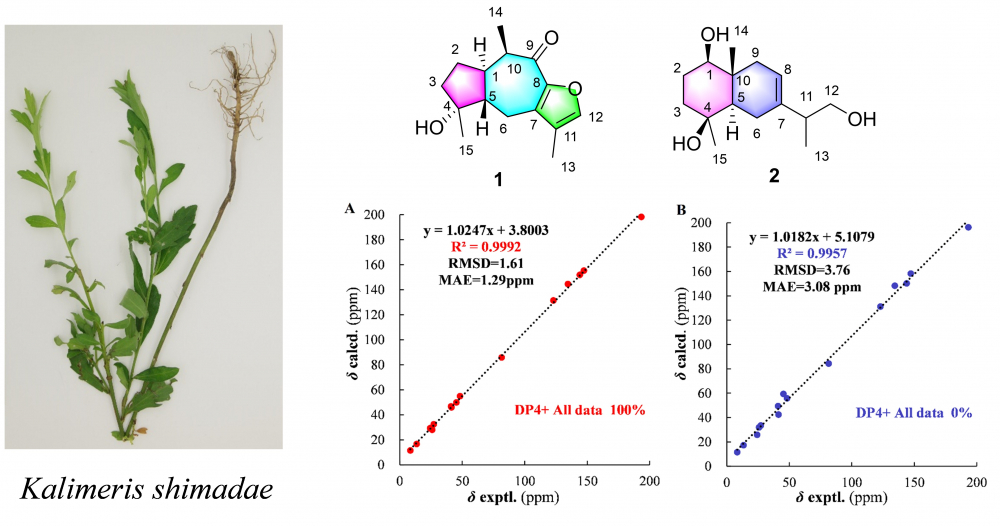
Five sesquiterpenoids were isolated from Kalimeris shimadae, of which compounds 1 and 2 were undescribed guaiane-type and eudesmane-type sesquiterpenoids, named kalshinoids G (1) and H (2). Their structures and relative configurations were elucidated based on HR-MS, NMR and chemical calculations. The inhibitory activity of those sesquiterpenes against nitric oxide (NO) production were also evaluated.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.369.2210.2604 Keywords Kalimeris shimadae sesquiterpene chemical calculations DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.17) Essential Oil Compositions and Antimicrobial Activity of the Leaves of Alphonsea monogyma Merr. & Chun and Goniothalamus banii B. H. Quang, R. K. Choudhary & V.T. Chinh from Vietnam
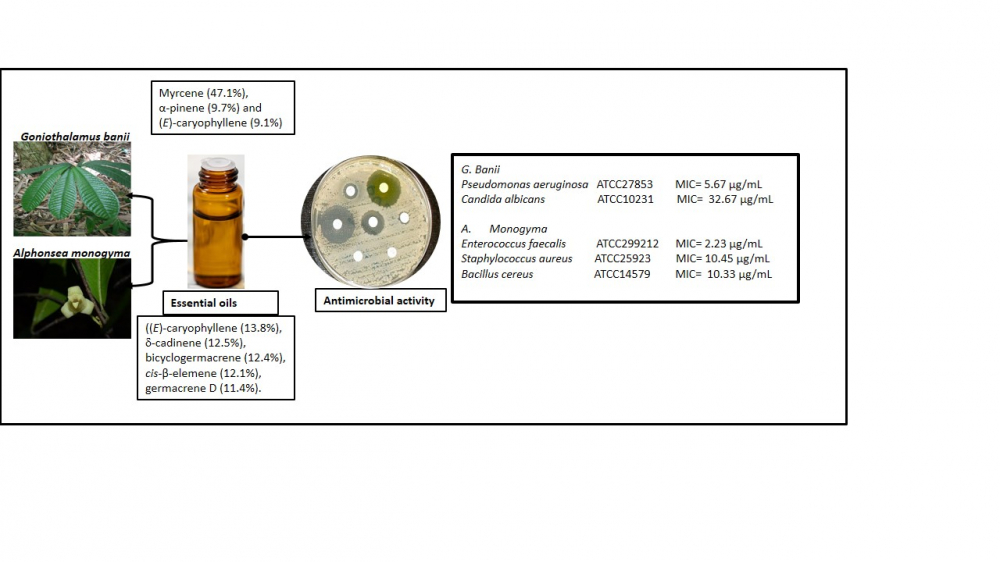
Essential oils from the leaves of Alphonsea monogyma Merr. & Chun and Goniothalamus banii B. H. Quang, R. K. Choudhary & V.T. Chinh from Vietnam were obtained by hydrodisitllation and the chemical components determined by gas chromatography (GC) and gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (GC/MS). Also the microdilution broth assay was used to test the antimicrobial activity of the essential oils. The respective yields of the essential oils were 0.18% (v/w) and 0.355% (v/w), respectively. The major components of A. monogyma were (E)-caryophyllene (13.8%), d-cadinene (12.5%), bicyclogermacrene (12.4%), cis-β-elemene (12.1%), and germacrene D (11.4%). However, myrcene (47.1%), α-pinene (9.7%) and (E)-caryophyllene (9.1%) were the dominant constituents of the essential oil of G. banii. The leaf essential oil of A. monogyma displayed potent antimicrobial activity towards the Gram-positive microorganisms of Enterococcus faecalis ATCC299212, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC25923 and Bacillus cereus ATCC14579 with minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values of 2.23 µg/mL, 10.45 µg/mL and 10.33 µg/mL, respectively. On the other hand, essential oil from G. banii exhibited the most effective antibacterial against Gram-negative Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC27853 (MIC 5.67 µg/mL), and anti-candidal action towards Candida albicans ATCC10231 (MIC 32.67 µg/mL). The chemical constituents and antimicrobial activity of the essential oils of A. monogyma and G. banii were being reported for the first time.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.367.2208.2547 Keywords Alphonsea monogyma essential oil composition terpenes antimicrobial activity anti-candidal activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2023 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.