Records of Agricultural and Food Chemistry
Year: 2024 Volume: 4 Issue:3 Special Issue: Abstracts 3rd. TCS, International Food Chemistry Congress February 29-March 03,2024 Antalya Türkiye
1) Importance of the Uncertainty of Measurements in Food Analysis
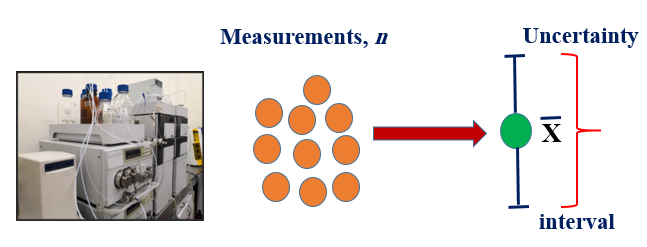
Food analysis holds the key to understanding food composition, safety and quality. Uncertainty is an inherent companion to any analytical endeavor starting from sample preparation to instrument calibration and measurement. Understanding uncertainty is critical to ensuring reliable results that support critical decisions about food production, regulation, and consumer health. The sources of uncertainty in food analysis are diverse, including the type of food matrix, competence of the analyzer, accuracy of the equipment, reference materials and the repeatability of measurement. The consequences of ignoring uncertainty estimation i.e. inaccurate results can lead to mislabeling of food products, posing health risks to consumers with allergies or intolerances. Regulatory compliance becomes a gamble, as producers face financial losses or even legal repercussions due to inaccurate analyses. The comparability of research results is affected when uncertainty is not properly taken into account, which hinders scientific progress and innovation in the food sector. Therefore, a rigorous approach to uncertainty estimation is crucial. International standards and guidelines provide frameworks for quantification and reporting of uncertainty in food analysis particularly ISO GUM and EURACHEM/CITAC Guide. These standards rely on statistical methods to estimate precision (repeatability of measurements) and bias (systematic deviations from the true value) as Type A and Type B. By expressing the uncertainty as a confidence interval, we acknowledge the inherent limitations of our measurements and provide a clear picture of the range within which the true value is likely to lie. By recognizing the inherent variability in food analysis, we can make informed decisions, build confidence in our food systems, and ultimately contribute to a safer and more informed food future.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.2996 Keywords Food sample uncertainty estimation safety limits compliance DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.2) The Role of Polyphenols in Cancer Prevention and Treatment
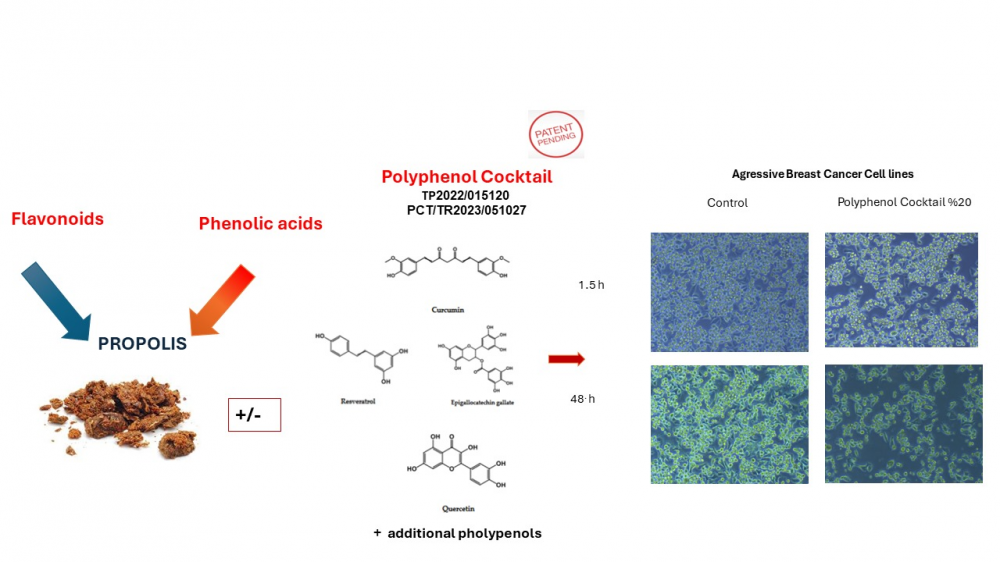
Polyphenols are plant-based compounds that have gained attention for their biological activities, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties. They are found abundant in fruits, vegetables, tea, coffee, and red wine, and have been extensively researched for their role in cancer prevention and treatment and in the other wide range of diseases, including heart disease, and neurodegenerative disorders. A large volume of literature data suggests that a diet rich in fruits and vegetables, mostly due to the contribution of natural polyphenols, could reduce the incidence of specific cancers. Polyphenols can inhibit tumor generation, induce apoptosis in cancer cells, and interfere in the progression of tumors. It's important to note that while polyphenols have potential health benefits, it's crucial to consume them as part of a balanced diet and not rely solely on them for health improvements. Regarding cancer therapy, research has suggested that polyphenols may have potential benefits in cancer prevention and treatment. They have been studied for their ability to inhibit the growth of cancer cells, induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) in cancer cells, and interfere with the processes that promote tumor growth and metastasis. Polyphenols and flavonoids have been found to modulate diverse signaling molecules, including kinases, transcription factors, and inflammatory mediators, thereby exerting broad-spectrum effects on cancer cells. Due to their ability to modulate these pathways involved in cancer progression, they are promising candidates for the development of novel cancer therapies. In addition, their low toxicity and favorable safety profile make them attractive agents for combination therapies with conventional cancer treatments. Polyphenols have a diverse nature that enables them to target multiple hallmarks of cancer, making them potential candidates for the development of personalized cancer treatment strategies. Polyphenols have shown potential in complementing existing cancer treatment modalities, from inhibiting the growth of cancer cells to enhancing the sensitivity of tumors to chemotherapy and radiation. As research in this field continues to evolve, the potential of polyphenols in personalized cancer treatment plans becomes increasingly evident. The relationship between natural products and cancer signaling pathways has attracted significant attention, especially in the case of terpenes, polyphenols, and flavonoids. These compounds, which come from plants, have shown great potential in regulating important signaling pathways that are involved in the initiation, progression, and spread of cancer. This has created new opportunities for targeted cancer treatments.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.2997 Keywords Propolis cancer phenolic compounds DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.3) The Importance of Olive Oil in Mediterrenean Diet
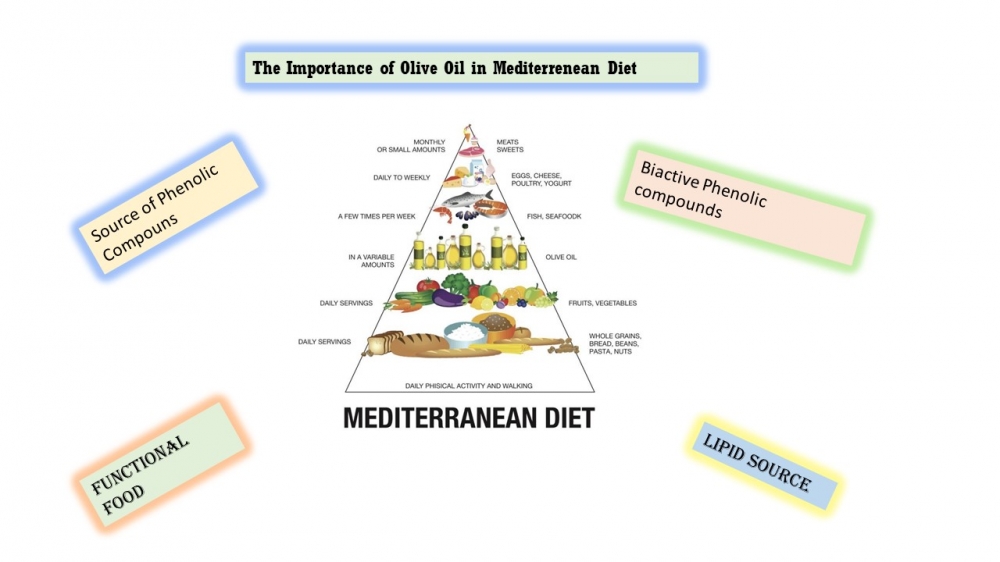
The Mediterranean diet is linked to numerous health benefits. Traditional descriptions of the Mediterranean diet originate from various countries including Greece, Italy, France, Spain, Portugal, Turkey, Tunisia, Algeria, Lebanon, Morocco, and others. The Mediterranean diet is traditionally associated with low rates of chronic diseases and high adult life expectancy. The Mediterranean diet is unique due to its relatively high intake of nuts, olive oil, and moderate consumption of wine, particularly red wine, during meals. It can be considered a primarily plant-based diet. Olive oil, which is the main source of lipids in this diet, contains bioactive components with biological properties. Extra virgin olive oil is a functional food that contains a major saponifiable fraction, oleic acid, as well as saturated and unsaturated acids such as linoleic, palmitic, and stearic acids. Additionally, it contains a minor unsaponifiable fraction that includes tocopherols, polyphenols (such as tyrosol, hydroxytyrosol, and oleuropein), sterols, phospholipids, carotenoids, chlorophylls, waxes, squalene, and other hydrocarbons. These compounds have protective and antioxidant effects. Most studies linking olive oil consumption to increased life and health spans also show potential benefits. These include preventing type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, obesity, cancer, cognitive decline, and cardiovascular disease mortality, among others [1–5].
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3048 Keywords Olive oil antioxidant mediterrenean diet functional food DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.4) Measurements in the Food Sector, A Vital Component for Consumer Protection

The food sector is an essential component of the global economy. It is a highly regulated sector, requiring measurements to ensure product safety, quality, and compliance to protect public health and safety. The National Metrology Institute of South Africa (NMISA) recognizes this importance and has prioritized food and agriculture in its work program, to support food testing laboratories with these critical measurements. The absence of suitable matrix reference materials and proficiency testing scheme (PT) schemes impedes the validation and benchmarking of analytical methods by laboratories, most notably when new food regulations are introduced, new generation chemicals are being applied or when Maximum Residue Limits (MRLs) are changed. Consequently, this has also resulted in poor agreement between laboratory results and disputes between the inspection bodies and food producers. NMISA produces customized reference materials and PT schemes to assist with resolving these analytical challenges. The materials reflect the local food products, seasonal variations, and contaminant levels typical of the region. Two recent cases concerning South Africa’s Sodium Reduction regulation R214 in multiple food categories, and the determination of highly polar pesticides in plums and avocados, to meet new EU reduced MRLs will be described. In these cases, the production of custom matrix reference materials and the evaluation of PT performance has allowed the regulators and agricultural growers associations to address the possible sources of measurement result discrepancy, which has supported improvements in the implementation of national health promotion strategies and consumer protection.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3096 Keywords Sodium reduction regulations pesticide residues customised proficiency testing DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.5) The Lamiaceae Family: Biodiversity and Uses

Plants play a significant role in human nutrition, shelter, clothing, and the treatment of diseases. There are approximately 400,000 estimated species of plants on Earth, with around 70,000 species utilized for various purposes. Currently, roughly 7,000-10,000 plant species are cultivated by humans, with 90% of the nutritional needs met by 30 plants. The Lamiaceae family encompasses numerous medicinal and aromatic plant species used for both nutrition and disease treatment. Members of the Lamiaceae family grow in various elevations and habitats, excluding polar regions, ranging from sea level to high mountainous regions. The Lamiaceae family, the sixth-largest plant family, comprises approximately 7,000-8,000 species belonging to 230-240 genera worldwide. Among the genera with the highest number of species globally, Salvia leads with around 1,000 species, followed by Scutellaria (480 species), Stachys (370 species), Nepeta (300 species), Teucrium (300 species), Thymus (270 species), and Vitex (210 species). In Türkiye, the Lamiaceae family is represented by 614 species (approximately 800 taxa) across 45 genera. The genera with the highest number of species in Türkiye include Salvia (102 species), Stachys (90 species), Sideritis (45 species), Thymus (42 species), Nepeta (39 species), and Teucrium (38 species). The Lamiaceae family has been divided into 12 subfamilies based on recent phylogenetic classifications, with representatives of 5 subfamilies distributed in Türkiye. The taxa of the Lamiaceae family, which is one of the most important families in terms of medicinal uses among plant families, consist of potent aromatic plants. Different organs (leaves, rhizomes, stems) of these plants are used for food purposes, dye extraction, various disease treatments (nervous, circulatory, respiratory, reproductive systems), insect repellent production, ornamental purposes, volatile oils as food additives and preservatives, as well as in the perfume and cosmetic industry, thus having a wide range of applications. Evidence of their use for these purposes throughout human history has been found in archaeological excavations and ancient inscriptions. Remains of genera such as Ajuga, Mentha, Teucrium, Ziziphora, and Sideritis have been unearthed from Neolithic sites in Türkiye such as Çatalhöyük, Aşıklı, and others. Moreover, Dioscorides compiled information on the use of approximately 40 Lamiaceae members in his book "Materia Medica". In contemporary Türkiye, they are commonly used by the local people for upper respiratory tract and urinary tract infections, pain relief, wound healing, and sedation, with 221 taxa from 29 genera identified for various purposes. Recent studies have also determined that many members of the Lamiaceae family possess high levels of antioxidants, anti-cholinesterase, antifungal, antimicrobial, and other effects. The results obtained from these studies highly support the local use purposes that have continued since ancient times.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3112 Keywords Lamiaceae Salvia ssp. Origanum ssp Sideritis trojana DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.6) Chemical and Biological Studies on Dietary Plants
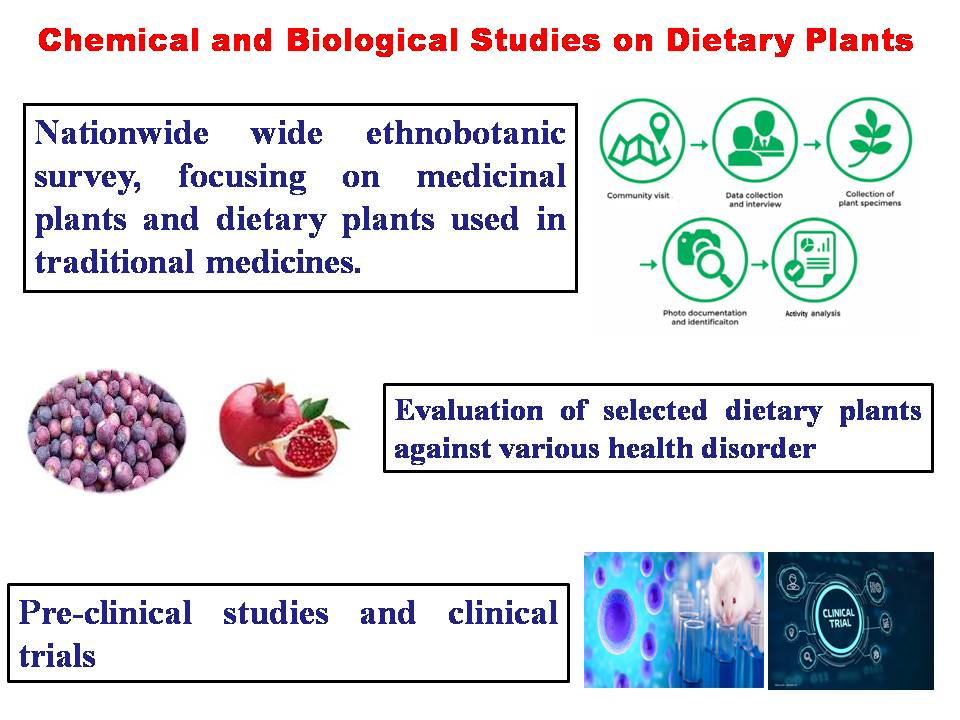
Dietary plants historically have made remarkable contributions to pharmacotherapy. Dietary plants-based formulations against prevailing and emerging diseases have gained a major scientific interest in post-COVID-19 era. Nevertheless, isolating bioactive constituents and their subsequent development are not without the challenges. Our work in the past two decades has been widely focused on the discovery of new drug leads from medicinal and dietary plants, as well as synthesis of their bioactive analogs by biocatalytic transformations. We have been working largely at the interface of chemistry and biology for the discovery of chemical constituents from dietary plants used in traditional medicines. This has resulted in the identification of several novel drug leads against various therapeutic targets. Emphasis has been on the discovery of novel drug like molecules and dietary plants-based formulations against neglected and prevalent diseases, such as leishmaniasis, dengue infection, cardiovascular, inflammatory, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s and Parkinson's diseases. Some aspects of their development for clinical use will be discussed. During this presentation, the underlying philosophy and approach of our research on cost-effective and sustainable discovery of natural-based drug leads and plant formulations against infectious and prevalent diseases will also be discussed.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3130 Keywords Drug discovery Alzheimer diseases dietary plants DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.7) Microbial Degradation Mechanisms of Mycotoxins
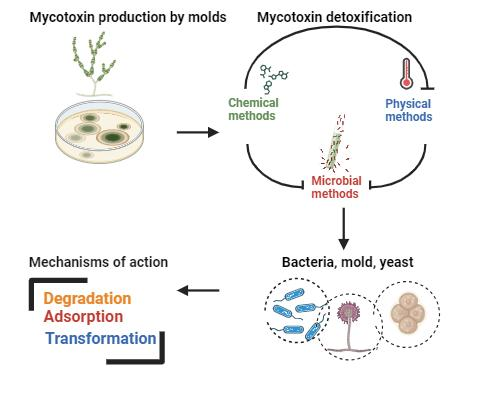
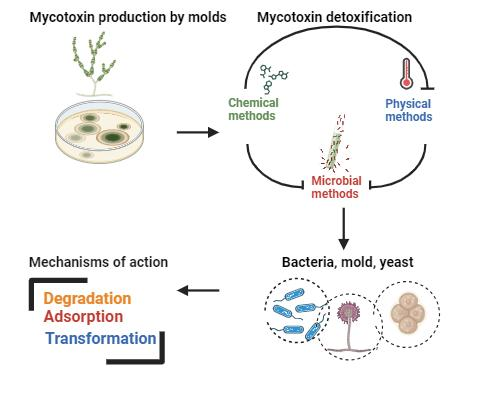
Mycotoxins are highly toxic secondary metabolites produced by molds that seriously contaminate food and endanger human health. Mycotoxins pose a major health threat to animals and humans [1]. Mycotoxins cause huge economic losses in the food industry and animal husbandry every year [2]. Therefore, comprehensive strategies to control and/or neutralize mycotoxin production in food and feed are needed. For this purpose, physical (high temperature, high pressure, sterilization, cooking, grinding, cleaning, etc.) [3,4] and chemical methods (ozone, ammonia and hydrogen peroxide) [5] can be used. Traditional physical and chemical methods have some limitations such as limited effectiveness, safety problems, loss of nutritional value and taste of food and feed, as well as the need for expensive equipment to apply these techniques. The common disadvantage of these methods is the high difficulty in completely removing toxins and maintaining the sensory quality of food and feed. However, microbial methods offer a suitable alternative for mild reaction conditions, potentially high efficiency, and preservation of the quality of food and feed [6]. Biodegradation of mycotoxins is promising as it works under mild and environmentally friendly conditions. Although significant progress has been made in developing strategies for this, there are still obstacles to be overcome and gaps to be filled in order to design effective mycotoxin management techniques. This is partly due to a lack of understanding of why molds produce mycotoxins. It is seen that many microorganisms are used in research on the biological degradation of mycotoxins. The action mechanisms of these microorganisms can generally be examined under the headings of adsorption, degradation, and transformation. In this paper, these mechanisms will be explained.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3131 Keywords Mycotoxins degradation transformation DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.8) Effect of Commercial and Household Processing on the Residue Behaviors, Reduction Rates, and Processing Factors of Pesticide Residues in Foods
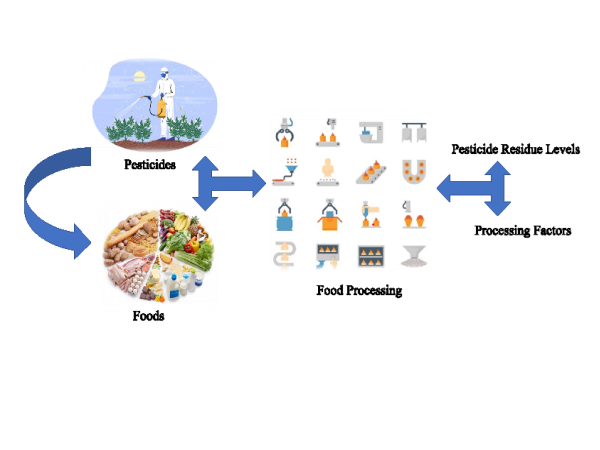
Pesticides are widely used around the world to improve product quality and yield of agricultural products against weeds, fungi and insects. However, excessive, or incorrect use of pesticides results in pesticide residues in the final product, and chronic exposure to dietary pesticides is known to be linked to the development of many diseases. Pesticide analysis results in raw agricultural products are evaluated according to the maximum residue limits (MRL) determined by field trial studies into account for each pesticide. MRLs are not sufficient for risk assessment studies of processed products, especially since many agricultural products are processed before consumption. Therefore, it is necessary to investigate how these active substances or degradation products/metabolites change during processing and to determine the processing factors in order to obtain more information about the dietary intake values of humans. However, whether pesticides remain or are absorbed on the crop surface after application largely depends on the physicochemical properties of the pesticide molecules and the crop itself. Therefore, it is important to develop an effective method to reduce pesticide residue levels in agricultural products. While most pesticides are known to remain on plant surfaces, most can be removed by simple washing and/or peeling or by treatments with different chemical solutions. Although consumers try to prevent the uptake of pesticide residues into the human body by peeling fruits and vegetables or washing them with tap water, the level of reduction remains limited. Various techniques (washing, peeling, boiling and cooking, fermentation, juicing, etc.) and methods used during processing at the industrial or household level often play a role in the process of reducing pesticides; thus, each processing technique has a cumulative effect on reducing pesticide residues. However, some processes may lead to increased residue levels due to concentration effects and/or affinity to the lipid moiety. Herein, a detailed summary of the effects of different food processing techniques of commercial and household processing on the fate of pesticide residues in foods, their reduction rates, and the impact of processing factors is presented. [1–6].
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3135 Keywords Pesticide residue commercial and household processing processing factors foods DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.9) Functional Foods and Nutraceuticals with Antioxidant and Neuroprotective Properties in Ameliorating Neurodegenerative Diseases

Functional foods are whole foods or food products which are specifically designed to prevent our health beyond their basic nutritional content. They are consumed as part of a regular diet which can include everyday items like fortified cereals, omega-3 enriched eggs, probiotic yogurt, beverages with added antioxidants. Nutraceuticals are products derived from food sources that provide health benefits beyond basic nutritional value. They can include dietary supplements, fortified foods, herbal products, and some other naturally occurring substances. Nutraceuticals can take various forms, including pills, capsules, powders, extracts, and other concentrated forms. Since plants are very rich in antioxidant compounds (flavonoids, anthocyanins, tannins, and other polyphenolics), they were studied for their potential implications in neuro-degenerative diseases, particularly Alzheimer (AD) [1, 2] and Parkinson diseases (PD) [3, 4] by many groups. Although not fully understood, the pathological process associated with AD is believed to be multifactorial. Neuroprotective strategies involving multiple mechanisms of action are important for the prevention and treatment of AD [1,7]. Therefore, secondary metabolites of the plants may play vital roles as preventive and ameliorating agents in some neurodegenerative diseases, such as dementia, Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases [1-7]. Marine sources, particularly omega-3 acids, potentially protect neurodegeneration as well as improve memory and cognitive functions. Many natural compounds show anti-Alzheimer activity through specific pharmacological mechanisms like targeting β-amyloid, beta-secretase1 and acetylcholinesterase, and they are further investigated through molecular docking studies recently [2,7]. In the last 20 years, our group has investigated some plant extracts and secondary metabolites, namely from Lamiaceae and Apiaceae families, for antioxidant, neuroprotective and anticholinesterase activities. For this purpose, many Salvia and Sideritis extracts and their pure compounds have been screened as well as a series of Teucrium and Nepeta species (in vitro). From the Apiaceae family, Heracleum, Prangos and Ferulago plants’ species have been investigated, and the results obtained are promising [2, 5-7] to prepare for new functional foods and nutraceuticals.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3136 Keywords Functional foods nutraceuticals bioactive compounds antioxidants anticholinesterases DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.10) The Relationship Between Biodiversity and Sustainable Food Supply
.png)
Traditional dishes, food-related customs and traditions, especially biodiversity and the products produced from them are an important part of the culture of every region. This culture will have a very important place especially in terms of access to sustainable food and food security in the future. By transferring this knowledge of natural plant and animal use, gained through thousands of years of experience, to food technology, it makes very important contributions to ecological production by ensuring rural development by preventing migration from village to city by using local resources that are more resistant to ecological factors and protecting genetic resources with the use-protection balance.There is no doubt that food-related problems are one of the biggest human problems in this century. As much as human beings' right to life and health, protecting the biodiversity in the ecosystem in which they survive is equally important. In fact, today the right to food is considered one of the fundamental human rights. The right to food includes access to food as well as access to safe and healthy food. The main reason for the recent decline in food production worldwide is the decrease in biodiversity and the destruction of the habitats of this diversity. The most important factors affecting this situation are; global climate change, pesticides used in industrial agriculture, harmful chemicals, destruction of agricultural lands, unplanned urbanization and concreting. According to the report prepared by FAO, the most threatened species are plants, birds, fish and mushrooms. Pollinators, which contribute to three-quarters of the world's food production, are under serious threat. Not only bees and other insect pollinators, but also almost a quarter of vertebrate pollinators such as bats and some bird species are in danger of extinction. Achieving sustainable nutrition linked to biodiversity is possible by realizing the potential of biodiversity for food extraction in an increasingly globalized, urban, and commercial environment. It requires broad recognition across many sectors that food production requires the integration of marketing, consumption, and health concerns of both urban and rural communities. In this context, great importance should be given to the protection and development of indigenous species and traditional production methods from past to present, especially in agriculture, animal husbandry and aquaculture, and to observe the concept of interregional equality and intergenerational justice, especially in the use of biodiversity and genetic resources.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3137 Keywords Biodiversity genetic resources plant food traditional production DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.11) Potential for The Use of Natural Fruits in Functional Cereal Products
Nowadays, the development of functional food formulations has gained importance due to the increasing demand of consumers for healthy products. Adding dried natural fruits such as berries is one of the easy ways to enrich foods. Berries, such as blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.), aronia (Aronia melanocarpa) and cherry laurel (Laurocerasus officinalis Roem.) are good sources of phenolic compounds. They have strong antioxidant capacities related to health-promoting potentials on several diseases such as obesity, diabetes, hypertension, pro-inflammatory conditions, cardiovascular diseases and cancer. This study focuses on the effects of berries on the technological, nutritional and sensory quality of cereal products. There are many studies in the literature on the use of berries in cereal products, such as bread, pasta, noodles, cookies, cakes and crackers, which are widely consumed around the world. Functional cereal products enriched with berries can be used to prevent nutritional deficiencies of many nutrients. The incorporation of berries can enhance ash, dietary fiber, vitamin and mineral contents of cereal products and decrease their fat content. On the other hand, the inclusion of berries can provide a long shelf-life in bread samples and improve the oxidative stability of cakes because of their antioxidant and antibacterial properties. Furthermore, the addition of 5% dried berry powder can increase the firmness of pasta and cake samples. Berries at 5 and 10% levels can be used to prepare functional cereal products with consumer acceptability and high antioxidant capacity.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3144 Keywords Natural fruits berries cereal products functional foods DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.12) Protein Extraction Methods from the Edible Insects
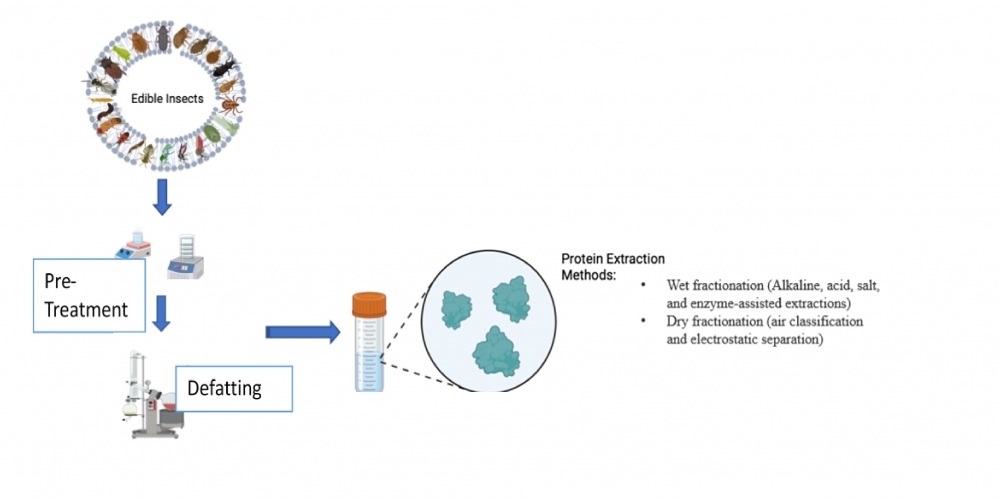
In response to the recent growth in the global population and the resulting scarcity of protein resources, there is a pressing need to develop novel, sustainable, and natural sources of protein from invertebrates, including insects. Edible insects represent valuable sources of protein (35-62%), fat (3-57%), and chitin (3-12%). The main protein components found in insects consist of albumin, globulin, and glutenin. Protein extraction methods from these insects can be classified into various groups, including wet and dry fractioning, solvent extraction (alkali, acid, and salt), enzyme extraction, and physical methods. Wet fractioning processes encompass alkali extraction, acid extraction, salt extraction, and enzyme-assisted extraction, while dry fractioning methods involve air classification and electrostatic separation. In addition to these techniques, innovative green methods such as ultrasound, pulsed electric field, and supercritical CO2 extraction can be employed for protein extraction. To extract protein from edible insects, pre-steps such as harvesting, washing, inactivating, drying, and defatting are carried out. Alkali extraction, using NaOH as a solvent, is a commonly utilized method, particularly after defatting. While effective, alkali extraction may lead to reactions in the protein backbone, causing denaturation, hydrolysis, racemization, and the formation of cross-linked molecules like lysinoalanine, resulting in decreased functionality and nutritional value. Other approaches, such as stepwise protein extraction (including aqueous extraction, salt extraction, alcohol extraction, alkali extraction, etc.) and enzymatic hydrolysis (utilizing enzymes such as papain, protease, pepsin, pancreatin, etc.), can also be employed. Enzymatic hydrolysis requires specific conditions for each enzyme, and although its yield is lower than solvent extraction, it remains a viable method. Proteins obtained from edible insects demonstrate antioxidant, anti-diabetic, anti-hypertensive, anti-cancer, anti-microbial, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory properties. In addition to health benefits, insect proteins exhibit diverse functional characteristics, including the ability to create foam, emulsify, and gel. The extracted protein from edible insects finds applications in various industries, including animal feeds, pet foods, human foods, cosmetics, and more. This review aims to explore protein extraction methods from edible insects and discuss the potential applications of the obtained extracts [1-4].
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.2976 Keywords Edible insect protein extraction enzyme extraction antioxidant animal feed DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.13) Use of Herbal Tea as an Approach to Water Remediation from Contaminants
This study explores the viability of herbal tea as an eco-friendly solution for water remediation. Herbal teas, including hibiscus, mint, and chamomile, are rich in bioactive compounds such as antioxidants and polyphenols, known for their ability to absorb various contaminants present in water. Therefore, this investigation focused on chamomile tea's ability to remove lead from aqueous solutions. Systematic variations in adsorbent quantity, solution concentration, mixing conditions, and pH levels [1] were conducted to identify optimal experimental parameters. Quantitative assessment of metal concentration, specifically lead (Pb) pre-and post-treatment, was performed using ICP-OES (Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission Spectrometry). The morphological characteristics of the biosorbents were explained through SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy). The outcomes of the study revealed exceptional efficacy, underscoring the potential of these agricultural waste-derived materials for practical use in daily water treatment. The biosorbents demonstrated significant advantages over conventional methods, including cost-effectiveness, high selectivity, and biodegradability, positioning them as promising candidates for sustainable water purification applications.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3007 Keywords Chamomile residues heavy metal ICP-OES SEM DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.14) Comparation of Nutritional Value of Salmon and Sturgeon Caviar

This review examines the differences in physical and nutritional properties of sturgeon and salmon caviar. When examining their physical characteristics, sturgeon caviars are characterized as smaller and blackish color roes, while salmon caviars are characterized as larger and reddish-hued roes. There is no similarity between salmon caviar and sturgeon caviar in terms of both color and size. Considering the nutritional value, salmon roe has higher protein content than sturgeon roe. Although sturgeon caviar has a higher total lipid content, salmon caviar has higher omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) like EPA and DHA. Salmon caviar, which is a caviar substitute, has a more favorable profile in terms of nutrition. Additionally, it appears as a cheaper alternative for caviar consumption
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3024 Keywords Caviar sturgeon roe salmon roe PUFAs protein DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.15) Determination of Chemical Components of Some Plant Species Used as Food in Kahramanmaras Province

Herbs are of great importance in human nutrition. Especially in these days when the prices of vegetables and fruits increase abnormally, and the widespread use of the organic nutrition trend has increased the importance of natural herbs. Today, as a result of modern agriculture in vegetable and fruit growing, wild plant and herb species that grow spontaneously in nature are in danger of extinction. In the first year of the research, information about the local names of the herbs (weeds and wild herbs) consumed as food and how these plants are used were obtained from the Technical staff working in the Kahramanmaras provincial and district Agriculture and Forestry Directorate and the district people by interviewing 30 people from each district by oral survey method. In order to collect data within the scope of the study, local markets and herbalists were visited, especially in the districts where people living in rural areas market the plants they collected from nature. For these reasons, the leaf fruits of grass species, shrub and tree species consumed as food in Kahramanmaras province were analyzed in the laboratories of Karhamanmaras Sütcü Imam University, University-Industry-Public Cooperation Development Application and Research Center (USKİM). The nutritional contents of the identified plants were found to be important for human nutrition. Weed species commonly used as food in Kahramanmaras province are Foxtail lilly (Eremurus spectabilis M. Bieb.), Little hogweed (Portulaca oleracea L.), Cuckoopint (Arum maculatum L.), Rhubarb-currant (Rheum ribes L.), Dwarf Mallow (Malva neglecta Wallr.), Stinging nettle (Urtica dioica L., U. urens L.), Wild mustard (Sinapis arvensis L.), Red beetroot (Beta vulgaris L.), Thyme (Thymus sipyleus Boiss.), Baconweed (Chenopodium album L.), Sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) [1]. In addition, there are some species of trees in Kahramanmaras province that are used for food. Mulberry molasses is made from Syrian juniper (Juniperus drupacea Lab.) and from White mulberry (Morus alba L.), spices from Sicilian sumac (Rhus coriaria L.), and Terebinth (Pistacia terebinthus subsp. palaestina (Boiss.) Eng.) is widely used in the spice and coffee industry [2]. The chemical components of these plants have been identified separately.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3030 Keywords Kahramanmaras herb weed food chemical component DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.16) The Chemical Mechanism of the Fermentation Steps in Turnip Juice
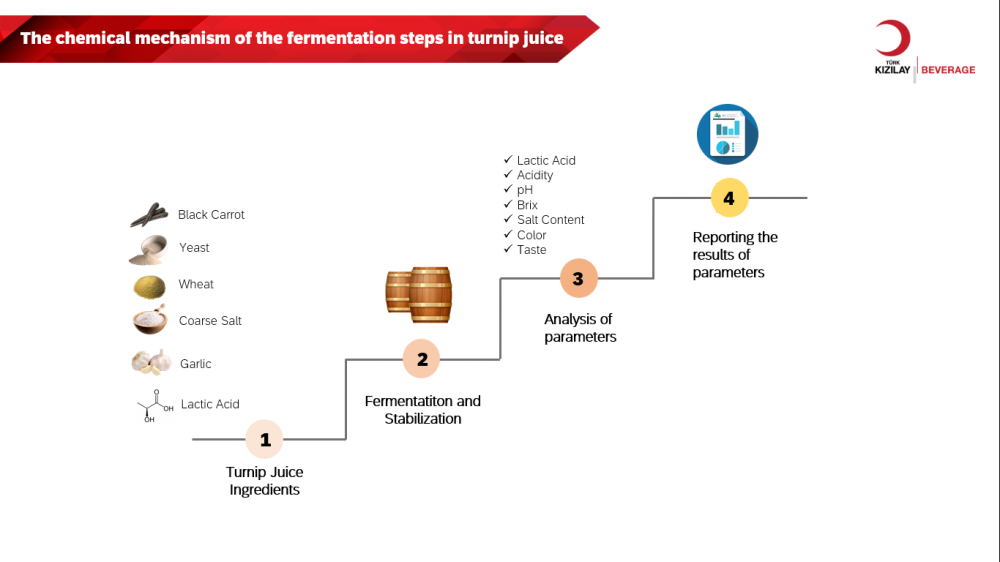
Turnip juice, a fermented beverage, will be considered a functional drink due to its antioxidant potential derived from the carotenoids, chlorogenic acids, and anthocyanins in its composition. In the production of turnip juice, black carrot, yeast, wheat, salt, garlic, and lactic acid are used. There are two main production methods: traditional and direct methods. In both methods, the result is obtaining red-colored and sour-flavored turnip juice due to the passage of colored components into the liquid during the fermentation process and the increase in total acidity due to the effect of lactic acid bacteria. Changes in pH, brix, salt, total acidity, lactic acid, taste, smell, and color parameters are observed in turnip juice during the fermentation process. One of the main reasons for these changes is the fermentation reactions carried out by lactic acid bacteria. The fermentation process in turnip juice affects the pH value, which can change the color of turnip juice. This highlights the ability of anthocyanins to be present in different colors or colorless forms at different pH levels. The acidic environment formed by the accumulation of lactic acid prevents the proliferation of harmful microorganisms, enhancing the microbial stability of turnip juice. This result also affects the formation of the specific taste and aroma of turnip juice. Reactions of this kind during fermentation create the unique taste and aroma of turnip juice. The fermentation period in turnip juice enhances its organoleptic properties and increases antioxidant capacity. The interpretation of these reaction results is possible through laboratory analyses performed during the fermentation process [1-3].
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3040 Keywords Turnip juice fermentation lactic Acid DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.17) Value Added Product from Shalgam Pulp

Fermentation has been utilized by humans since the early days of food storage, with fermented herbal products gaining attention for their nutritional benefits. Among these products is shalgam, a traditional Turkish fermented beverage, also known as turnip or shalgam juice. Shalgam is produced using raw materials like black carrot, turnip, bulgur flour, yeast, salt, and water. The traditional method involves a two-stage process: dough fermentation, where lactic acid bacteria proliferate, and the main fermentation, resulting in the formation of the beverage. Wooden or modern tanks are used for fermentation, and the process takes 3-10 days. Alternatively, direct production skips the dough fermentation stage and directly ferments the ingredients. The final product is filtered, bottled, and stored in cold conditions. The pulp formed after turnip production has the potential to be used as a valuable organic matter in animal feed production, soil fertilization, as an energy source in bioenergy production, or as an extra fiber and nutrient source in some products in the food industry. Carrot waste, constituting up to 50% of raw material post-industry processing, is typically used for animal feed or discarded, adversely impacting the environment. Within the framework of the Farm to Fork Strategy, emphasis is placed on sustainable food consumption and the prevention of food loss and waste. In recent times, numerous entities in developed nations have initiated endeavors aimed at mitigating the economic, environmental, and social repercussions associated with the problem of food waste. According to recent research, the importance of food loss and food waste has increased over the last few decades. In this context, food processing residues, considered abundant, inexpensive, and sustainable sources, have garnered attention. However, this waste contains substantial residual compounds associated with nutritional and health benefits, including antioxidant properties linked to preventing cardiovascular diseases, cancer, diabetes, gastrointestinal issues, and ocular diseases. The recovery of these valuable bioactive compounds from carrot waste presents an opportunity to generate functional ingredients, enabling the incorporation of purple carrot waste into diverse food products with positive effects on human health. This comprehensive project explores the nutritional composition of purple carrot wastes, highlighting identified bioactive compounds, their applications in various food products and beverages [1–4].
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3041 Keywords Shalgam pulp food waste prebiotic DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.18) The Effect of Tunnel Pasteurization Parameters on Calcium, Magnesium, and Bicarbonate in Flavored Mineral Waters
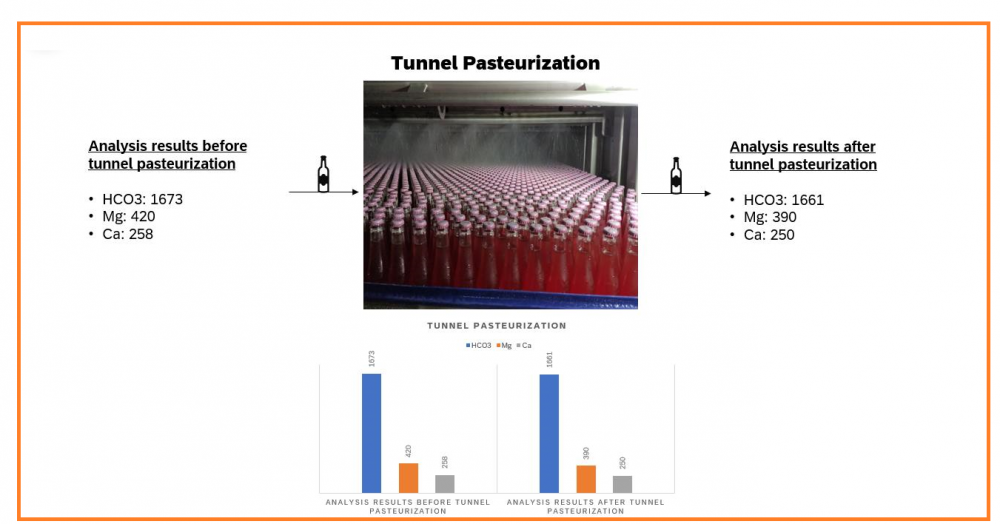
Tunnel pasteurization is a commonly preferred pasteurization method in the beverage industry. This method ensures the safe consumption of products by eliminating potential microorganisms in beverages. The process, which involves gradual temperature application, aims to effectively kill microorganisms by bringing the product, bottles, and caps to specific temperatures. Once the bottles enter the tunnel in tunnel pasteurization, they undergo preheating by exposure to water at 43-55°C. Subsequently, the pasteurization stage takes place at a temperature of 70-80°C, effectively killing microorganisms. Finally, a cooling process is carried out at 31-33°C, purifying the product from microorganisms. This process minimizes the risk of contamination while ensuring the safe consumption of the beverage. Flavored and fruit-flavored mineral waters entering the tunnel pasteurization system can lead to changes in calcium, magnesium, and bicarbonate minerals during the pasteurization process. To determine these potential mineral changes, detailed analyses are performed on samples taken before and after the flavored and fruit-flavored products. In a sample analysis, magnesium, calcium, and bicarbonate analyses were conducted on mineral water samples before and after tunnel pasteurization. The results indicated that tunnel pasteurization did not cause a significant decrease in magnesium, calcium, and bicarbonate values in mineral water, comparing the analysis results of samples taken before tunnel pasteurization and those taken at the tunnel pasteurization outlet. This finding demonstrates that tunnel pasteurization preserves product quality and ensures consumer safety [1].
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.op.3042 Keywords Turnip juice fermentation lactic acid DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.19) Determination of Plum Varieties Suitable for Fruit Juice Industry and Their Suitability for Drying
Plum is the common name given to the trees and drupe fruits of many species belonging to the Prunus genus of the Rosaceae family. According to 2021 data of the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), 12 million tons of plums were produced annually worldwide. Turkey ranks 6th among plum producing countries worldwide with a share of 2.8% [1]. Turkey also exports 38.6 tons of plums annually and is ranked 7th among all plum exporting countries. Plums and products made from plums (plum concentrate and prune) have been reported to have many health benefits [2]. The combination of fibre, sorbitol and chlorogenic acids contained in plums has many beneficial effects on the digestive system, including the prevention of constipation, tooth decay and gingivitis, stomach ulcers and colon cancer [3]. In addition, it has been observed that the metabolites of quinic acid and certain phenolic compounds (chlorogenic acids and proanthocyanidins) contained in plums have a bacteriostatic effect in preventing urinary tract infections [4]. It has been suggested that phylloquinone (vitamin K1), found in relatively high amounts in plums, is important for cardiovascular health, bone metabolism and glucose/insulin regulation, and has a synergistic effect with boron and copper, which are abundant in prunes [5]. Plum species are grouped into 3 groups according to their homeland (gene centers): European-Asian, Far Eastern and North American species [6, 7]. The presented project determines the suitability of 34 plum varieties, adapted in the collection garden of the Erzincan TAGEM Horticulture Research Center, for the fruit juice industry and drying process through conducted analysis. Pomological and quality characteristics of the mentioned varieties, and general quality analysis, sugar and organic acid profiles, and carotenoid contents of fresh plums in puree form were determined. The results of these preliminary analyzes were evaluated using multivariate statistical analysis methods and 10 varieties were selected to determine their suitability for drying. After the selected varieties were dried by the traditional method, their concentrates were prepared with a process compatible with industrial production. The results obtained by determining the sugar, sugar alcohols and organic acid profiles, beta carotene, total phenolic substance contents and color properties of the prepared concentrates were re-evaluated with statistical analysis and the three most suitable varieties for the production of prune juice concentrate were determined. In the next stage, our company plans to establish plum gardens where these three varieties are planted. The presented study is the first project in Turkey to work with such a wide variety of plums in line with industrial targets.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3043 Keywords Prune plum dried fruit juice juice production DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.20) Biodegradable Food Packaging Materials
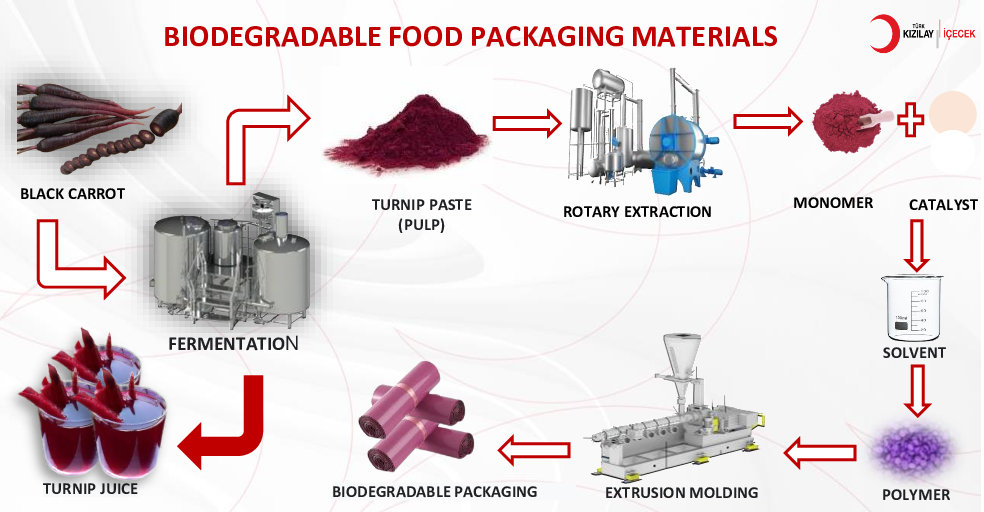
With the growth of the food industry and the increasing world population, the management of waste generated during the processing of fruits and vegetables has become increasingly important. These wastes contain not only nutritional values but also bioactive components. In particular, the turnip and the pulp which is produced during the production of turnip juice which is a traditional drink, is produced by fermenting turnips and radishes and all these are generally used in the fertilizer or feed industry. However, utilizing this waste material with innovative applications such as the synthesis of bioactive components and biodegradable packaging can provide significant advantages in terms of sustainability. As the use of plastic packaging causes environmental problems worldwide, the development of biodegradable packaging offers a solution-oriented approach. These packaging are often produced with materials derived from edible or renewable resources and can be degraded by microorganisms in industrial composting facilities or in natural environments. These features allow biodegradable packaging to be considered an environmentally friendly alternative. The use of such packaging can reduce fossil fuel use, lower the carbon footprint and make waste management more sustainable.Evaluation and recycling of waste is an important step to increase sustainability and efficiency in the food industry. The evaluation of waste products such as turnips together with bioactive components can contribute to the adoption of a broad approach in waste management strategies. This allows economic benefits to be achieved while supporting environmental sustainability, as well as encouraging more efficient and conscious use of natural resources. Therefore, utilizing waste products can contribute to the development of more sustainable and environmentally friendly practices for the future food industry. This research records the recycling strategies of biodegradable packaging products by examining them with specific applications.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3045 Keywords Polymer biodegradable food waste DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.21) Profiling Metabolites in Regional Monofloral Turkish Honeys Using GC-MS
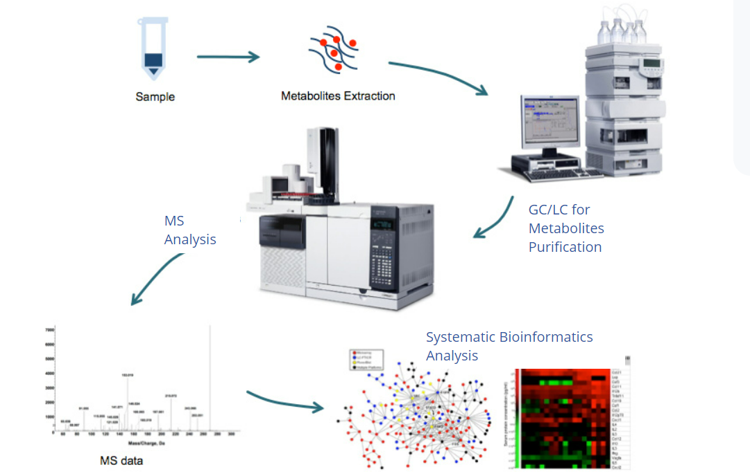
Bees play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of nature and the overall ecosystem. Not only do they contribute to the pollination process, ensuring the reproduction of various plant species, but they also provide essential products for human consumption, such as honey, royal jelly, propolis, and pollen. Honey, a primary bee product, is composed of various sugars, along with proteins, amino acids, vitamins, and other vital nutrients. Despite the numerous benefits associated with honey, there is a limited amount of research on its molecular composition. Moreover, studies specifically focusing on Turkish honeys are sparse and often lack comprehensive quality. Typically, research tends to concentrate on specific components like flavonoids and volatile compounds. Some studies analyze honey metabolites based on the floral origin, while others explore metabolomic differences between mature and immature honey. However, a comprehensive study that systematically profiles the metabolite composition of regional monofloral honeys in Turkey is currently lacking. The primary objective of this study is to identify and characterize the maximum number of metabolites present in monofloral honeys originating from diverse regions in Turkey. Additionally, the collected data will undergo rigorous bioinformatic analysis, aiming to systematically categorize and offer profound insights into the molecular composition of these honeys. Once the appropriate extraction solvent was determined, the honeys were subjected to extraction throughout the day. Subsequently, they were taken from the supernatant and dried in a speed vacuum. After the drying process, the dried honeys underwent suitable amidation and silylation procedures before being analyzed using GC-MS. Metabolite profiles of honeys collected from 10 different regions of Turkey were obtained using GC-MS. Significant differences were observed among honey samples from different regions in terms of the types and number of identified metabolites. The bioinformatic analysis indicates an average identification of approximately 25-30 metabolites in each honey sample with the composition ranging from 85-90% sugar and sugar derivatives and 15% other components (organic acid) depending on the region. Classification studies based on molecular compositions were conducted, considering regions, monofloral origins, geographical conditions, and climatic factors. These studies are currently ongoing for the analysis of 17 honey samples. [1-3]
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3047 Keywords Honey metabolomics food analysis gas chromatography mass spectrometry DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.22) Tracking the Unique Compounds of Common Adulterants to Confirm Honey Authenticity Employing Orbitrap HR-MS Based Non-Targeted Metabolomics
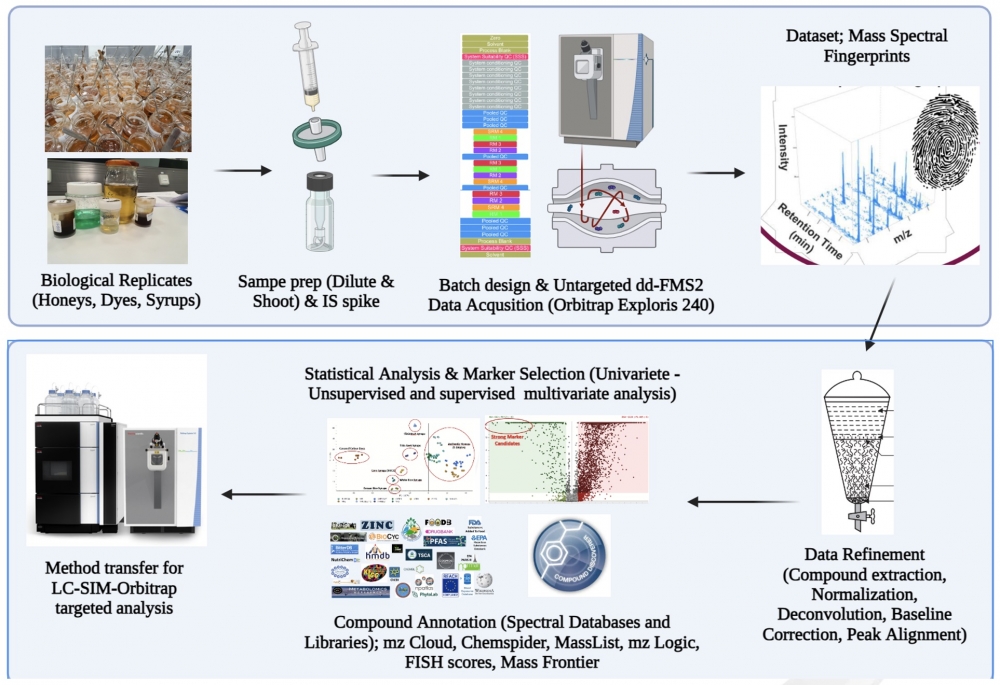
Fraudulent techniques are constantly evolving and the fact that QC activities have become the center of attention has necessitated the development of novel methods using modern instrumentation [1]. Currently, there are no practical and fruitful methods that can simultaneously highlight all common adulterants in honey by also declaring the adulteration origin leveraging a single shot analysis [2]. This work aimed to generate a non-sophisticated, qualitative screening method to confirm honey authenticity by exploiting a simple dilute & shoot preparation linked to a LC-SIM-MS acquisition. For this, we developed an analytical workflow starting with non-targeted metabolomic screening to underscore potential markers of honey adulteration. In the latter case, to integrate the final method into our QC workflows and possess a harmonizable nature, promising marker informations filtered from omic research were transferred to developed SIM-based targeted-MS method. Initially, the metabolomic profiles of food dyes, authentic honeys from different botanical origins, and as exogenous sugar syrups were obtained using HILIC separation coupled with Orbitrap HRMS system. For metabolomic runs, MS data acquisition was operated in a full MS-ddMS2 mode (top 5). Full scan spectrums were acquired in polarity switching from 90 to 1200 m/z at 180,000 FWHM. Detected markers were deeply criticized and selected visually after performing a data process using Compound Discoverer software. To conduct discriminant analysis, chemometric data processing tools including unsupervised PCA and volcano plots were used after log transformation. After the selection of the markers, targeted SIM-MS spectrums were acquired at a 15,000 FWHM using an inclusion list containing an m/z value and predicted RTs. Foreign polysaccharides in honey with an extended degree of polymerization (DP) were assumed as the accurate indicators of starch-based syrup usage. Fructooligosaccharides or maltooligosaccharide-type liquefied starch can be distinguished efficiently in our method by carefully analyzing the retention time indexes. Hence, starch-based syrups derived from different origins like agave, corn, rice, wheat, and cassava can also be distinguished by novel methods. For corn syrups, other than polysaccharide residues, 8 additional markers covering all corn syrup types (n=7) were selected. Again, other than polysaccharide residues, 5 discriminant markers for rice syrups suggested by the novel method. Furthermore, we realized that adding foreign amylases to artificially increase the diastase value of honey can preliminarily be reported by analyzing polysaccharide residues derived from the hydrolyzed starch content of the enzyme product. We defined 10 common markers for 7 different E150d dyes in place of imidazoles. Psicose and mannose were the rare monosaccharides and assumed as certain markers of inverted and corn syrups. These monosaccharides were also monitored in our method with improved resolution. Thin juice or thick juice obtained from beet rhizomes is used for invert sugar syrup production. The presented method in this study described 8 telltale markers and enabled detection of both beet syrup types. Acetyl maltose and anthranoside A along with caffeine were tentatively annotated and used as botanical origin markers for pine and citrus honey respectively. In the real sample analysis, carried out thanks to the new method, it was determined that most of the honeys in the market contained adulteration and this situation constituted a major problem in terms of food safety. The use of beet syrup was found to be the predominant type of adulteration. The described SIM-MS method using targeted multimarker detection represents a remarkable improvement over past analytical methods and reshaped the demonstrated approaches by providing a high degree of certainty in terms of adulteration identification.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3050 Keywords Adulteration honey metabolomic sugar syrups LC-MS E150d DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.23) A Study on the Elemental Composition, Nutritional Values, and Health Risks of Some Chocolate Brands Available in Turkish Markets
Chocolate, a widely consumed product across diverse age groups, underwent elemental analysis using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) following microwave-assisted acid digestion. The study focused on white, milky, and dark samples from the top 6 best-selling chocolate brands in Turkish markets. Although numerous studies in the literature have explored the benefits of chocolate, there is a scarcity of research on its potential health hazards. Results were employed to ascertain recommended daily allowances (RDA) and assess health risk levels. According to the results obtained from white, milky and dark chocolates, the mean values of the elements are as follows, respectively: Na: 1848-1564-273; Mg: 350-829-2344; P: 3471-3998-4562; K: 5728-8095-17138; Ca: 4334-3752-1438; Mn:0.48-5.99-25.95; Fe: 8.24-71.95-345.34; Cu: 0.50-5.21-19.71; Zn: 14.27-16.86-34.32 µg-1. The mean elemental levels in white, milky and dark chocolates demonstrated a cocoa-content-dependent increase particularly for Mg, P, K, Mn, Fe, Cu, and Zn and dark chocolate was found to be rich in these elements. However, an escalation in cocoa content corresponded to heightened health risks, with mean values for potentially toxic elements increasing in the same order as follows: Cr: 0.06-0.69-3.10; Ni:0.21-1.34-4.96; Cd: 0.16-0.14-0.21; and Pb: 0.079-0.096-0.141 µg g-1. Arsenic was not detected in any samples. Although the target hazard quotient (THQ) and hazard index (HI) remained below 1 for all samples (based on a 5-gram daily consumption), the carcinogenic risk (CR) for Ni, and Cr raised concerns. The carcinogenic risk values for Pb are 1.72x10-8-3.06x10-8; 1.36x10-6-2.02x10-6 for Cd; 9.03x10-6-2.15x10-4 for Ni; and for Cr it is in the range of 7.55x10-7-3.93x10-5. Notably, Ni and Cr presented moderate risks, escalating linearly from white to dark chocolate. Thus, it becomes crucial for consumers to balance the nutritional benefits with the potential health risks when consuming different varieties of chocolate. [1–4].
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3053 Keywords Chocolate elemental analysis ICP-MS health risk assessment carcinogenic risk DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.24) Extending the Quality Control Landscape of Royal Jelly Products by Simultaneous MRJP Proteotype Quantification and Adulterant Identification
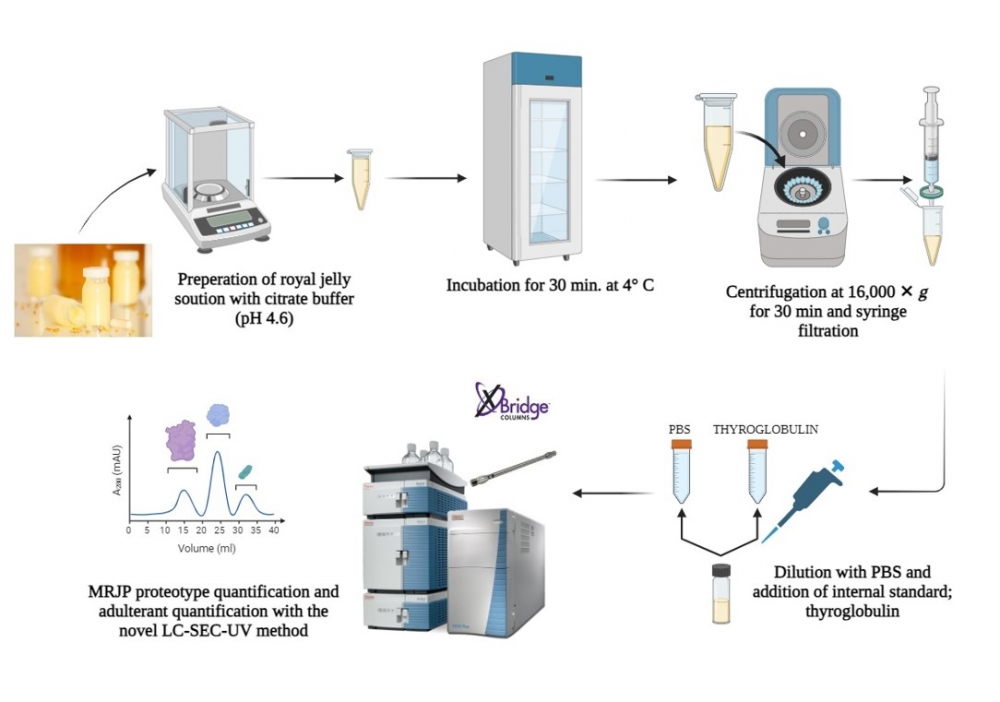
Polymorphism-derived proteotypes named MRJP-1 oligomer (Apisin), MRJP-2, MRJP-3, and MRJP-1 monomer (Royalactin) are predominant in RJ and the bioefficacy of the products greatly vary depending on their profile [1]. Legislations suggest following the total protein concentration and 10-HDA contents of the RJ products as the bioactive constituents. However, each MRJP variant has distinguished health benefits and MRJPs undergo a rapid structural change depending on storage conditions and shelf life, and their effectiveness may be modified or reduced [2]. Therefore, measuring the individual concentrations of each intact MRJP instead of the total protein and inspecting the modifications is crucial. In this study, it was aimed to develop a practical analytical method for the absolute quantification of MRJP variants. A novel MRJP purification workflow was also presented to obtain authentic standards for Native-LC-SEC-UV method development and for constructing the calibration plots. The supernatant of RJ proteome extract was subjected to tandem purification at FPLC performing cation, anion exchange, and size exclusion (SEC) respectively. Subsequently, obtained fractions were desalted and concentrated and purities were checked by SDS-PAGE. Protein annotation of each purified MRJP was accomplished by bottom-up proteomic assay. In-gel digested purified proteins were transferred to UHPLC fractionation and Orbitrap HRMS operated in FS-ddMS2 acquisition. Data was processed at Proteome Discoverer and sequences were retrieved from UniProtKB. Real sample analysis (n=15) was performed using the developed native mode LC-SEC-UV method. Thyroglobulin was spiked for normalization and the RJ proteome was extracted using a citrate buffer (pH 5.6). The LC system was operated under isocratic flow and all MRJP critical pairs were chromatographically resolved via SEC column. Ovalbumin, milk powder, and melamine as potential adulterants were simultaneously screened, thus mimicked RJ samples could also be reported. HRMS data in agreement with SDS-PAGE suggested that Apisin is mainly characterized at 250 kDa, meanwhile, MRJP-3, MRJP-2, and Royalactin are identified roughly at 70, 53, and 57 kDa respectively. LC-SEC presented an accurate quantification for all MRJP proteoforms. MRJP-2 and MRJP-3 results were between 1.1-29.5 mg, and 0.6-22.8 mg respectively. Royalactin was quantified between 0.4-10.4 mg while Apisin was found between 1.2-78.2 mg. It was determined that storage conditions dramatically affect the protein composition and Apisin was the most fragile variant. Higher temperatures, inefficient lyophilization, or improper packaging promote Maillard reactions resulting in higher glycation-derived protein loss. Furthermore, it was observed that the lyophilization process can induce MRJP3 to be fragmented and Royalactin to be oligomerized. None of the samples contained any adulterants, but as the bee products rescript will come into effect soon, it is considered to be vital to analyze the potential adulteration. These results proved that adapting the novel LC-SEC-UV method into the QC workflows can reliably indicate the quality of the final RJ products.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3058 Keywords Royal Jelly protein size exclusion quality HPLC DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.25) Unveiling the Pyrrolizidine Alkaloid Residues in Honey and Bee Pollen Samples by Employing Novel Online-SPE Configured LC-MS Analysis
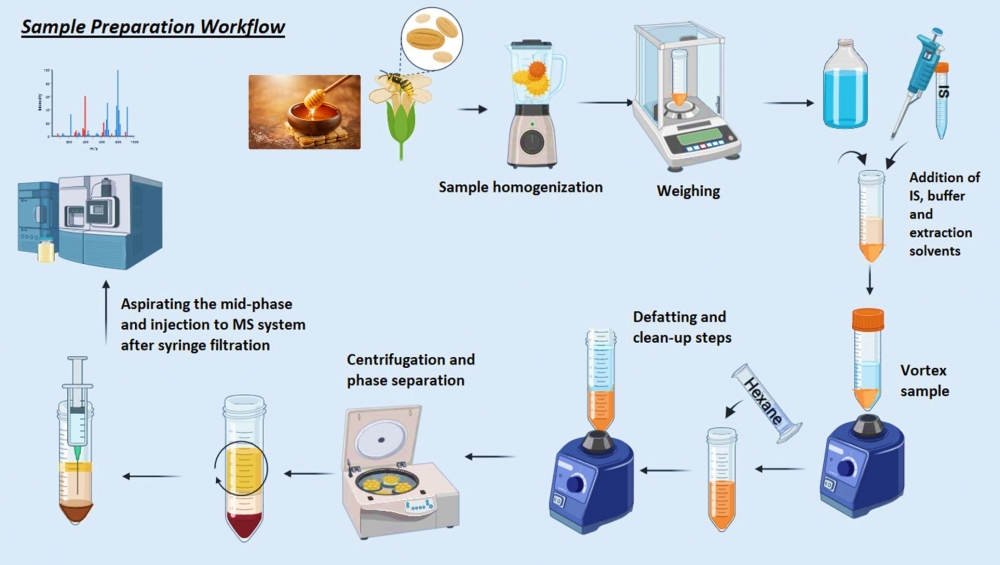
Pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs) and N-Oxide forms (PANOs) are one of the harmful secondary metabolite subclasses of plants [1]. Besides their toxicity, the mutagenic, carcinogenic, and hepatotoxic effects were also demonstrated [2]. According to the EFSA, honey, and bee pollen are susceptible to containing high levels of PAs/PANOs. Commission Regulation 2020/2040 amended Regulation 1881/2006 as regards maximum levels of PAs/PANOs in foodstuffs. New MRL was set as 500 µg/kg for pollen-based foods. Thus, undesirable concentrations should be monitored meticulously by using sensitive and accurate methodologies. This research reports an overview of actual residue profiles for honey and bee pollen samples by introducing a straightforward and sensitive LC-MS method for the quantitation of 28 PAs/PANOs. Online SPE was optimized for the first time as an alternative automated pretreatment instead of the traditional acidified extraction followed by offline SPE. A fully automated online-SPE strategy allowed us to integrate the effortless dilute & shoot technique without matrix suppression and led us to gain increased sensitivity. Samples were psychologically classified; 15 bee pollen and 19 color-distributed bee pollen were supplied to clarify the main contamination source. Next, a validated method was applied to pre-classified honeys (n=29) and pollen. PAs in pollen samples were extracted using ACN and McIlvaine buffer (pH 6.5) and defatted with hexane. After centrifugation, aqueous phase was used for analysis. Dilute & shoot preparation was conducted for honey samples. Separation was performed on Thermo UHPLC, and C18 Strata trap cartridge was the extractive stationary phase. Thermo Altis triple quad MS was operated in +ESI with dynamic MRM, acquiring two transitions for each PA. Validation results showed that all parameters for both matrices are consistent with the requirements. Recovery ranged from 93.1 to 98.6%. The intra and inter-day RSDs% ranged from 2.9 to 7.6% and from 10.8 to 15.8%, respectively. Observed LOQs (0.25 μg/kg) were below the minimum requirements. R2 was consistently above 0.99. Real sample analysis indicated that total PA/PANO concentrations in honey ranged between 0.28 to 28.3 μg/kg and in pollen ranged from 10.9 to 6243 μg/kg. Erucifolin, Europine, Lycopsamine, Intermedine, Europine N-oxide, Retrorsine, Seneciphylline, Heliotrine, Seneciphylline N-oxide, Echimidine, Senecivernine, Senecionine, Lasiocarpine were the most frequent in honeys and Europine with 21.87 μg/kg was the highest residual concentration. Monocrotaline, Ericifolin, Intermedine, Europine, Lycopsamine, Europine N-oxide, Intermedine N-oxide, Lycopsamine N-oxide, Retrorsine, Seneciphylline, Heliotrine, Seneciphylline N-oxide, Heliotrine N-oxide, Seneca Vernine, Senecionine, Senecivernine N-oxide, Senecionine N-oxide, Echimidine N-oxide, Echimidine, and Senkerkine were dominantly quantified in bee pollens. Seneciphylline, Senecivernine, Senecionine Echimidine and N-oxide forms are the most prevalent and 4317 ug/kg was the highest concentration for Echimidine. Echium and Phacelia pollens were found as the main source of Echmidine and Echmidine N-oxide residues. The data does not suggest that bee pollen composition has a significant effect on PA concentration in honey. 86% of the honey and all pollen samples were contaminated with PAs/PANOs and the sum of the 28 target analytes was higher than 500 µg/kg in 21% of the bee pollen samples meaning these samples exceeded the EU MRL limits. In regard to food safety, implementation of the strict QC mindset and adapting innovative methodologies are needed to prevent human exposure to PAs in bee products.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3059 Keywords Honey bee pollen residue LC-MS pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PA) DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.26) Determination of Microplastic Release from Disposable Plastic Cups to Beverages
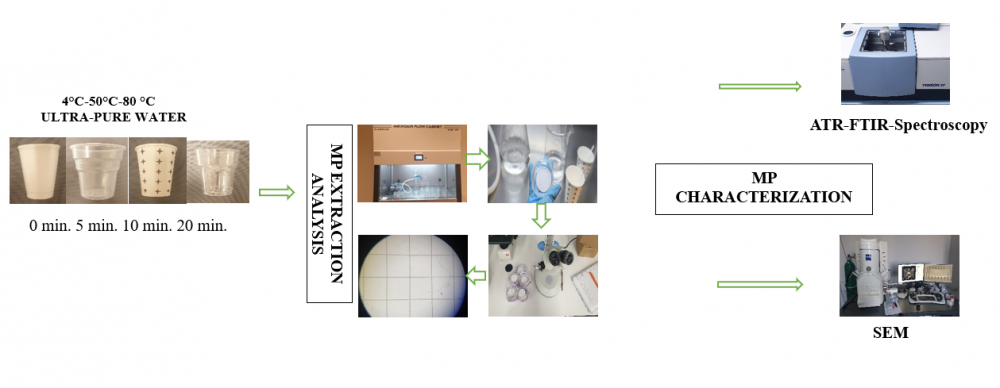
Microplastics (MPs) are one of the most important food and environment pollutants arise in recent years. Plastics are commonly used in many places and reduced to micron- and nano-size by physical effects such as sunlight, winds, flows, living organisms, waves, external impact and/or intentionally for industrial purposes. Plastic particles <5 mm in size are named MPs, and these particles, which are found everywhere in the ecosystem, can also enter the human diet by food systems. Studies have clearly shown that packaging materials could be one of the major sources of MPs present in the food and beverages. In this study, the number of MPs released from 5 types of disposable plastic cups (PS, PE coated paper cups, EPS, PP, PET) into water at different temperatures (4 °C, 50 °C, and 80 °C) were analyzed. For this purpose, numbers of MPs at different exposure times (0, 5, 10 or 20 min) were determined. Standard filtration techniques were used to determine the number of MPs released into the plastic cups. The filters were stored in glass petri dishes for characterization of MPs, and the particles were classified according to color and shape characteristics. The chemical and morphological changes caused by different temperatures on the inner surface of plastic cups were determined by ATR-FTIR and SEM. The average number of MPs obtained was 574.33±374.12 particles/L. The highest MP particle was determined in PP cups with 1420 p/L (50 °C 20 min.) while the lowest MP was in PE-coated paper cups with 126 p/L (4 °C, 0 min). SEM images demonstrated the abrasion on the surface of the plastic cups as a result of hot water exposure. Again, FTIR results showed that intensities of absorbance levels at some wavelengths were decreased after the water treatment although the spectra of the plastics did not change. The average MP intake of the consumers was also calculated; for example, the MP exposure during the consumption period was determined as 18720-73840 MPs/year. In conclusion, the result of this study confirmed that disposable plastic cups could be a critical source of MP contamination of the beverages consumed in daily bases, and a necessary attention must be taken into account for their risks to humans and the environment.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3065 Keywords Microplastics contamination human exposure beverages DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.27) Recent Trends in the Determination of Sugars and Organic Acids for Fruit-based Products

Sugars and organic acids represent nutritive and flavoring components of fruit-based products, significantly influencing their soluble solid content and sensory characteristics. When processing fruit products and storing them, the sugars and organic acids in them are less likely to undergo changes compared to other components such as pigments, antioxidants, and flavor compounds. Therefore, analyzing the composition of sugars and organic acids in fruit-based products, like fruit juices, can be useful in verifying the authenticity of the juice and ensuring quality. Moreover, microbial growth can be effectively monitored by analyzing various metabolic by-products they generate, including lactic acid, acetic acid, or ethanol. These products can be automatically regulated throughout the entire process, providing a simple and reliable method to ensure the quality and authenticity of the final product. Understanding the precise qualitative and quantitative distribution of characteristic sugars and organic acids in fruit-based products is essential for quality assessment. Chromatography techniques like HPLC, GC, LC-MS, and GC-MS are useful for identifying and quantifying sugars and organic acids. Recent advancements in MS instrumentation allow precise measurements and compound identification at low concentrations. However, these methods have low throughput characteristics, requiring complex sample preparation and longer analysis times. Alternative methods include capillary electrophoresis, biosensors, electrochemical sensors, and NIR spectroscopy for quick and sensitive analysis of fruit-based products. The food industry relies on rapidly and accurately detecting sugars and organic acids in fruit-based products to ensure their quality, authenticity, and nutritional value. In recent years, significant advancements have been made in developing new detection techniques to enhance sensitivity, specificity, speed, and cost-effectiveness [1-4]. This review presents an automated enzymatic approach for determining sugars and organic acids using automated analytical techniques, which provides fast, affordable, and efficient analyses compared to manual chromatography methods. Additionally, this review provides an overview of recent trends in rapidly detecting sugars and organic acids in fruit-based products and offers some future remarks.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3074 Keywords Sugars organic acids fruit juices automated enzymatic methods DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.28) The Antioxidant Activity of Essential Oils in Edible Oils
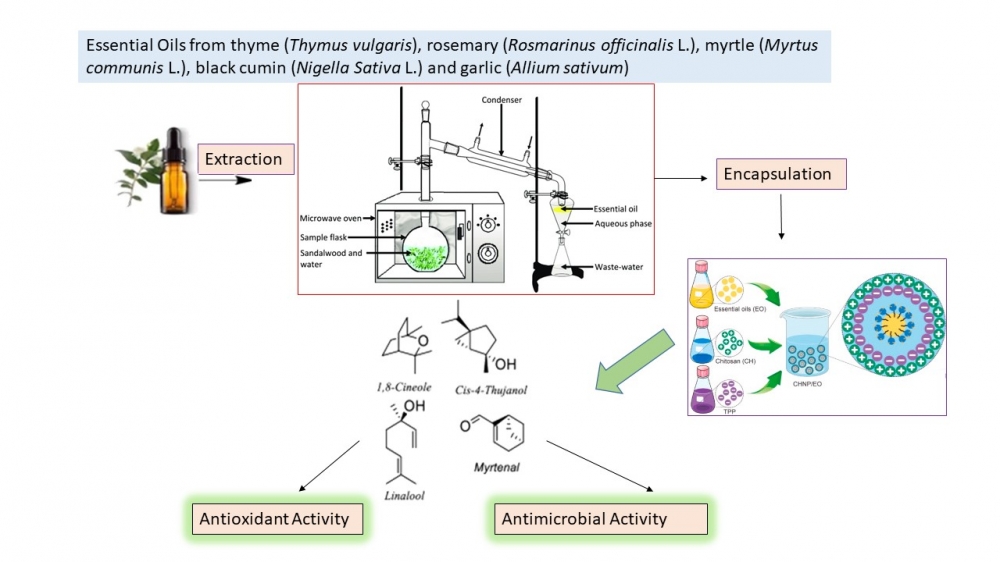
The methods of obtaining essential oils from various plants and their antioxidant activities of essential oils with antioxidant effects were presented in this study. Essential oils can be obtained from various parts of plants (leaves, fruits, barks and roots) through distillation, extraction and pressing methods [1-3]. It has been found that they have antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, antioxidative and antimutagenic effects. In this study, the antioxidant activities of the essential oils including thyme (Thymus vulgaris), rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.), myrtle (Myrtus communis L.), black cumin (Nigella Sativa L.) and garlic (Allium sativum), which are natural antioxidants, are synthetic compared to that of synthetic antioxidants such as BHA, BHT and TBHQ. The antibacterial activities of natural essential oils have also been investigated. In terms of food safety, the lack of carcinogenic and mutagenic effects of the essential oils and the increase in demand for natural additives resulted in the evaluation of their potential to be used instead of many synthetic food additives in oils and oil containing foods [4-5].
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3075 Keywords Essentail oil Myrtus communis L. Thymus vulgaris L. Rosmarinus officinalis L. Antioxidant Activity DPPH radical scavenging DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.29) Analytical Methods for Measuring Lipid Oxidation and Antioxidant Capacity in Food Systems
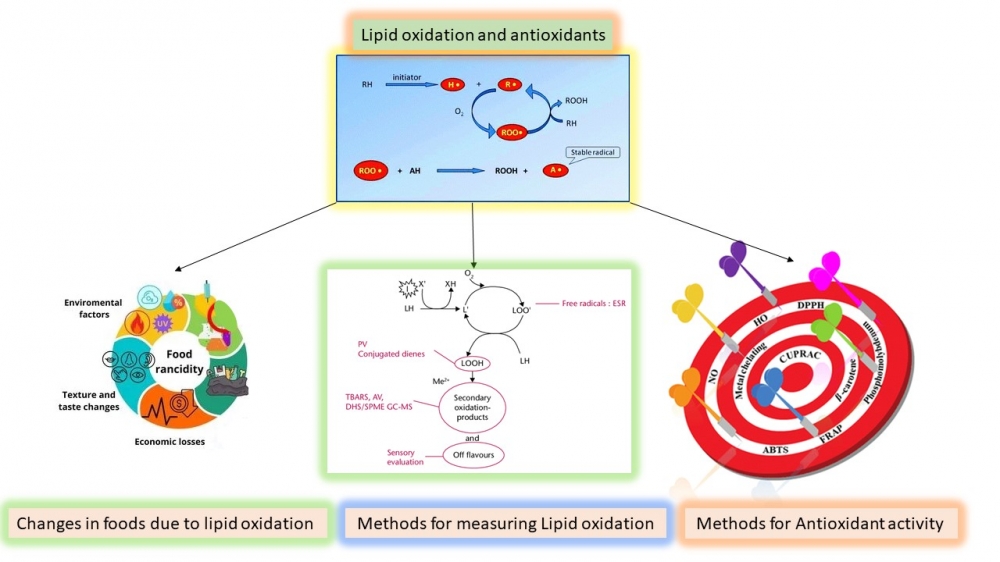
Lipid oxidation is a critical quality parameter in food. Several methods have been developed to determine the level of oxidation and antioxidant activity. This review compares the methods used to determine lipid oxidation and antioxidant capacity in food. The methods developed for lipid oxidation are based on the direct or indirect measurement of primary or secondary oxidation substances produced. Peroxide values and conjugated diene methods are commonly used to determine the primary oxidative products of lipid oxidation in edible oils and high-fat products. Meanwhile, 2-Thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances and chromatographic methods are suitable for determining the secondary products of oxidation in fats. Indirect methods such as fluorometric and sensory analyses are also available. The antioxidant capacity of additives is determined indirectly using the lipid oxidation methods mentioned above or directly based on the free-radical scavenging activity of the antioxidant compounds. It is important to note that each lipid oxidation and antioxidant capacity method uses different approaches, and therefore, one method cannot be used for all foods. Therefore, selecting the appropriate method for specific foods is essential for accurately evaluating lipid oxidation or antioxidant capacity.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3080 Keywords Lipid oxidation antioxidant capacity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.30) Evaluation of Matrix Effects for the Analysis of Some Pesticide Residues in Citrus Fruits, Pepper, Tomato and Lettuce Samples using a Multi-residue Analysis Method
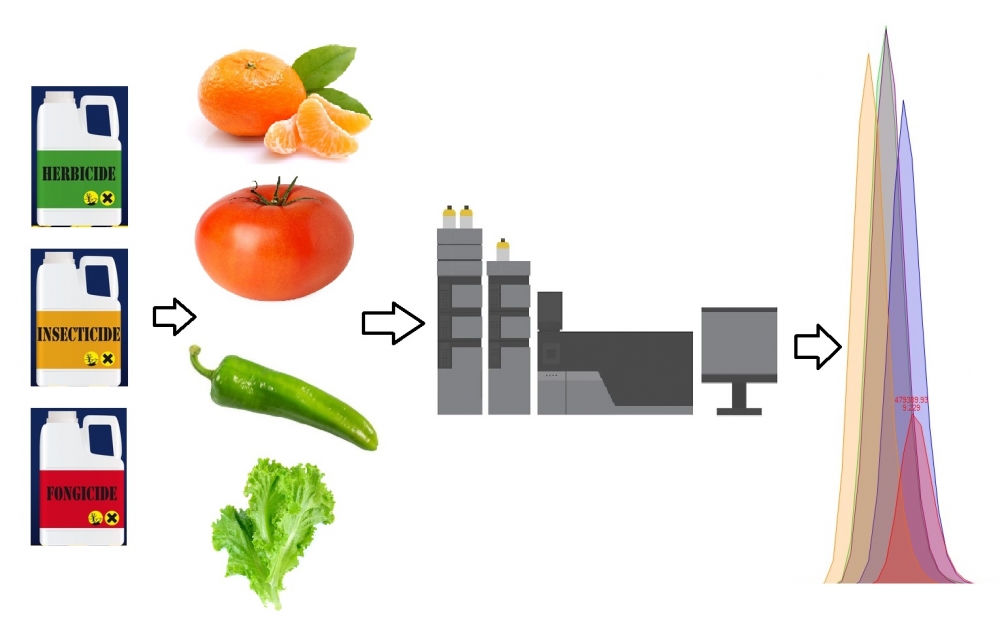
LC–MS/MS methods are widely used for pesticide analysis, because of their high sensitivity and selectivity with short analysis time. Nevertheless, LC–MS/MS has some disadvantages owing to the matrix effects. Matrix of the sample has a remarkable impact on the sensitivity and reproducibility of trace analysis of the pesticides [1]. The signal intensities of some pesticides, namely atrazine, avermectin, benzobicylon, bifenazate, bupirimate, chlormequate, cyromazine, fluopicolide, fluxapyroxad, terbuthylazine, terbutryn, triazophos and valifenalate, could be affected by different food matrices. In the current study, the effects of four different matrices such as citrus fruits, pepper, tomato, and lettuce were demonstrated during the analysis of 13 pesticides using the QuEChERS procedure and LC-MS/MS [2]. The multi-residue analysis of the 13 active compounds on tomato matrix was found compatible with the SANTE/11312/2021 Guidelines. [3]. 11 of analysed pesticides from pepper, tomato and lettuce showed negligible matrix effects (−20–20%) compared with the responses obtained in acetonitrile. But, in all matrices signal suppressions of 69.34-80.11% and 36.91-55.71% were detected for chlormequate and cyromazine respectively. In addition, significant signal suppressions were observed for 10 pesticides in citrus fruit samples. The rates of signal suppressions for atrazine, avermectin, bupirimate, chlormequate, cyromazine, fluopicolide, fluxapyroxad, terbuthylazine, terbutryn, triazophos and valifenalate were detected as 22.85, 84.57, 80.11, 55.71, 91.38, 93.95, 42.64, 50.99, 52.53 and 50.02%, respectively, for citrus matrix. However, a strong signal enhancement (38.46 and 236.95%) occurred for a bifenazate metabolite (bifenazate diazen) for pepper and lettuce matrices. Changing some steps in the extraction process can help to improve sensitivity of the analysis. [4]. For that reason, profiles of diluted citrus extracts were generated in this study. Dilution for citrus fruits led to a significant decrease in the matrix effects. With the modified extraction methods, the rates of signal suppressions were significantly reduced for atrazine, avermectin, fluopicolide, terbuthylazine, terbutryn and triazophos in citrus samples.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3081 Keywords Analytic method fresh foods matrix effect pesticide residue QuECHERS method DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.31) Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry for Geographical Origin Authentication and Adulteration Determination in Food Products
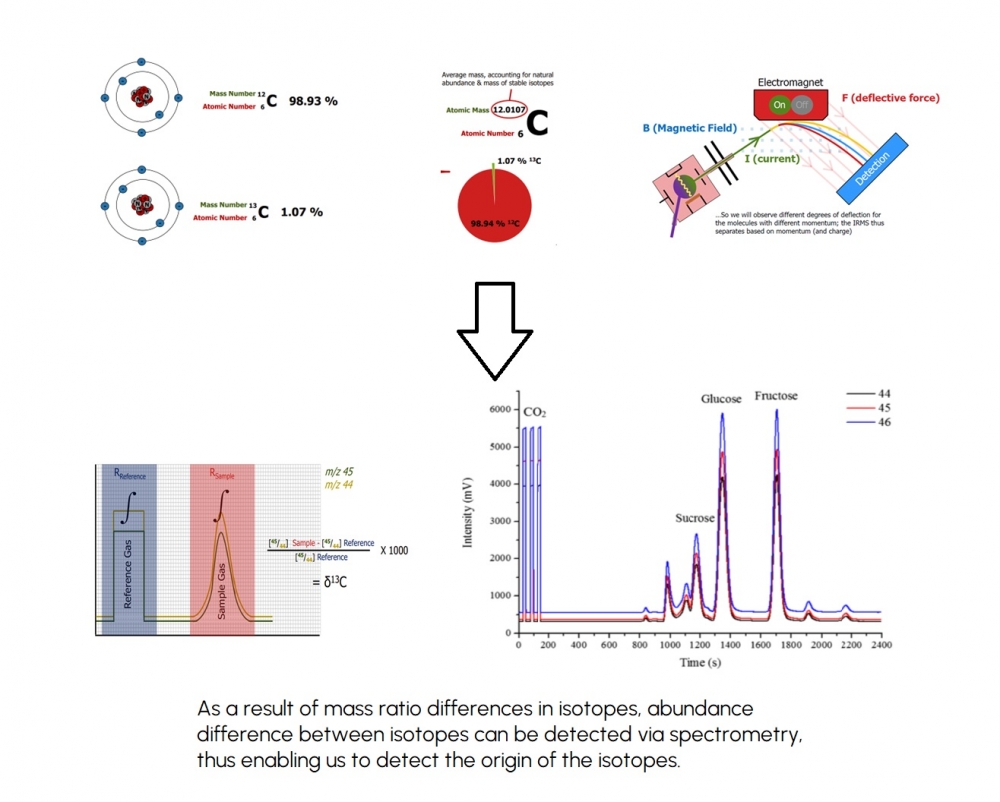
The determination of food adulteration is of primary importance in protecting consumers against fraud and to reveal fraudulent use of deceptive additives in the food industry. Another important factor affecting the behaviors of consumers of agricultural products that has also attracted considerable attention from an analytical determination standpoint is that of geographical origin as consumers are increasingly viewing quality being linked to it. This study comprises a review of selected recent peer-reviewed publications on the topic of isotope ratio mass spectrometry (IRMS) in food analysis. The technique is already verified by plenty of studies in determination of food adulteration. Geographical origin authentication and adulteration determination are two practical implementations of the technique towards the assessment of food product quality. Geographical origin authentication studies combine various additional analytical techniques with IRMS in many cases (ICP-MS, NMR, etc.). The publications covered establish the suitability of multi-elemental, bulk, and compound specific stable isotope analysis for geographical origin authentication. Herein we report here EA/LC-IRMS method development and evaluation of data are presented.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3091 Keywords EA/LC-IRMS food adulteration food analysis adulteration detection geographical origin authentication DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.32) Utilization of Poultry Industry Wastes as Food Supplements
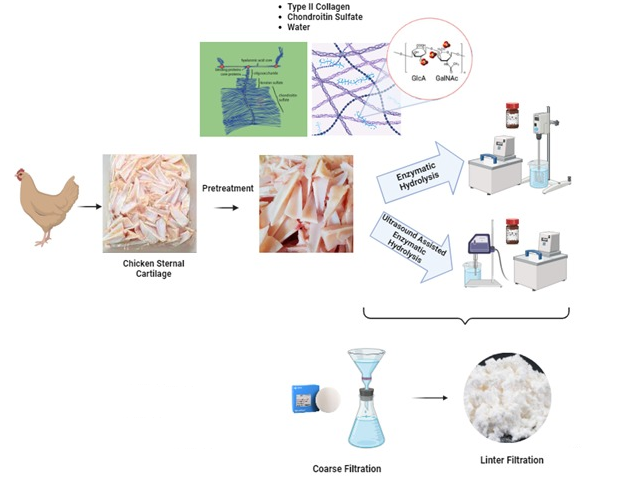
Osteoarthritis is a musculoskeletal disorder that is widely prevalent worldwide and is characterized by the deterioration and wearing down of joint cartilage. This condition leads to symptoms that significantly impact the quality of life, including pain, stiffness, and limited mobility [1]. Chondroitin sulfate (CS), a widely used glycosaminoglycan, is a popular dietary supplement for the treatment of osteoarthritis [2]. The beneficial effects of CS have been reported in osteoarthritis patients for joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. CS is a component of connective tissues and plays a significant role in numerous biological processes, such as supporting flexibility through its polyanionic structure, maintaining the structural integrity of cartilage, and preserving synovial fluid in the bone joints. Additionally, CS performs various functions in the human body, including the control of intracellular ions, preservation of connective tissues, management of osteoarthritis, protection of the cornea, nerve protection, anti-inflammatory properties, antiviral effects, anticancer activity, wound healing, and prevention of clotting [3]. The presented study aims to re-evaluate at least 6000 tons per year of generated cartilage waste in the poultry processing industry in Turkey. In the enzymatic extraction of the CS, chicken breast cartilage was processed using protease enzymes such as papain and alcalase which is the most used method due to the specificity of the protease. Additionally, enzymes like flavourzyme and neutrase, which target reactive groups in proteins, have been used to improve taste and aroma profiles. To increase the process efficiency and rapid release of chondroitin sulfate components, ultrasound-assisted extraction has been conducted during enzymatic hydrolysis. After the extraction, various purification steps were used to filtrate the solution containing chondroitin sulfate and Type II collagen such as coarse filtration, linter filtration to remove residual fat, and microfiltration to remove fine particles and bacteria. CA and type II collagen were separated by using membranes with different MWCO values in diafiltration, taking advantage of the difference in molecular weight. After obtaining CS and type II collagen hydrolysate separately, some characterization tests were conducted to specify their properties. The presence of chondroitin sulfate and Type II collagen obtained by diafiltration has been evaluated through tests such as FTIR and SDS-PAGE. The commercial chondroitin sulfate FT-IR spectrum shows peaks corresponding to sulfate at 856.9 cm-1. The peak at 1411.2 cm-1 represents C-O stretching vibration, variable angle OH vibration, and the presence of free COO- groups. The 1257.9 cm-1 and 1057.4 cm-1 peaks represent S=O and C-O-S stretching vibrations, respectively. SDS-PAGE analysis demonstrated specific bands at molecular weights corresponding to chondroitin sulfate (~37 kDa) and Type II collagen hydrolysate (~7.5 kDa) in the samples extracted with papain. The chemical characterization tests revealed a protein content of 46.29%, moisture content of 10.5%, and ash content of 23%. As a result of the study, CS was obtained successfully and has been confirmed through comparison with literature and commercial samples. The presented study aims to re-evaluate at least 6000 tons per year of generated cartilage waste in the poultry processing industry in Turkey. In the enzymatic extraction of the CS, chicken breast cartilage was processed using protease enzymes such as papain and alcalase which is the most used method due to the specificity of the protease. Additionally, enzymes like flavourzyme and neutrase, which target reactive groups in proteins, have been used to improve taste and aroma profiles. To increase the process efficiency and rapid release of chondroitin sulfate components, ultrasound-assisted extraction has been conducted during enzymatic hydrolysis. After the extraction, various purification steps were used to filtrate the solution containing chondroitin sulfate and Type II collagen such as coarse filtration, linter filtration to remove residual fat, and microfiltration to remove fine particles and bacteria. CA and type II collagen were separated by using membranes with different MWCO values in diafiltration, taking advantage of the difference in molecular weight. After obtaining CS and type II collagen hydrolysate separately, some characterization tests were conducted to specify their properties. The presence of chondroitin sulfate and Type II collagen obtained by diafiltration has been evaluated through tests such as FTIR and SDS-PAGE. The commercial chondroitin sulfate FT-IR spectrum shows peaks corresponding to sulfate at 856.9 cm-1. The peak at 1411.2 cm-1 represents C-O stretching vibration, variable angle OH vibration, and the presence of free COO- groups. The 1257.9 cm-1 and 1057.4 cm-1 peaks represent S=O and C-O-S stretching vibrations, respectively. SDS-PAGE analysis demonstrated specific bands at molecular weights corresponding to chondroitin sulfate (~37 kDa) and Type II collagen hydrolysate (~7.5 kDa) in the samples extracted with papain. The chemical characterization tests revealed a protein content of 46.29%, moisture content of 10.5%, and ash content of 23%. As a result of the study, CS was obtained successfully and has been confirmed through comparison with literature and commercial samples.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3092 Keywords Chondroitin sulphate type II collagen hydrolysate diafiltration DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.33) Evaluation of Anti-inflammatory and Cytotoxic Activities of Extracts of Waste Petals, Leaves, and Stems of Turkish Artichoke (Cynara scolymus) by Phenolic Content
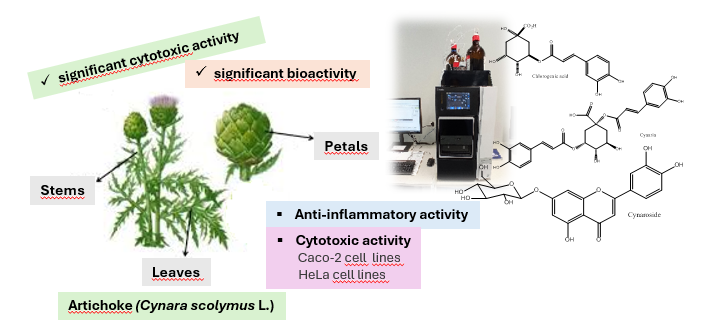
Cynara scolymus L. (artichoke) is a member of the Asteraceae family and is widely cultivated in Mediterranean countries. In Türkiye, the average annual production is around 40.000 tons in the Aegean, Marmara, and Mediterranean regions. Since it has been used for therapeutic aspects alongside its usage in the Mediterranean diet, it is recorded in various pharmacopeia and monographs [1]. Some of the biological properties reported for artichokes are anticarcinogenic [2], antigenotoxic, hypocholesterolemic [3], antidiabetic [4], hypoglycemic, and hepatoprotective [5]. In addition, it is known to have significant medicinal properties such as antifungal, anti-HIV virus, and antibacterial properties [6]. Except for the edible part, C. scolymus L. generates much agricultural waste. Meanwhile, the packaging of harvested artichoke produces over 60% of waste. Cancer is considered one of the most fatal diseases all around the world. It is known that extracts obtained from the edible part of artichoke positively affect cancer cell lines. Therefore, to use the waste part of the artichoke, we aimed to study the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and cytotoxic activity of cooked and uncooked extracts together with their phenolic ingredients. The artichoke was collected from Dalaman-Muğla. The heat-treated and untreated portions of the artichoke's stem, petals, and leaves were dried in the shade. Different pH differentiation extractions were applied to cooked and raw parts of C. scolymus. The obtained extracts containing various amounts of phenolic compounds were studied for their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and cytotoxic properties. Cytotoxic activity was performed against human cervical and colon carcinoma cell lines. According to the results, the cooked artichoke extracts, containing a higher amount of cynarin, cynaroside, chlorogenic acid, 1,3-, and 1,4-di-caffeic acid quinic acids, possessed better results on human cervical cancer cell (HeLa) and colon carcinoma cancer (Caco-2) cells than the extracts obtained from uncooked parts.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3094 Keywords Artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) anti-inflammatory activity cytotoxic activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.34) Liquidambar orientalis Leaf Tincture: Exploring of Urease Inhibition Activity and Determination of Chemical Components by HPLC-DAD
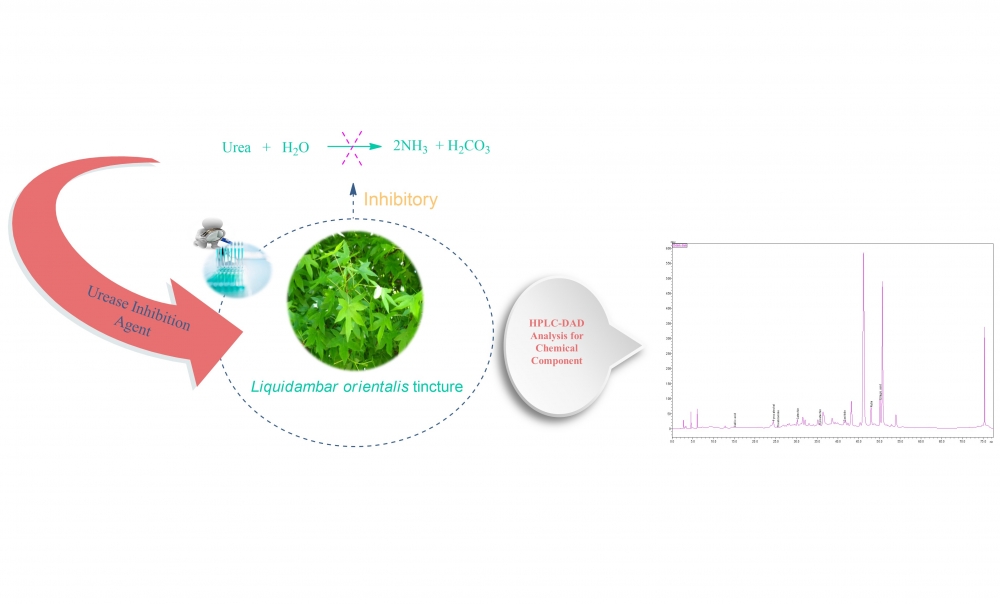
Urease catalyzes the hydrolysis of urea and has received significant attention due to its effects on living organisms' health and quality of life. The persistence of urease activity in human and animal cells may cause some diseases and pathogen infections. Urease can be a virulence factor of infections in the urinary and gastrointestinal tracts. It protects the bacteria from the low pH in the gastric fluid by creating CO2 and NH4+ from urea with the urease enzyme secreted by Helicobacter pylori after colonizing. However, besides being toxic to gastric epithelial cells, NH4+ increases the effect of cytotoxins secreted by the agent by reducing intercellular adhesion. This formation can cause gastritis, peptic ulcer, and gastritis cancer. In this context, proton-providing and urease inhibitors are used to treat H. pylori infection. Urease inhibitors also offer effective therapies in the treatment of diseases caused by urease-dependent pathogenic microorganisms. Urease inhibitors such as phosphorodiamidates, hydroxamic acid derivatives, and imidazoles have limited clinical use because they are toxic and have low stability [1]. In this context, research focuses on the potential of natural products (present in standardized extracts or pure compounds) as clinical urease inhibitors continue to increase [2]. Liquidambar orientalis, which dates to the 6th and 7th centuries, is rich in phenolic compounds. It is generally known as sweetgum or amber tree (amber tree) in Turkey. It is reported that Liquidambar oils were used as medicine in the "Ala'im-i Surgery" (16th-century medical book). It has been utilized in treating skin diseases such as fungus and scabies and treating stomach problems, asthma and bronchitis [3]. Tinctures, which have an effect based on experimentation and proof and an impact that has been going on traditionally for centuries, are still widely used therapeutically today [4]. Tinctures are the most effective form of herbal medicine and are an ancient method. Tinctures are the most commonly used form of medicine in herbal treatments such as homoeopathy, phytotherapy, and Bach flower therapy. Tinctures prepared with alcohol may have an extended shelf life if appropriately prepared. In this study, twenty-four tinctures, which may present natural urease inhibitor potential, were prepared in various plant/solvent ratios at different percentages of ethanol/water mixtures from the leaves of the endemic L. orientalis. The phenolic content of each L. orientalis leaf tincture is determined by HPLC-DAD [5]. The urease inhibitory activity of all tinctures was defined according to the Weatherburn method. [6]. The tincture prepared in 1/1 ethanol/water exhibited the best inhibitory activity with the highest amount of phenolic ingredients.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3095 Keywords Liquidambar orientalis tincture urease inhibition activity HPLC-DAD DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.35) The Changes in Chemical Ingredients of Rosmarinus Officinalis Essential Oils Obtained Under Different Conditions and Chemometric Approach

Rosmarinus officinalis L. (Lamiaceae) is a small evergreen plant that grows wild in most Mediterranean countries [1]. This herb shows particularly antiproliferative effects on various tumor cell lines. A population-based study suggested an overall risk reduction in cancer incidence was associated with patients consuming these herbs, including rosemary [2]. Rosmarinus officinalis L. has long been associated with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties [3]. It is widely cultivated in the Mediterranean area, including Mugla city, for its phototherapeutic and aromatherapeutic properties. In this study, we aimed to search for the standardization method for essential oil production of Rosmarinus officinalis, showing enzyme inhibitory activity. For this purpose, various essential oils were obtained by hydrodistillation method using a Clevenger apparatus from R. officinalis exposed to multiple factors. Briefly, R. officinalis collected from Muğla was divided into four different parts. One part was not subjected to hydrodistillation without drying. The other parts were dried under the sun in a dark environment and in the fruit dryer. The samples were dried under the sun and in a dark environment for four days, and the essential oil was obtained from these samples separately each day. The sample in a fruit dryer, however, was dried for one day. Moreover, the essential oils for each sample were obtained at different pH levels, such as 5.8, 7.0, and 8.0, respectively. A total of 30 essential oils were obtained, and their chemical contents were analyzed by GC and GC-MS. In addition, the enzyme inhibitory activities of 30 essential oils were tested against acetylcholinesterase, butyrylcholinesterase, tyrosinase, α-amylase, and α-glucosidase. The data were evaluated using chemometric techniques. The major constituents of the essential oils α-pinene, eucalyptol, camphor, borneol, and verbenone differed due to the drying and pH effects. Other major constituents in the European Pharmacopoeia, such as camphene, β-pinene, myrcene, p-cymene, limonene, α-terpineol, and bornyl acetate, showed high variation in % constituent amounts. Within the scope, it was observed that the content of the essential oils triggered with various factors, and enzyme inhibitory assays exhibited differences. The essential oils obtained from the sample dried using the fruit dryer were most suitable with European Pharmacopoeia. Since the study results are significant in terms of essential oil extraction from the plants, it is considered necessary for crucial oil-producing companies to protect public health.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3099 Keywords R. officinalis essential oil changes in essential oil content with different factors anticholinesterase activity tyrosinase α-amylase. DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.36) Enzyme Inhibitory Activities of Anatolian Propolis Collected from 15 Regions of Türkiye with Chemical Ingredients

Propolis is a natural substance collected by honeybees from the environment. It is gathered from plants such as poplar, palm, pine, conifer secretions, gums, resins, mucilage, and leaf buds. The typical composition of raw propolis is 50% plant resins, 30% waxes, 10% essential and aromatic oils, and other organic compounds. The scientists focused on propolis chemistry and its bioactivities in the last two decades. The literature revealed that propolis is practical and can prevent and treat colds. It has also been reported that propolis has diverse bioactivities, including anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antioxidant, antitumor, antiulcer, and anti-HIV activities. Therefore, it is suggested to use it against wounds and ulcers, rheumatism, sprains, heart disease, diabetes, and dental caries. Modern medical treatments have recently suggested propolis usage due to its well-investigated chemical composition. Until 2000, over 300 chemical components belonging to the flavonoids, terpenes, and phenolics have been identified in propolis [1]. The Turkish propolis samples collected from 15 regions of Türkiye were extracted using 95% ethanol. After drying, the extracts were analyzed for their chemical ingredients using HPLC-DAD coupled with a C18 (5 µm, 4.6 mm x 250 mm) column [2]. Antioxidant (DPPH, ABTS, CUPRAC) activity, anticholinesterase (AChE and BChE), and α-glucosidase inhibition and α-amylase inhibition activity methods were also used for these extracts. According to the HPLC, naringenin (ranged from 10.64 to 103.89 mg/g), chrysin (ranged from 0.88 and 42.97 mg/g), caffeic acid (ranged from 1.81 and 14.33 mg/g), ferulic acid (ranged from 0.1 and 11.33 mg/g), and cynarin (ranged from 6.44 and 16.61 mg/g) were in reasonable amounts. Other compounds, such as vanillin, vanillic acid, apigenin, p-coumaric acid, kaempferol, luteolin, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, trans-2-hydroxycinnamic acid, pyrocatechol, trans-cinnamic acid, and propyl gallate were also quantified. The extracts exhibited spectacular antioxidant activity in DPPH, ABTS, and CUPRAC assays. Moreover, they exhibited AChE significant inhibitory activity (IC50 ranged from 39.77±3.01 and 449.35±0.75 mg/mL). BChE inhibitory activity (IC50 ranged from 6.55±3.16 and 30.92±8.53 mg/mL). and a-glucosidase inhibitory activity (IC50 ranged from 27.06±3.92 and 256.93±16.25 mg/mL). To reveal the possible use of propolis against Alzheimer's disease and antidiabetes, further studies should be performed. The continuing future search is to identify the responsible inhibitory compounds for AChE, BChE, and a-glucosidase.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3101 Keywords Propolis flavonoid phenolic compounds HPLC-DAD antioxidant activity anticholinesterase activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.37) Investigation of Physico-Chemical, Microbial and Antioxidant Properties of Viburnum opulus Fermented with Water Kefir Grains
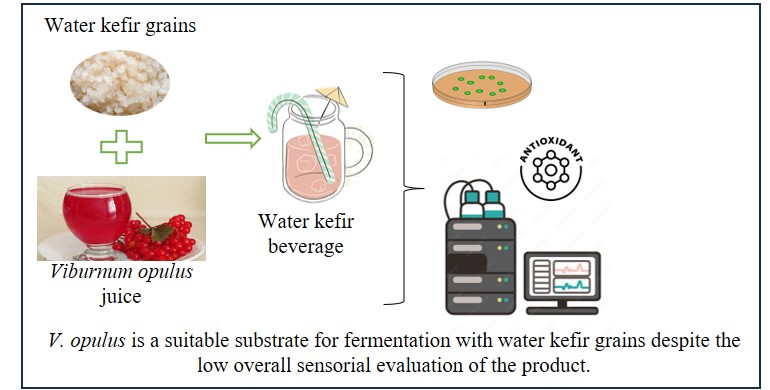
Water kefir is produced by fermenting a plant-based carbon source with water kefir grains under favourable conditions. The resulting drink has different flavours and aromas, high antioxidant capacity, and probiotic microorganism content. In this study, water kefir grains were fermented with nectar obtained from Viburnum opulus for 24 hours at 25°C. The study investigated the organoleptic, physico-chemical, antioxidant capacity, and microbiological content of water kefir. The results showed that the sensory evaluation of the water kefir beverage obtained by fermenting V. opulus was generally low, but the product's colour and fermented odour were highly appreciated. Additionally, the study found a lactobacilli, lactococci, and yeast count of approximately 6 Log cfu/mL after fermentation. Even though the Birx value was as low as 1.0, the microbial development in the plant nectar was favourable. The total antioxidant capacity was determined as 937 mg GAE/L based on the results of the antioxidant capacity analysis. The conclusion drawn was that V. opulus is a suitable substrate for the fermentation of water kefir grains, despite the low overall appreciation of the product by consumers.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3104 Keywords Antioxidant capacity fermentation Viburnum opulus water kefir DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.38) Usage of Chlorine Dioxide Against Infectious Agents for Human, Animal and Environmental Health
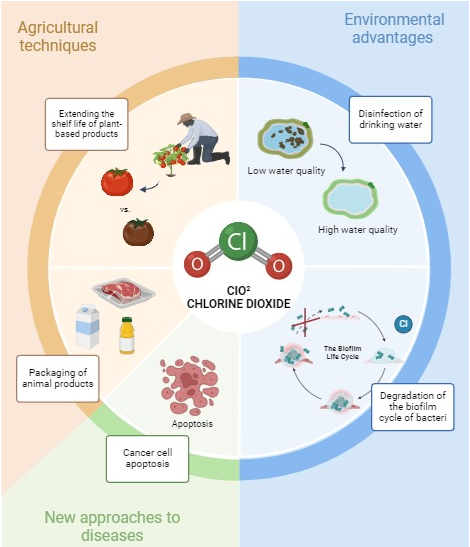
Research is being carried out on environmentally friendly agents to protect human and animal health. Different forms of chlorinated disinfectants are frequently used in food businesses. Chlorine dioxide is an extremely effective biocide and is used in the food industry and in the disinfection of drinking water. Chlorine dioxide, a strong oxidant, has its own electron exchange mechanism. Oxidizing agents are chemical compounds that can easily accept electrons from electron donors. Being a reactive radical for the surfaces it comes into contact with, it has an anti-infective effect due to its oxidation effect. Chlorine dioxide disperses the cell walls and membranes of microorganisms, killing them or eliminating their infectivity. However, healthy tissues and microorganisms that feed on oxygen are not affected by chlorine dioxide [1,2]. The fact that chlorine dioxide has a very unstable structure is the secret of its success in killing pathogens. This feature also prevents the development of resistance [2]. It is used safely in the livestock industry, in slaughterhouses, production and packaging areas of animal products. Washing fruits and vegetables with chlorine dioxide solution extends their shelf life and disinfection with chlorine dioxide is performed in food packaging [3]. Recent studies have shown that chlorine dioxide is a more effective disinfectant against Cryptosporidium oocysts than free chlorine [2]. It has been observed that it is effective on cancer cells by inducing apoptotic cells [1,4]. It was stated that the patient with pancreatic metastatic adenocarcinoma returned to normal and the course of the disease improved without metastasis and remained stable for 18 months [5]. Another patient with hormone-refractory metastatic prostate cancer was reported to experience a sharp decline in PSA level while improving general health [5].
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3106 Keywords Human animal environmental health infection chlorine- dioxide usage DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.39) Palm Oil Facts and Sustainability
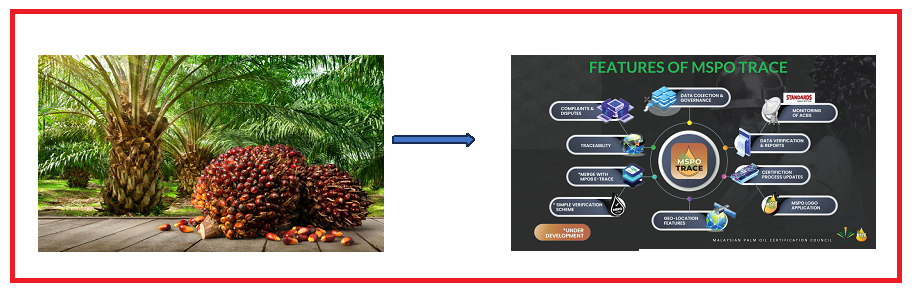
Palm oil is one of the most versatile and sustainable oils used in food and non-food applications as well. Palm oil is extracted from the pulp of the fruit whereas palm kernel oil is extracted from the kernel of the fruit. Both oils are fractionated by physical means to produce olein, stearin, and mid fractions. The versatility of physical properties provided by palm oil and its fractions increase the use of palm oil in bakery, confectionery, snacks, horeca, cheese and cream analogs, etc. Sustainability and health-related concerns also developed as a result of the high demand for palm oil and its fractions. Malaysia is one of the two major worldwide exporters of palm oil and palm oil-based products. Malaysian Palm Oil Council (MPOC) supports business and project development related to palm oil whereas the Malaysian Palm Oil Certification Council (MPOCC) is the certification body responsible for the Malaysian Sustainable Palm Oil Standard (MSPO) [1-3]. The major aim of this paper is to explore palm oil facts on:production; food use, trans fatty acids elimination mitigation strategies, palm-based additives, and clarify sustainability standards for Malaysian palm oil.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3117 Keywords Palm oil sustainability DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.40) Examining the Effect of Cream Process Parameters on Product Performance
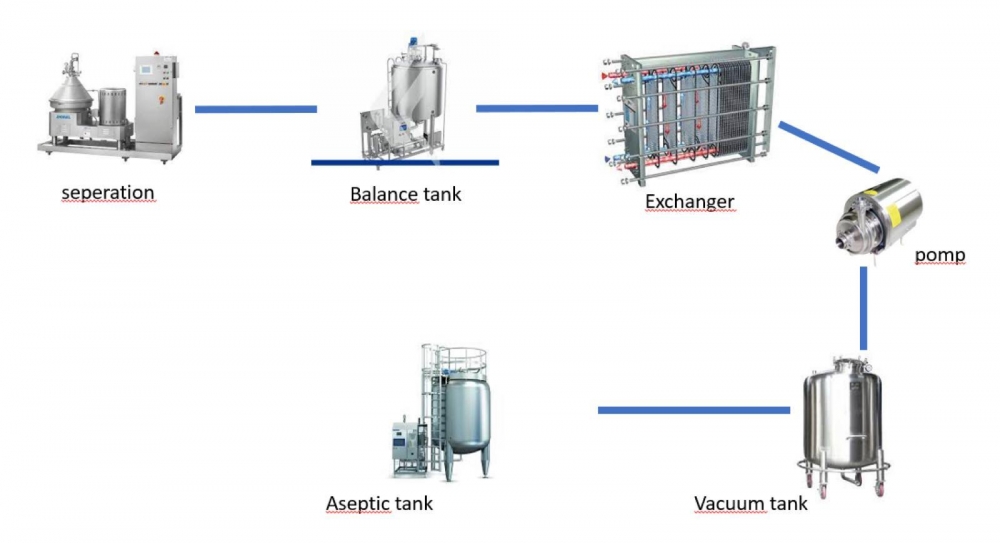
Milk is an important nutritional source with very high biological value. The most important biochemical parameters of milk include milk fat and protein. Milk protein and fat are also of great importance for the industry that processes milk. Cow’s milk contains 3.7-4.9% fat and 3.1-3.8% protein, depending on breed. According to the Turkish Food Codex Cream and Cream Communiqué, cream; It is defined as "the fat-rich emulsion of milk fat obtained by physical separation from milk in skim milk." Sterilization is one of these methods and, in general terms, is the process of destroying all living microorganisms (vegetative and spore forms) by chemical and physical methods. However, since there may be negative changes in the nutritional profiles of foods during this process, commercial sterilization norms are generally used to suit the food. Two different methods are used to sterilize milk in this way: direct and indirect. In the direct method, heat exchange is carried out between the milk and the steam mixed with the milk, while in the indirect method, plate or pipe heat exchangers are used. Direct method is divided into two: Steam-injection method and Steam-infusion method. In the steam injection method; The milk is first preheated to 80°C, then sent to the steam injection section via a pump, where steam is injected into it under pressure. In this section, water vapor gives its heat to the milk in a very short time, heating it to high temperatures such as 135-150°C. The milk is kept at this temperature for 2-4 seconds and is immediately taken into the vacuum tank, the water in it is evaporated with a sudden expansion under pressure and its temperature drops to 80°C. The vacuum in the vacuum tank is adjusted in such a way that the amount of water evaporated is equivalent to the amount of water previously mixed with the milk. After the sterilized milk is cooled to 80°C, it is homogenized, cooled to packaging temperature and packaged aseptically. In the steam infusion method; It is a UHT sterilization method applied by spraying milk into steam as a thin film. Drinking milk produced by this method is also called pulverized milk. Plate and tubular heat exchangers are used. As a homogenization method; It is an upstream (homogenization before heat treatment) and downstream (homogenization after heat treatment) method. Downstream is used in the direct system, and both upstream and downstream are used in the indirect system. In the production of cream and whipped cream, standard production direct (steam injection) and downstream are generally used. The purpose of this study is to investigate whether we can achieve the same product quality with different process methods. Scope of work; Different process parameters were evaluated in 35-fat animal cream, 18-fat animal cream, 33-fat vegetable fat cream and 26-fat whipped cream. Direct system-downstream, which is the standard production produced in the industry, and direct system downstream, indirect system downstream and indirect system upstream parameters produced in the pilot were evaluated by applying. The parameter we base the evaluation on is viscosity values. When the viscosity of 35 fat cream is examined; The indirect upstream process closest to the standard production direct downstream process was measured as 350-380 cp. When the viscosity of 18-fat cream is examined; The pilot production closest to the standard production direct downstream process was measured as 500-550 cp. When the viscosity of 33-fat herbal cream is examined; The indirect upstream process closest to the standard production direct downstream process is recorded as 200-220 cp. When the viscosity of 26-fat herbal whipped cream was examined; The indirect production downstream process closest to the standard production direct downstream process was measured as 120-140 cp. When the data is examined; It has been concluded that the viscosity ranges of all products comply with the standards. In conclusion; It has been concluded that different process parameters can produce positive results on products in order to produce products of the same quality, and in the light of these results, testing different process parameters in the industry can have positive results on product quality.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3119 Keywords Cream process vicosity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.41) Mineral Oil (MOH) Contamination in Refined Vegetable Oils and Prevention-Mitigation Methods
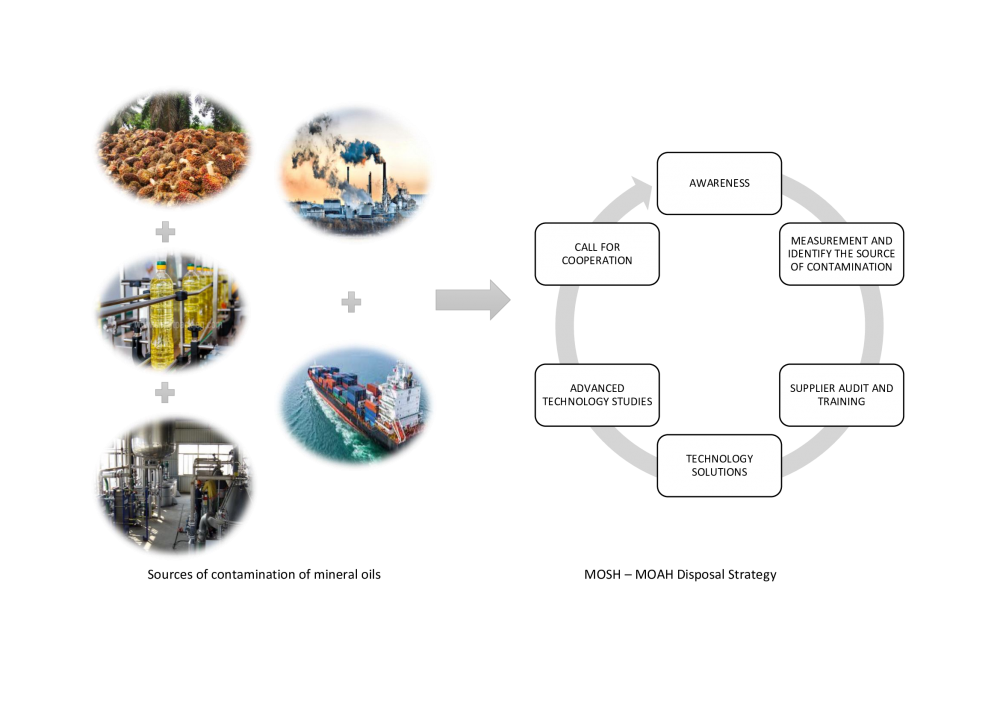
Mineral oil (MOH) contamination stands out to be one of major food safety risks for the food industry. MOH comprises two major components namely MOSH and MOAH. MOSH are mainly paraffins of straight and branched alkanes of various C numbers, whereas MOAH refer to mostly alkylated aromatic hydrocarbons. Potential contamination stages of MOH to vegetable oils are agricultural stages, transport of raw material, processing, refined oil transport, packaging, and adulteration-misuse of oils [1]. EFSA opinion on MOH refers to various toxicity limits for MOSH and MOAH, emphasizing MOAH of certain aromatic rings. Unfortunately, there is still uncertainty regarding the maximum limits of MOH for oils. Standard methods of analysis for determination of MOH in vegetable oils is mostly GC-FID. Literature and various chromatographic methods are still being investigated. Mitigation studies for MOH during refining is another crucial area for oil manufacturers. Food safety policy of IFFCO Turkey realizes the principle of being the pioneer of the oils, fats, margarine sector. We achieved a sustainable mitigation strategy for the last challenge of contaminants namely GE and 3-MCPDE. In this presentation IFFCO strategy on detection, determination, prevention, and mitigation of MOH will be summarized by our quality and R&D team [2,3].
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3125 Keywords MOH food safety mitigation DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.42) Role of Propolis in Cancer Chemoprevention
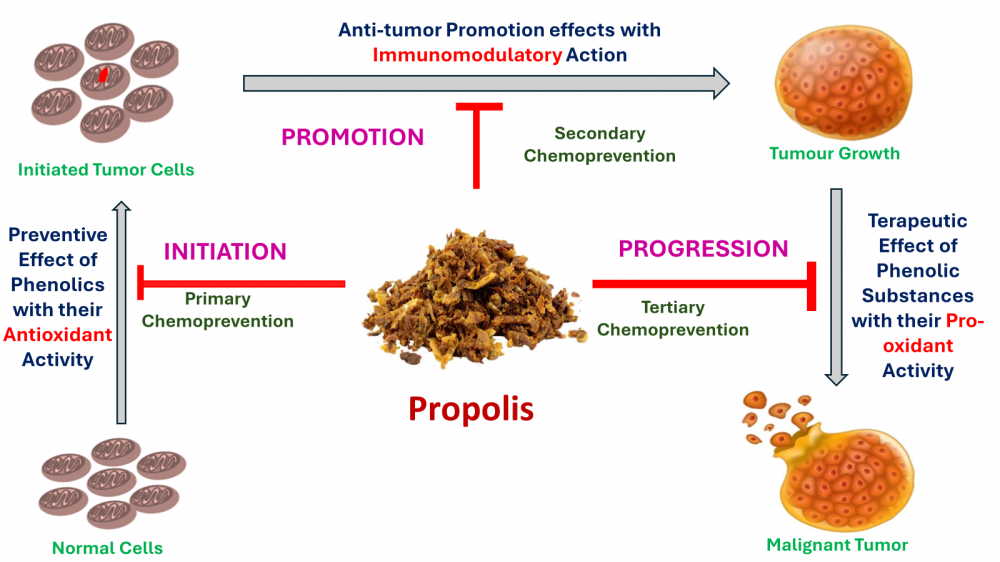
Cancer is a deadly disease caused by the uncontrolled proliferation of abnormal cells in a part of the body. Although conventional methods such as surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy and targeted therapies are widely used in cancer treatment, the search for alternative methods continues due to inadequate treatment and serious side effects. Chemoprevention is an approach with great potential in controlling the incidence of cancer. Chemoprevention works in different ways to stop, delay, and control cancer incidence and progression [1]. Research showed that most cancers can be prevented, treated, or the incidence can be delayed. Some natural products were reported to reduce various risk factors associated with different types of cancer through their chemo preventive role. Propolis, a natural substance produced by honeybees (Apis mellifera L.), has been widely used for therapeutic abilities such as antioxidant anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory and antimicrobial in Traditional Medicine [2]. Although the composition of propolis is closely related to its botanical origin, processing, and environmental conditions, it contains many types of bioactive phenolic compounds [3]. Many studies have shown that the phenolic and flavonoid components of propolis are mainly responsible for their biological activities [4]. Numerous in vitro and in vivo studies have shown that different types of propolis and their phenolic compounds can also be used in the prevention and treatment of cancer. Because the hydroxyl groups of phenolic compounds can neutralize free radicals by donating electrons, they also show a dose-dependent pro-oxidant effect in the presence of transition metals such as free iron and copper due to the Fenton reaction [5]. For this reason, low doses of phenolic compounds contained in propolis can be used as prevention of cancer with their antioxidant effects, while high doses can be used as therapeutic agents with their pro-oxidant effects. Propolis can also inhibit the promotion of cancer with its immunomodulatory activity [6]. Herein, the mechanism of those effects of propolis will be discussed in the light of the studies carried out by our group.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3127 Keywords Propolis phenolic compound cancer chemoprevention DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.43) Deep Eutectic Solvent Pretreatment of Rye Bran for The Production of Aspergillus niger A42 (ATCC 204447) Inulinase

The aim of this study was to produce inulinase enzyme from rye bran (RB) by deep eutectic solvent (DES) pretreatment. RB samples were mixed with choline chloride (ChCl):glycerol (Gly) at different molar ratios (1:2, 1:4, and 1:6) and pretreated at 80°C for 24 hours. The DES pretreated samples were then hydrolysed in an autoclave with 1% H2SO4 at 121°C for 1 minute. RB was hydrolyzed under these conditions without DES pretreatment as the control group. The levels of sugars (glucose, xylose, fructose, sucrose, maltose and arabinose) and furans (furfural and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF)) in the samples were determined. ChCl:Gly (1:2) provided the highest fermentable sugar concentration as 56,48 g/L. Therefore, hydrolysate pretreated with ChCl:Gly (1:2) was used in the fermentation of Aspergillus niger A42 inulinase. To determine the effect of yeast extract ratio on inulinase activity, yeast extract was added to the hydrolysates at two levels, 1% and 5%. At a yeast extract ratio of 1%, the maximum inulinase and invertase activities were 120.56 U/mL and 68.91 U/mL, respectively. When the yeast extract ratio was increased to 5%, the maximum inulinase and invertase activities also increased to 364.88 U/mL and 475.69 U/mL, respectively. The results indicate that an increase in yeast extract ratio led to an increase in inulinase and invertase activities. Fermentations at 5% yeast extract were used to calculate the kinetic parameters. The fermentation process lasted for a period of 14 days, during which the rate of sugar consumption was determined to be 96.57%. The study found that the maximum sugar consumption rate was 22.62 g/L/day, which occurred between days 2-3. Additionally, the maximum inulinase production rate was calculated to be 145.50 U/mL/day, while the maximum invertase production rate was 157.95 U/mL/day. The total dry biomass concentration at the end of fermentation was determined to be 42.40 g/L. The final pH of the fermentation broth was determined to be 6.21. The maximum consumption rate was 14.78 g/L/day, occurring between the 3rd and 4th day of fermentation. The maximum inulinase production rate was 103.16 U/mL/day, and the maximum invertase production rate was 173.67 U/mL/day. The total dry biomass concentration at the end of fermentation was 53.00 g/L and the final pH of the fermentation broth was 6.07. In conclusion, deep eutectic solvent pretreatment was a successful application in the bioconversion of RB to inulinase enzyme.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3128 Keywords Deep eutectic solvent pretreatment inulinase lignocellulosic biomass Aspergillus niger A42 DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.44) Chemical Contents and Activities of Some Commonly Consumed Origanum L. (Lamiaceae) Species

The genus Origanum L. is a well-known genus of the Lamiaceae, and species of this genus are used as spices or herbal teas around the world. The genus contains 42 species and is mainly distributed in the Mediterranean, Euro-Siberian and Iranian-Siberian regions. [1]. Turkey is an important genetic centre of diversity of the genus, which comprises 21 species with three subspecies (24 taxa) and 13 hybrids, of which 25 are endemic [2]. In Turkey, Origanum, Satureja, Thymbra, Thymus, and Coridothymus species, belonging to the Lamiaceae family, are known as thyme “kekik”. Among these species, Origanum is the most widely cultivated and traded species and is commonly used as thyme, especially Origanum onites (İzmir kekiği, bilya kekik), O. vulgare (Istanbul kekiği) and O. majorana [3]. This study aimed to investigate the biological activity and chemical content of the most used Origanum species O. onites, O. vulgare ssp vulgare, O. vulgare ssp. hirtum, O. vulgare ssp. viride, O. majorana, O. syriacum, O. bilgerii, O. munitiflorum by scanning publications (PubMed/Web of Science/Scopus, 20.2.2021). These different reported activities showed that Origanum species are important medicinal plants and herbal treatments for several therapeutic indications.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3133 Keywords Origanum activity secondary metabolites phenolics essential oil DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.45) Some Physical and Chemical Properties of Functional Turkish Delight Produced with Purple Carrot and Inulin
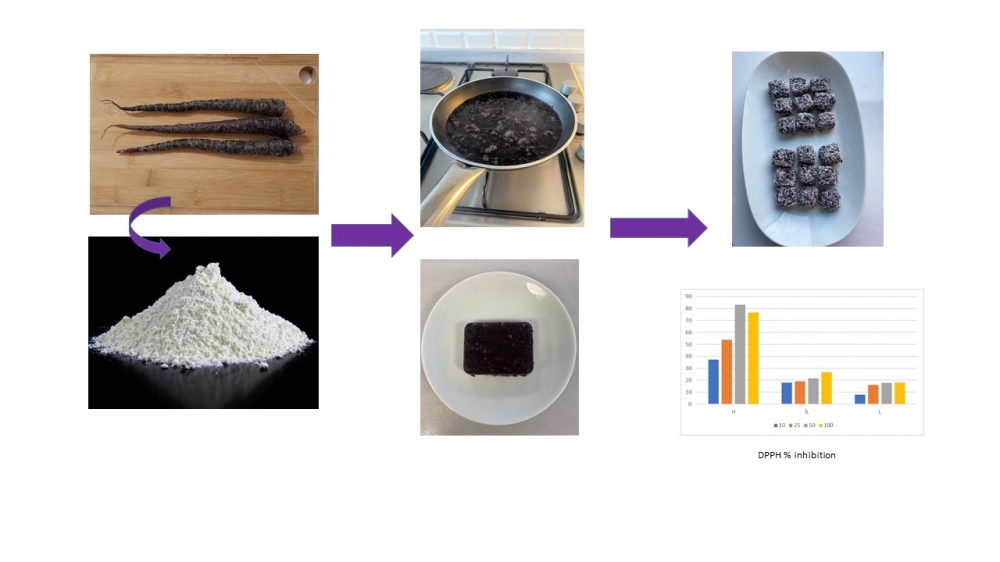
Recently, with people's preference for healthy living and the increasing awareness of healthy products, functional foods have also attracted great interest and demand. Therefore, the food industry is conducting innovative research on the formulation of various products. Purple carrots are rich in natural components such as polyphenols, anthocyanins and carotenoids. These components exert antioxidant effects by fighting free radicals in the body [1]. Inulin is a polysaccharide composed of fructose chains and is indigestible. It is naturally obtained from chicory plants and can be used as a sweetener due to its fiber content, prebiotic effect, low calorie content and functional properties [2], as well as a carbohydrate-based fat substitute with properties such as gel formation, texture, viscosity and water retention capacity [3] The main objective of this study is to produce functional Turkish delight based on purple carrot, which is a functional food source, supplemented with prebiotic inulin. A formulation with purple carrot as the main ingredient was created to produce a Turkish delight. In addition, the proportion of corn starch, raisins, hazelnuts and inulin, other ingredients considered to have an influence on the texture and organoleptic properties of the product, were also taken into account. Thanks to purple carrot, a Turkish delight that is considered to be healthier will be obtained, which is colored without using artificial colorants and sweetened while gaining prebiotic properties with inulin. The Turkish delight was also analyzed in terms of total phenolic value, total anthocyanin value and DPPH radical scavenging activity.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3134 Keywords Turkish delight functional food inulin total phenolic content total anthocyanin content DPPH DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.46) Food Components: Protein with all Aspects
Proteins, as the most important part of the human diet, contribute significantly to human development, structural functions, and biological properties. It is not hard to see that due to these essential roles, proteins also play a crucial role in the food industry. Beyond their dietary properties, proteins are used to create structure (such as foam, elasticity, etc.), enhance taste, aroma, and color in food products [1]. In recent years, consumer preferences regarding dietary proteins have shifted due to health, ethical, and environmental concerns [2]. Consumers are increasingly opting for proteins derived from alternative sources such as plants, fungi, and microorganisms. Another critical aspect of proteins is their bioavailability. If the human body cannot effectively digest and absorb proteins, consuming them becomes meaningless [3]. Despite the significant impact of proteins on food structure and dietary benefits, there is still insufficient information about their interactions with other food components, alternative protein sources, and methods to enhance their bioavailability. In our research, we aim to clarify these gray areas and uncertainties. To address our questions, we conducted a detailed literature search and prepared a presentation summarizing our findings.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3138 Keywords Protein protein-food interactions consumers choices bioavailability DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.47) Detection of Adulteration of Safflower Oil in Sunflower Oil Using Fatty Acid Composition, Triglycerides and Sterols by Principal Component Analysis
Vegetable oils are very important energy sources for human body and their authenticity has become a major issue for producers, consumers, and policy makers. Adulteration, a type of fraud, is performed by addition of cheap oils to the expensive ones. Although many advanced methods have been available to detect the adulterations in vegetable oils, it has still been an important problem for all stakeholders. While olive oil is the most adulterated vegetable oil due to its high price, the others can also be subjected to adulteration depending on their market price. Sunflower oil is one of the most consumed seed oils in the world, but it can also be adulterated with some other cheaper oils. Since both oils have very similar chemical compositions, detection of safflower oil in sunflower oil is a big challenge. In order to prevent consumer fraud, it is crucial to study the traceability of authentic vegetable oil. This study aimed to detect the adulteration of sunflower oil (SFO) with safflower oil (SFFO) using fatty acids, triacylglycerol components and sterol compositions. For this purpose, the blends of SFFO: SFO (2:98, 4:96, 6:94, 8:92, 10:90, 14:86, 18:72, 22:78, 26:74) were prepared and the changes in fatty acids, triacylglycerol and sterol compositions were determined. All findings were also analyzed by Principal Component Analysis (PCA) as statistical technique. As the amount of safflower oil in sunflower oil increased in adulterated samples, there was observed an increase in the amounts of linoleic acid and palmitic acid as fatty acids, LLP and LLL as triglycerides, and campesterol and ∆-7 stigmastanol as sterols.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3139 Keywords Sunflower oil adulteration authentication fatty acids triacylglycerols PCA DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.48) Decreasing Sugar Level by Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Lactose in Fruit Yogurt
Kluyveromyces lactis β-Galactosidase was used to hydrolyze lactose in compound milk that was used for the production of stirred fruit yogurt. Hydrolysis was simultaneously conducted with the fermentation which was done at 38 °C until 4.65 pH was obtained. The sucrose added was decreased to tolerate the sweetness which gained due to lactose hydrolysis. Lactose and sucrose concentration in the recipe issued to study was 4.7% lactose and 7.1% sucrose (w/w). Trial products were produced by reducing the sucrose levels of 5.3% and 5% in yogurt milk with the addition of lactase. For each recipe sensory evaluations were done. For the recipe that contains %5,3 lactose, sweetness showed a non-significant difference between the control sample (α = 0.05). At the end of fermentation, lactose was analyzed, and 97.8% lactose conversion was observed. The percentage of sucrose decreased in the recipe which showed no difference was 25%. As a result, for 1 g of hydrolyzed lactose, 0.4 g of sucrose was decreased from the recipe while obtaining the same sweetness. Besides sensory evaluation, shelf-life analysis was also conducted to see how post-acidification was affected by hydrolyzed lactose. pH values in both the control and trial samples were in the acceptance range at the end of shelf life.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3077 Keywords Fruit yogurt lactose hydrolysis lactose DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.49) Headspace Solid-Phase Microextraction (SPME) Use for the Characterization of Flavored Hookahs
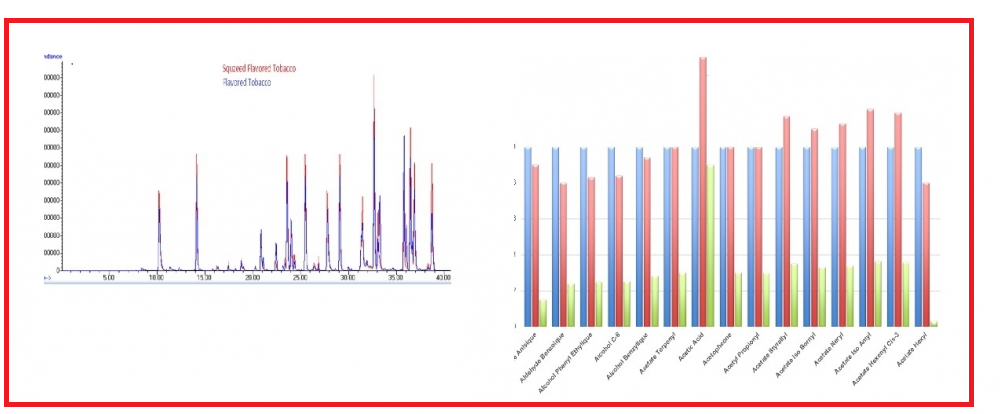
Over the past two decades, there has been an increased interest and usage of tobacco flavor additives [1]. Dried cured tobacco leaves are consumed by various ways such as in cigarettes, cigars, flavoured tobacco, hookah, snuff, chewing tobacco, dipping tobacco and snus. Tobacco is one of the most widely abused substances in the world and is found to be highly addictive for its major alkaloid stimulant-nicotine. The tobacco plant is a part of the genus Nicotiana and of the Solanaceae (nightshade) family. While more than 70 species of tobacco are known, the chief commercial crop is Nicotiana Tabacum [2]. The mechanism of hookah tobacco smoking is unique. First, the tobacco is heated indirectly with charcoal, then the smoke passes through a water bowl and finally is inhaled by the smoker through a rubber hose fitted with a mouthpiece [3]. In this study, we aim to answer the basic question: What are the aromatic substances in flavored hookah? Collection of volatiles using SPME led to the identification of 15 volatile compounds. The final product, hookah, was prepared with a sweetening agent of known formulation at a dosage of 5%. The aroma of the prepared hookah was left to rest for 5 days before being transferred to tobacco. The prepared hookah GC-MS device was read with 2 different methods using the SPME method. A 2 g sample was taken directly from the flavored hookah tobacco prepared in one of these methods into a headspace bottle and entered into the GC-MS device. In the other method, 2 g of flavored hookah tobacco sherbet was squeezed, diluted with 10 milliliters of chloroform, and 300 µl of this solution was injected into the headspace vial. An Agilent 19091n-136 gas chromatograph interfaced directly with an HP-INNO Wax mass selector Detector was used to separate and analyze tobacco headspace components. Unsplit injections were performed at 250 °C using a manual solid-phase microextraction (SPME) syringe equipped with commercially available SPME fibers. Separation was performed using an HP-INNO Wax column (60 m × 250 μm × 0.25 μm). The initial oven temperature was 40°C for 1 min and then increased to 240°C at a rate of 5°C/min. Mass spectrometric detection was performed in scanning mode. As a result of the analysis, the amount and characterization of 15 volatile compounds in tobacco at 5% dosage were determined. Volatile components in the formulation; acetate hexenyl cis-3, acetate hexyl, acetate iso amyl, acetate isobornyl, acetate neryl, acetate styrallyl, acetate terpenyl, acetic acid, acetophenone, acetate propionyl, alcohol benzylique, alcohol c-6, alcohol phenyl ethylique, aldehyde anisique, aldehyde benzoique. In order to determine the characterization of flavored tobacco, GC-MS SPME method study was carried out with two different methods and according to the chromatography results of each of the 6.66% volatile components in the formulation, 93% success was obtained by capturing 6.22% of the volatile components obtained from tobacco sherbet compared to the components obtained from tobacco.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3087 Keywords Flavor hookah GC-MS SPME DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
50) An Acid Hydrolysis Method for the Detection of Twelve Pesticides Approved by TestQual and QS Proficiency Tests
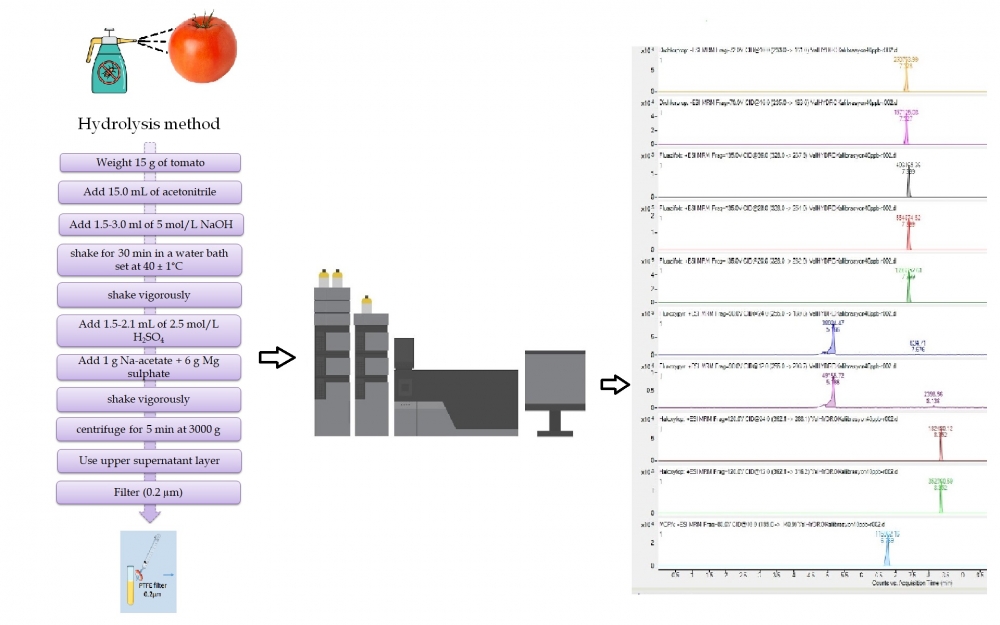
Pesticides with acidic properties, such as 2,4-D, 2,4-DB, acibenzolar-S-methyl, clopyralid, dichlorprop, haloxyfop, fluazifop, fluroxypyr, mecoprop, MCPA, MCPB and quizalofop, could pose health risks, because of their neurotoxicant potentials and adverse effects on endocrine and reproduction systems. Since the use of these compounds are still permitted in several countries, their residues on fresh agricultural commodities should be monitored with proper analysis methods. Unfortunately, determination of their residues is difficult due to their tendencies to form various conjugates with matrix components. Although the QuEChERS method is commonly used for extraction of pesticide residues on fresh vegetables and fruits [1], it is not appropriate for reliable and accurate analysis of the acidic pesticides due to transform their several esters and conjugates [2]. To overcome the drawbacks of QuEChERS method during the analysis of acidic pesticides, addition of a hydrolysis step in sample preparation may be taken into consideration [2,3]. The aim of the current study was to optimize and validate an LC-MS/MS method for the detection of acidic pesticides on fresh foods using alkaline hydrolysis of their esters and conjugates. The multi-residue analysis of 12 active compounds was found compatible with the SANTE/11312/2021 Guidelines. [4]. The quality of the developed method was also testified by both TestQual and QS proficiency tests. The scope of these proficiency tests is the evaluation of the performance of laboratories for the determination of pesticide residues on foods and they provide information to demonstrate the quality of the analysis. Thus, our method was found as reliable and effective to use for the detection of acidic pesticides in fresh foods using LC-MS/MS. In the current method, these pesticides were extracted by using a modified QuEChERS method (AOAC 2007.01) involving the addition of acetonitrile and NaOH together to the sample tube for simultaneous extraction and hydrolysis. The tubes were shaken for 30 min in water bath set at 40°C and then the reaction was neutralized by the addition of H2SO4. After the addition of buffer-salt mixture, the sample was immediately shaken vigorously and centrifuged. Lastly, the supernatant was transferred to vials and tested with LC-MS/MS. PSA-clean up step is not performed in the method. This study was funded with as a research project (grant number ULUTEK STB079417) by Perla Fruit Company.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3088 Keywords Acidic pesticides alkaline hydrolysis analytic method food safety modified QuECHERS method DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.51) Investigation of Anti-Alzheimer Activity of Royal Jelly in an in vitro Human Digestive System Model
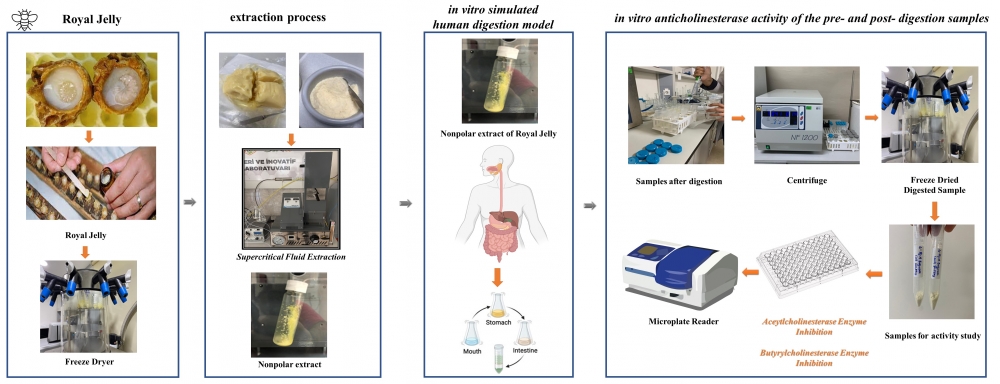
Human beings have never given up on natural products despite the modern medicines that have emerged with the developing technology. On the contrary, with the development of technology, natural products have been examined and the active compounds in their content have succeeded in obtaining better quality natural products and even developed complementary treatment methods. Apitherapy, defined in the Regulation on Traditional and Complementary Medicine published by the Ministry of Health in 2014, involves the complementary and supportive use of bee and bee products in the treatment of diseases. Bee products, including honey, pollen, propolis, royal jelly, bee venom, and beeswax are well-known. Royal jelly is particularly favored due to its rich content. Royal jelly, one of the most valuable bee products, is a viscous nutrient similar to milk produced by worker bees (Apis mellifera L.) to feed queen bees [1]. Royal jelly is an important functional nutrient widely used in commercial products, such as cosmetics and dietary supplements [2]. For this reason, the effectiveness of royal jelly, which is widely used both directly and in mixture with bee products such as honey and pollen, in the digestive process, has been a subject of curiosity and in vivo studies have been reported in this field. It has been reported that royal jelly reduces the activation of substances that reduce cognitive activity in animals given royal jelly [3]. Although there are bioaccessibility studies on many natural products, there are no sufficient studies on in vitro gastrointestinal digestion models of bee products. Bioaccessibility consists of stages, such as digestion of active metabolites in the GI system, absorption, metabolism, distribution to tissues and physiological response. In this study, the anticholinesterase activities of royal jelly extracts before and after in vitro digestion were investigated. Two different extracts rich in polar and apolar compounds were obtained from lyophilized royal jelly by supercritical fluid extraction. The pre- and post- digestion anticholinesterase activities of the apolar extract digested by in vitro human digestion model were determined by spectrophotometric methods using AChE and BChE enzymes.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3147 Keywords Royal jelly anticholinesterase 10-HDA simulated digestion DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.52) Isolation of Bioflavonoid Fustin from the Heartwood of Eurasian Smoketree (Cotinus coggygria Scop.)
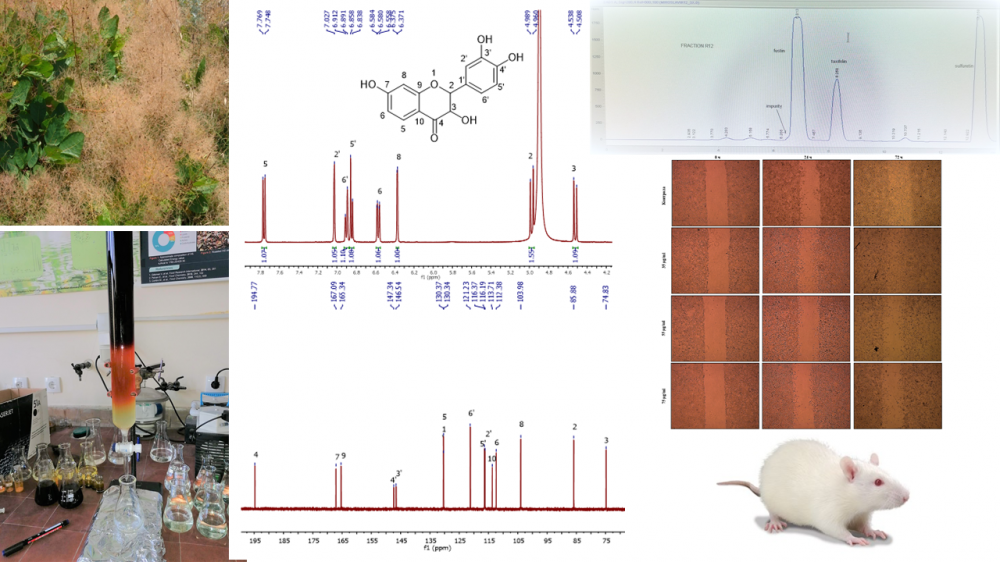
The research on medicinal plants and their biologically active components, and the identification of new molecular targets is relevant to the development of new remedies and functional foods. Eurasian Smoketree (Cotinus coggygria Scop., Anacardiaceae) is a popular medicinal plant with a significant therapeutic potential, widely distributed from Southern Europe to Central China. It has a high content of polyphenols, including the flavanonol fustin, which is poorly studied for biological activity in preclinical experiments. The aim of the present study was to isolate and purify fustin from the heartwood of Eurasian Smoketree (C. coggygria) by appropriate extraction procedure. C. coggygria heartwood was collected at the Protected Area “Deliblato Sand”, Vojvodina province, Serbia, in May 2022. Plant material was identified by Prof. Milan Veljic, Faculty of Biology, University of Belgrade, and compared to Herbarium specimen BEOU 17422 of the Institute of Botany and Botanical Garden in Belgrade, Serbia. The heartwood was air-dried and milled to a fine powder. Quantity of 1 kg of wood powder was extracted three times with 10 L of methylene chloride/methanol 1:1 for 24 h at room temperature and extracts were combined. After evaporation, 76 g of crude extract was fractionated by column chromatography (CC) on Merck silica gel column (750 × 45 mm) with particle size 0.063-0.200 mm, using methylene chloride-methanol gradient solvent system as a mobile phase with increasing methanol content. CC was screened by analytical thin layer chromatography (TLC) on aluminium plates precoated with Merck silica gel 60 F254 (0.25 mm thickness), and the fractions with similar retardation factor (Rf) values were combined. Fustin-rich fractions, detected by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy were eluted with methylene chloride/methanol at approximately 90/10 to 80/20. Those fractions were used for further purification and isolation of fustin by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) following the method described by Novakovic et al. (2019) [1]. Pure fustin was isolated from these fractions by reversed-phase (RP) semi-preparative HPLC on an Agilent Technologies 1100 Series HPLC-DAD with Zorbax Eclipse XDB C18 column (150 × 9.4 mm, i.d. 5 μm) at 254 nm for detection, and water/acetonitrile system using the following program: 0-20 min, 20-37% CH3CN; 20-21 min, 37-50% CH3CN; 21-27 min, 50% CH3CN; and 27-30 min, 50-100% CH3CN. Fustin was purified up to 98% on RP-HPLC using the following program: 0-20 min, 25-40% CH3CN (Rt= 5.1 min). NMR-spectroscopy was used for the structure elucidation. Fustin purity was proved by HPLC and NMR. The NMR spectra were obtained on a Bruker Avance III 500 (500 MHz for 1H; 125 MHz for 13C), in CD3OD as solvent. Chemical shifts (δ) were expressed in ppm and coupling constants (J) in hertz (Hz). As a result, 1.01 g fustin (≥98% purity) was isolated and further used in tests for biological and pharmacological activity on cell cultures and Wistar rats.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3029 Keywords fustin silica gel column chromatography semi-preparative HPLC NMR spectroscopy DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.53) Aronia Melanocarpa Fruit Juice Prevents the Hepatic Impairment in an Experimental Model of Metabolic Syndrome
.png)
Hepatic injury is a feature of the metabolic syndrome (MS) [1]. Fruits of Aronia melanocarpa are distinguished by their high polyphenol content. Aronia melanocarpa fruit juice (AMFJ) has been studied for its potential hepatoprotective effects in animal models of liver damage [2]. The goal of this study was to elucidate the effects of AMFJ on the liver in an experimental model of high-fat, high-fructose (HFHF) diet-induced MS. Fifty rats were allocated to five groups (control, MS, MS+AMFJ2.5, MS+AMFJ5 and MS+AMFJ10). In the course of a 10-weeks, the control group was fed a standard rat diet, whereas the other groups were provided a HFHF diet. Daily oral treatment was performed during MS induction and it included administration of 10.0 ml/kg distilled water (control and MS groups) or AMFJ at doses of 2.5, 5.0, and 10.0 ml/kg (the other three groups, respectively). At the end of the 10th week, liver tissue samples were collected. Hematoxylin-eosin staining was used to explore the histological changes under light microscopy. The immunohistochemical expression of the pro-apoptotic marker Bax, the anti-apoptotic marker Bcl-2 and the pro-inflammatory marker MAC387 was determined by the universal highly sensitive visualization system for antibody detection EnVision FLEX, using rabbit polyclonal Bax and Bcl-2 antibodies, and a mouse monoclonal MAC387 antibody. The expression was assessed semi-quantitatively by determining the expression in fifty cells from each sample in randomly selected fields. For each cell, the intensity of the cytoplasmic expression was assessed as: 0 – lacking, 1 – weak, 2 – moderate or 3 – strong. The mean expression score of each marker was calculated for each group. In addition, Bax/Bcl-2 ratio was calculated to determine the susceptibility of hepatocytes to apoptosis. In MS rats, hepatocytes exhibited steatotic, inflammatory, and degenerative alterations, non-specific granulomas were found and the expression of Bax and MAC387 was markedly elevated (p<0.001 vs. Control group) while Bcl-2 expression was decreased non-significantly. The Bax/Bcl-2 ratio was significantly increased (p<0.001 vs. Control group) indicating a pro-apoptotic phenotype. These alterations were prevented in the AMFJ-treated groups and the hepatic histological and immunohistochemical picture of the treated groups resembled those of the control group. Compared to MS group, the expression of Bax and MAC387 decreased significantly (p<0.001 vs. MS group) and Bcl-2 increased, with a significant effect detected in MS+AMFJ5 group (p<0.01 vs. MS group). Bax/Bcl-2 ratio in all AMFJ-treated groups decreased dose-dependently (p<0.001 vs. MS group) indicating an anti-apoptotic phenotype. In conclusion, AMFJ prevented the inflammatory, steatotic, degenerative and pro-apoptotic changes in the liver, proving the hepatoprotective properties of the juice in a rat model of MS.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3057 Keywords Aronia melanocarpa fruit juice polyphenol metabolic syndrome hepatoprotective liver DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.54) Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Evaluation of the Protective Effect of the Flavonoid Fustin in a Rat Model of Paracetamol-induced Acute Liver Damage
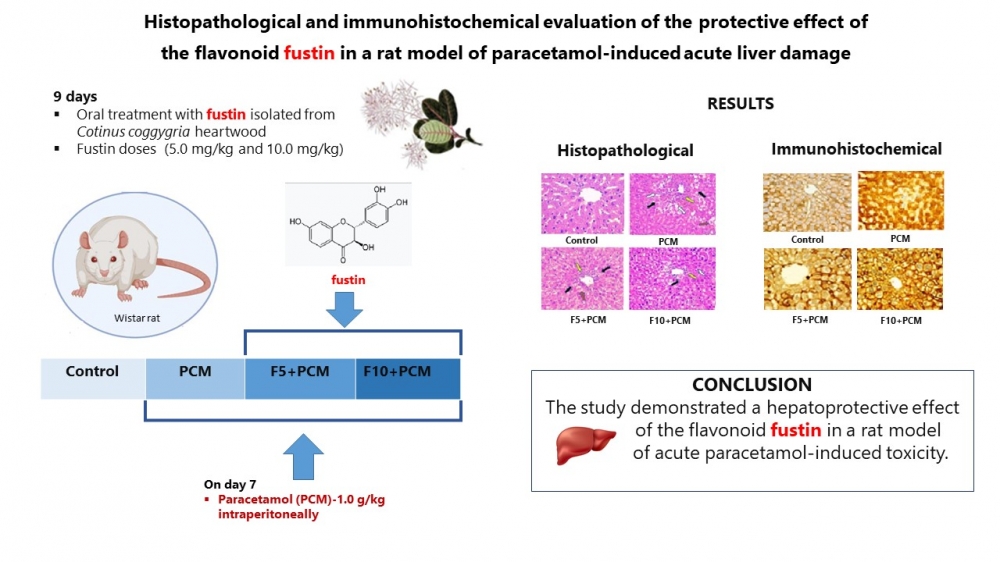
Cotinus coggygria (smoke tree) is a medical plant with health-promoting activities proven in experimental and clinical studies. It has а high content of polyphenols, including, the dihydroflavonol fustin [1]. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the effects of the fustin, isolated from Cotinus coggygria heartwood, on the histopathological and immunohistochemical changes in the livers of rats exposed to acute PCM overdose. Male Wistar rats were allocated to four groups (n=12): Control, PCM, F5+PCM and F10+PCM. The rodents were treated daily orally for 9 consecutive days as follows: groups F5+PCM and F10+PCM – with fustin (suspended in a vehicle) at doses of 5 and 10 mg/kg, respectively; groups Control and PCM – with the vehicle. PCM was injected intraperitoneally (1.0 g/kg) on day 7. On the 10th day of the experiment, liver samples were taken and fixed in 10% buffered formalin. Later, they were embedded into paraffin wax, sliced into tiny sections of 4 µm and stained with hematoxylin and eosin and observed by light microscopy. Histopathological liver changes such as necrosis, steatosis, and ballooning degeneration as well as inflammation and cell apoptosis were scored according to a grading system. Immunohistochemical study of the expression of NF-κB was carried out using a rabbit anti-NF-kB-p100 polyclonal antibody (E-AB-32222; Elabscience, USA) by universal highly sensitive visualization system for antibody detection EnVision FLEX. The results showed that PCM induced extensive and confluent necrosis, degenerative changes of the hepatocytes predominantly in the centrilobular and partly in the intermediate zones of the liver lobules as well as increased number of apoptotic bodies. Hepatocytes with ballooning and fatty degeneration were observed in close proximity with central veins and intermediate zones. Compared to PCM group, in F5+PCM and F10+PCM groups, the liver necrosis, steatosis, ballooning degeneration and inflammation were significantly reduced. The immunohistochemical expression of NF-κB in PCM group was significantly increased (p<0.001 vs. Control). In F5+PCM and F10+PCM groups, NF-κB expression was significantly reduced (p<0.001 vs. PCM group) and localized predominantly in the sinusoids. The mechanisms behind the described hepatoprotective effect of fustin proven by histopathological and immunohistochemical stadies might be a reduction of oxidative stress and enhancement of endogenous antioxidants [2] as well as suppression of the inflammatory signaling pathway of NF-κB.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3060 Keywords Fustin liver paracetamol Cotinus coggygria DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
55) Determination of Thymoquinone in Black Cumin Oil and in Flavor Using High Performance Liquid Chromatography
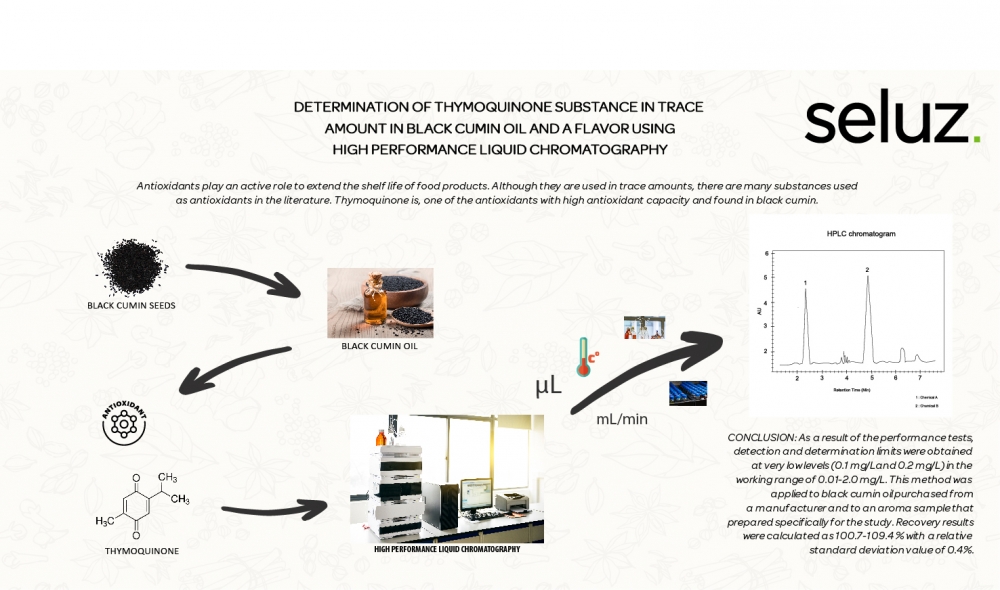
Antioxidants play an active role to extend the shelf life of food products. Although they are used in trace amounts, there are many substances used as antioxidants in the literature. Many substances such as Ascorbic Acid, Alpha-Tocopherol and Thymoquinone are used as natural antioxidants. Thymoquinone, which has a higher antioxidant capacity than these substances used, is determined with the help of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) [1–3]. In this study, High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) method specific to the Thymoquinone substance found in Black Cumin Oil was developed and a recovery study was achieved with real samples. It is aimed to introduce a new method to the literature by optimizing system and method parameters such as flow rate, column temperature, injection volume and mobile phase using HPLC. As a result of the performance tests, limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) limits were obtained at very low levels (0.1 mg/L and 0.2 mg/L) in the working range of 0.01-2.0 mg/L. This method was applied to black cumin oil purchased from a manufacturer and a flavor sample that prepared specifically for this study. Recovery results were calculated as 100.7 – 109.4%, with a relative standard deviation value of 0.4%.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3066 Keywords Thymoquinone antioxidant HPLC flavor black seed oil DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.
56) Comparative Study of the Anti-inflammatory Effect of Ethanol Infusion from Cotinus coggygria Heartwood and the Flavonoid Fustin in a Rat Model of Carrageenan-induced Paw Edema
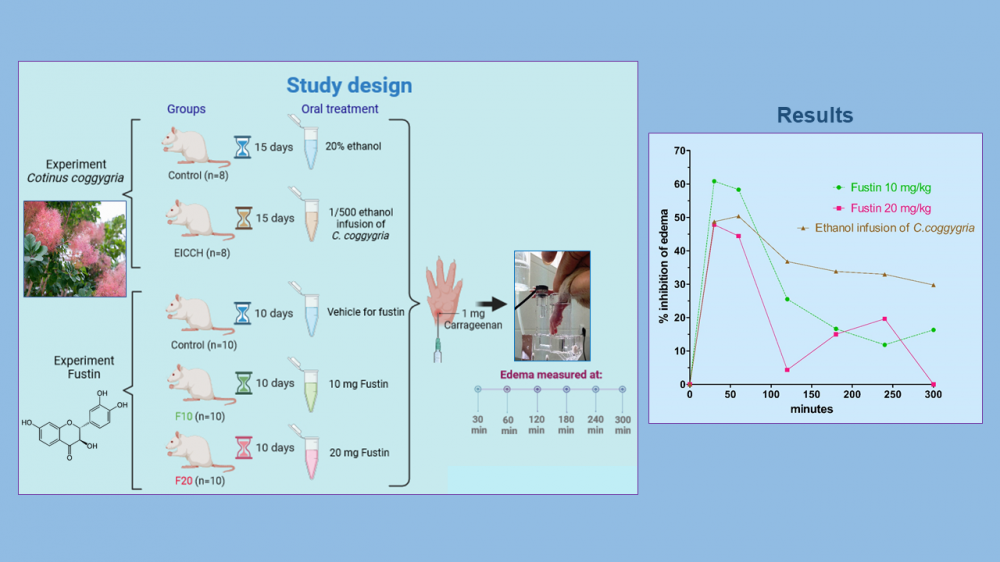
Cotinus coggygria Scop. is a medicinal plant, rich in tannins and flavonoids. The main flavonoid in C. coggygria heartwood is fustin. Studies have shown that C. coggygria extracts and fustin exert anti-inflammatory action [1-2]. Carrageenan-induced paw edema in rats is a widely used model of acute inflammation. The aim of the present study was to compare the percent of inhibition of carrageenan-induced paw edema by 1/500 ethanol infusion from C. coggygria heartwood (EICCH) and fustin at doses 10 mg/kg and 20 mg/kg. Two experiments were performed. In the first experiment 16 male Wistar rats were allocated in two groups: Control and 1/500 EICCH. EICCH group was pretreated orally for 15 days with 10 ml/kg 1/500 EICCH (1 g heartwood in 500 ml 20% ethanol for 20 days extraction) and control animals received 20% ethanol. The second experiment was performed on 30 male Wistar rats allocated in three groups: Control, F10 and F20. Fustin was isolated from C. coggygria heartwood and purified by RP-HPLC [3]. Rats from F10 and F20 groups were pretreated for 10 days orally with fustin at doses of 10 mg/kg and 20 mg/kg, respectively. Distilled water was given to the Control group. After the pretreatment, 1 mg of carrageenan was administered subcutaneously in the left hind paw of the animals. Using a digital plethysmometer LE7500 (Panlab, Barcelona), paw volume (ml) was measured at 0, 30, 60, 120, 180, 240, and 300 minutes after the injection. The percent of inhibition of the paw edema was calculated. The results showed that the percent of inhibition of paw edema in rats treated with EICCH was 48.7%, 50.4%, 36.8%, 33.8%, 33% and 29.7%. at the 30th, 60th, 120th, 180th, 240th and 300th min, respectively. In animals, treated with fustin at the of dose 10 mg/kg, the percent of inhibition of the paw edema was 60.8%, 58.3%, 25.5%, 16.6%, 11.8% and 16.3% at the respective time points. The results of the group, treated with 20 mg/kg fustin, were respectively 47.8%, 44.4%, 4.3%, 15%, 19.6% and 0%. In the fustin experiment the most pronounced inhibition of paw edema occurred on the 30th min, being greater in animals treated with the dose of 10 mg/kg. In comparison, the animals pretreated with 1/500 EICCH demonstrated the greatest percent of inhibition on the 60th min. In conclusion, both ethanol infusion of C. coggygria heartwood and the flavonoid fustin, isolated from C. coggygria heartwood, demonstrated anti-inflammatory properties in carrageenan-induced paw edema and the effect is most significant between 30th and 60th minutes.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3068 Keywords Cotinus coggygria fustin carrageenan-induced paw edema rats DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.57) Current Knowledge of the Health-promoting Effects of Fustin – a Mini-review
.png)
Fustin is a bioactive flavanonol, found in high concentrations in Cotinus coggygria (European smoketree) heartwood and in Toxicodendron vernicifluum (lacquer tree) [1]. However, little is known about its health benefits. The objective of this paper was to summarize the current evidence about the health-promoting effects of fustin, registered in animal and human studies. In order to sum up the available data, a research was carried out in the global database Pubmed for published articles, related to the topic, in the period between 2015 and January 2024 using the keyword “fustin”. A total of 64 articles were found and after careful reviewing, 53 of them were ruled out due to lack of relevance to the topic. Fustin was documented to exert ulcer-preventive [2], anticancer [3], antidiabetic [3], antibacterial [3] and neuroprotective [4] effects in experimental studies. Clinical trials were scarce and anti-fibrotic effect was the only pharmacological activity documented in one human study [5]. These effects were ascribed to the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of the flavonoid [6]. Additional studies are required to investigate the health-beneficial effects of fustin both in experimental and clinical settings.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3069 Keywords Fustin flavanonol health-promoting DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.58) Anticancer Action of the Bioflavonoid Fustin in a Highly Metastatic Colon Cancer Cell Line
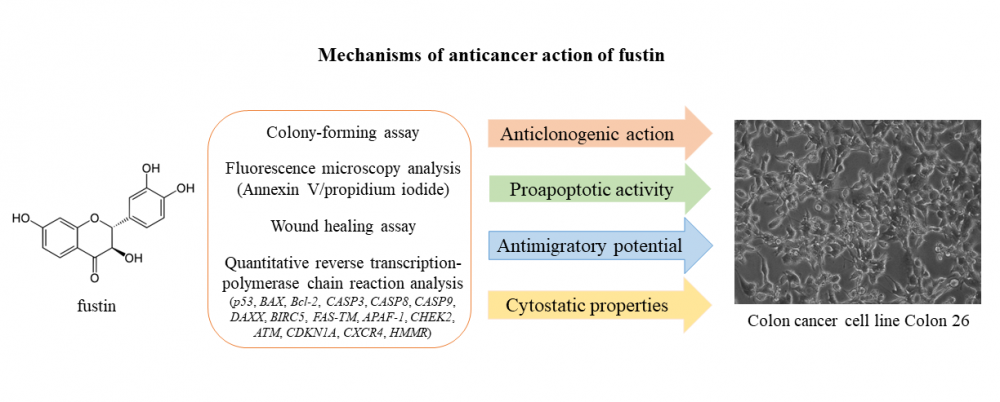
Colon cancer is among the most common and lethal cancer types worldwide. The disease is very heterogeneous and is attributed to the accumulation of genetic and epigenetic alterations affecting specific genes involved in the regulation of cell growth, proliferation, adhesion, and survival. About 20% of patients with colon cancer are diagnosed with distant metastases which is associated with worse prognosis and survival. The search for novel natural therapeutic agents with higher effectiveness against the diseases, and milder side effects is of great interest in oncopharmacology. Medicinal plants represents valuable source of biologically active compounds with a wide range of pharmacological activities. Our previous study detected antiproliferative properties of fustin isolated from the heartwood of Cotinus coggygria Scop. against the highly metastatic colon cancer cell line Colon 26 [1]. The aim of the present work was to investigate some of the molecular mechanisms underlying the anticancer properties of fustin in colon cancer cells. For this purpose, we applied clonogenic assay to evaluate single cell capability to form a colony, fluorescence microscopy analysis after staining with Annexin V/propidium iodide to assess the proapoptotic properties of the flavonoid, wound healing assay to study antimigratory potential of fustin and quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis of the relative expression levels of genes associated with the cell cycle control, programmed cell death, and metastasis. The obtained results revealed that fustin significantly suppressed the colony-forming potential of Colon 26 cells after treatment for a period of 7 days, induced early and late apoptotic events in cancer cells and considerably inhibited cellular migratory properties, with a statistically significant decrease in cell motility compared to the untreated control observed at the 72nd hour of treatment. Transcriptional analysis of gene expression supplied information on some molecular pathways of the anticancer action of fustin and provided directions for future more detailed research.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3070 Keywords Fustin Cotinus coggygria Scop colon cancer cell line anticancer activity DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.59) Effects of Fustin on Nuclear Factor Kappa B Expression in a Rat Model of Trinitrobenzene Sulfonic Acid-induced Colitis
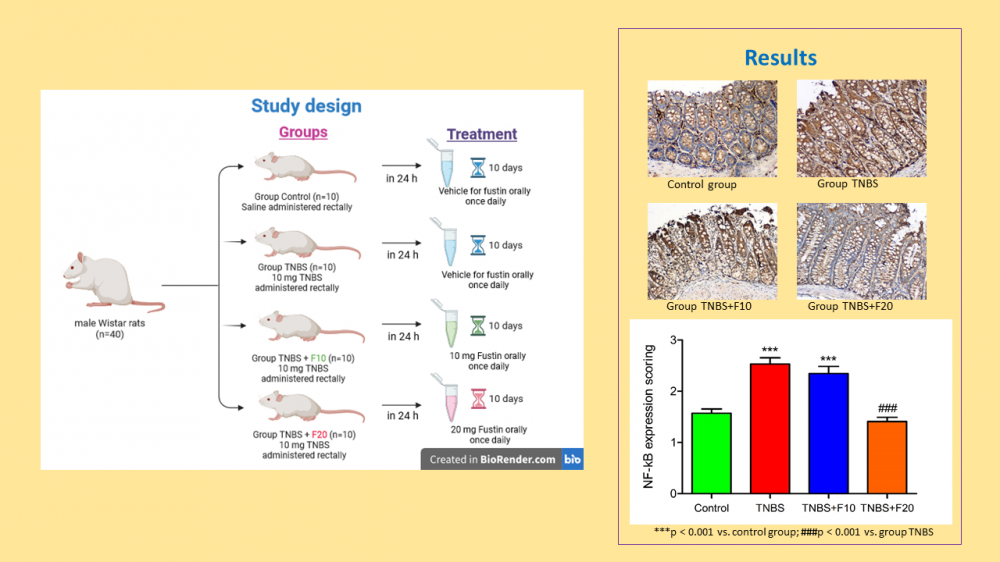
Cotinus coggygria is a shrub, rich in tannins and flavonoids, used in traditional medicine [1]. Nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) is a crucial modulator of inflammatory reactions and immune responses [2]. This study aimed to evaluate the effect of the flavonoid fustin on the immunohistochemical expression of NF-κB in a rat colitis model induced by trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid (TNBS). Fustin was isolated from Cotynus coggygria heartwood and purified [3]. Forty male Wistar rats allocated to four groups: Control, TNBS, TNBS+F10, and TNBS+F20. In groups TNBS, TNBS+F10, and TNBS+F20, colitis was induced by rectal administration of 10 mg TNBS. Treatment began 24 hours after colitis induction and continued for 8 days. Fustin at a dose of 10 mg/kg and 20 mg/kg prepared as a suspension was given orally to TNBS+F10 and TNBS+F20 groups, respectively, while the vehicle for fustin was given to groups Control and TNBS. On the 10th day of the experiment, samples of colon tissue from the site of injury were taken and processed for immunohistochemical investigations. Tissue sections, 4 µm thick, were placed on silanized slides. NF-κB expression was determined using a rabbit anti-NF-kB-p100 polyclonal antibody (E-AB-32222; Elabscience, USA), diluted 1:200, following the protocol for universal highly sensitive visualization system for antibody detection EnVision FLEX. Immunohistochemical evaluation was performed semi-quantitatively in 50 cells of each probe using the following score: 1 – no cytoplasmic staining, 2 – weak staining, 3 – moderate staining, 4 – strong staining. The average intensity of the immune reaction was calculated using the formula: number of cells of each type x corresponding coefficient (1, 2, 3 or 4) x total number of cells-1. The results showed that NF-κB immunohistochemical expression score in the control group was 1.57±0.57, while in TNBS group it was significantly higher (2.53±0.86; p<0.001 vs. Control). The antibody expression score of TNBS+F10 group (2.35±0.96) was slightly reduced. The score of TNBS+F20 group (1.41±0.57) did not differ significantly from the control value and was significantly lower (p<0.05) in comparison with that of TNBS group. In conclusion, fustin at a dose of 20 mg/kg reduced the proinflammatory transcription factor NF-κB expression which might contribute for its ameliorative effect against TNBS-induced damage.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3071 Keywords NF-κB colitis trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid fustin DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.60) Olive oil and Cretan - Mediterranean diet: The importance of olive oil constituents, and mainly polyphenols, in human health - The Redox system.
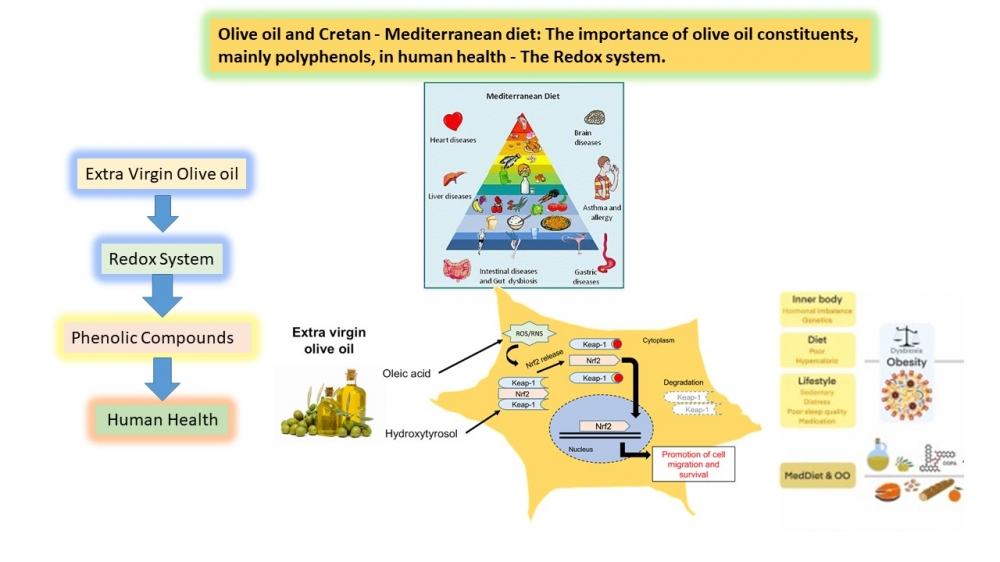
The Mediterranean diet, a term that was coined by Ancel Keys back in 1960, is one of the most studied and well-known dietary patterns worldwide. Descriptions of the traditional MedDiet have reflected food patterns typical of Crete, a part of the rest of Greece, and southern Italy in the early 1960s. Variations of the MedDiet exist but have been less well described in other parts of Italy, France, Lebanon, Morocco, Portugal, Spain, Tunisia, Turkey, and elsewhere in the Mediterranean region. MedDiet is characterized by a high intake of olive oil (especially virgin and extra virgin olive oil) used as the principal source of fat. The significance of macro- and micro-components of extra virgin olive oil, such as the oleic monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) and the phenolic compounds, will be discussed. Mechanisms of phenolic compounds preventing oxidation, extending shelf life, imparting bitterness and astringency, and stimulating the sensory properties of extra virgin olive oil will be explained. The preventive aspects of phenolic compounds against various chronic diseases, including coronary heart disease, cancer, and diabetes, are highlighted. There will also be a reference to the bioavailability and bioaccessibility of these biofunctional compounds, exploring their modulating effects on oxidative stress, telomere length, and successful aging through redox function and epigenetic modulation capacities. The adoption of healthy and sustainable diets and the transition to sustainable food systems are of principal importance in order to counteract the double burden of climate change and noncommunicable diseases. The Mediterranean diet (MD), widely recognized as a healthy diet, is also considered a resource with higher diversity in food plants and is sustainable with reduced land use, water use, eutrophication potential, and greenhouse gas emissions.
DOI Olive oil and Cretan - Mediterranean diet: The importance of olive oil constituents, and mainly polyphenols, in human health - The Redox system Keywords Olive oil bioactive compounds DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.61) Recombinant Production of a-Amylase Enzyme Used in Fruit Juice Production
Fruit juice production, which is one of the agriculture-based industries in our country, has become an industry branch that develops and gains importance day by day. High production speed, quality and stable product are among the most important parameters in fruit juice production. Pectic substances, starch, polyphenols, proteins etc. cause turbidity in fruit juice. These colloids must be broken down to their small molecules for a clear and stable juice production. For this purpose, pectinase and amylase group enzymes are widely used. The fact that these enzymes are not produced in our country leaves the producer dependent on abroad for accessing the enzyme, but also increases the costs of fruit juice production. In this study, a-amylase enzyme was produced under the control of inducible SNT5 promoter in methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris extracellularly. Shake flask experiments were conducted to evaluate the effect of pH (pH 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7) and temperature (20°C, 24°C and 28°C) on the production of a-amylase. The culture was harvested 120 hours later, the supernatants were analysed by SDS-PAGE, the enzyme activity and total protein concentration were also measured. The results showed that the maximum enzyme activity and protein concentration were obtained at 24°C and pH 7 conditions. The highest a-amylase activity and total protein concentration were determined as 288 U/mL and 623 mg/L, respectively.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3078 Keywords a-amylase Pichia pastoris SNT5 promoter DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.62) Investigation of Analytical Data and Sensory Profiles of Flavour Components of Mandarin Fruit from Different Regions
Mandarin (Citrus reticulata) is a fruit species belonging to the Citrus family (Rutaceae) that grows in temperate climates. It is characterized by its thin peel and easy peeling. Mandarin, which is orange and yellow in color, has a fleshy and juicy structure. Relatively little is yet known about the unique fruit quality traits of tangerines or the great variation in these traits among various natural subgroups and mandarin cultivars. For this reason, tangerines from different regions were used in our study. There are many varieties of mandarin grown in different regions, such as tangerina, nova, kinnow, fremond, klausellina, robinson, okitsu, satsuma, ankor, clementine, fortune, local, lee, fairchild marisol, minneola, ortanik, black, ovari. Each of them has different tastes and characteristic structures. In this study, Murcott, Okitsu and Satsuma mandarin varieties, which are more preferred for consumption, were examined and 23 different compounds were analyzed using the GC-MS/SPME method. SPME, or solid phase microextraction, is an analysis method that can be used in the determination of volatile flavour substances that are generally found in trace amounts in food products. The loss of these volatile substances can be observed in analyzes performed by various separation methods such as distillation and extraction. SPME analysis does not use solvents, and it is a method that can provide a single-step analysis by bypassing procedures that require multi-stage and complex equipment such as sample preparation, extraction, and concentration. When the analysis data were examined, it was seen that Okitsu mandarin had the highest limonene amount compared to Murcott and Satsuma mandarin, and Satsuma mandarin had the highest gamma terpinene amount compared to Okitsu and Murcott mandarins. Within the scope of this data, Satsuma has a more citrus profile, while Okitsu has a sweeter profile. Murcott mandarin has a higher amount of Valencene and beta-elemene, so it has a peely and sweet note. The analysis results were supported by sensory analysis. Panelists cited the intensity of each feature using a scale of 0 to 10. With this method, a detailed analysis of the peely, citrus, sweet, herbal, terpenic, floral taste and odor parameters and profiles of the tangerine fruit was conducted with 20 trained panelists.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3079 Keywords Mandarin flavor chemicals DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.63) Determination and Quantification of the Amitraz in Complex Matrix
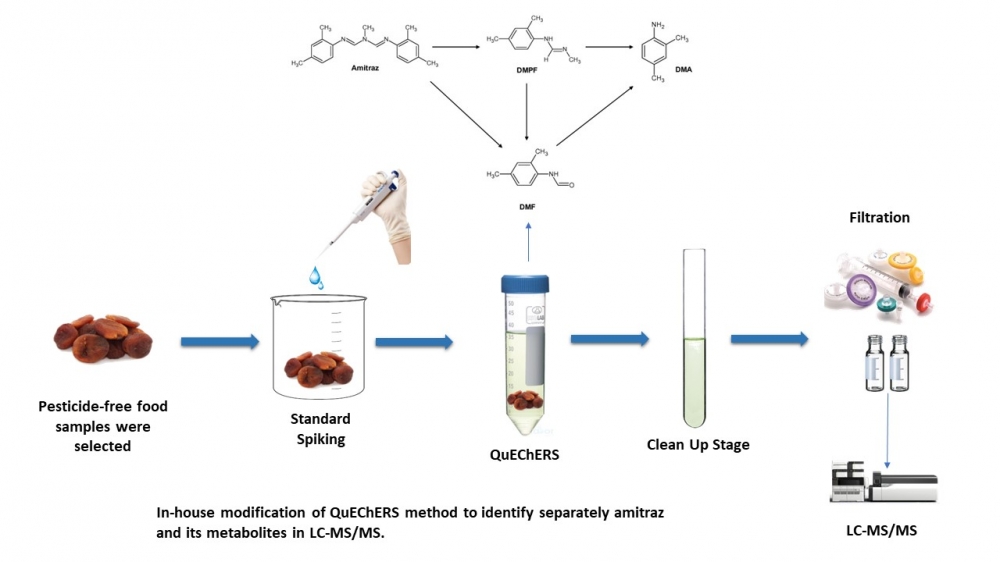
Amitraz is a broad-spectrum insecticide and acaricide used in veterinary medicine, agriculture, and horticulture. It belongs to the formamidine pesticide family, most of which (like chlordimeform, formparanate, and chlormebuform) are no longer in use, except amitraz and formetanate, which are particularly effective against pests resistant to organophosphates and carbamates. An accurate method was developed for the determination of amitraz and its metabolites N-[2,4-(dimethylphenyl)-.N-methylformamidine (DMPF), 2,4-dimethylformamidine (DMF), 2,4-dimethylaniline (DMA). There are two types of methods for the determination of amitraz. The first one is multi-residue methods which incorporate amitraz together with other pesticides, focused on the determination of only parent amitraz. The other methods are suitable for the direct determination of amitraz and/or its degradation products. However, most of these methods include the determination of amitraz and its only well-known metabolite DMA; other methods include the indirect determination of amitraz by hydrolyzing amitraz to its final metabolite DMA. This study aims to determine whether amitraz, which is not approved for use in apricot food matrices, is degraded in the pesticide mixture and is detected at incorrect concentrations as a result of enriching the concentration of its metabolites, using LC-MS/MS in terms of the EN 15662:2018 standard method and the QuEChERS method. Quantification calculated using matrix-matched standards calibration by using three orders of magnitude. This work reports the use of QuEChERS method for qualification of amitraz and single in house modified method for quantification of amitraz and its metabolites in apricots [1–3].
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3082 Keywords Amitraz pesticide QuEChERS DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.64) Bioethanol Production from Different Food Wastes
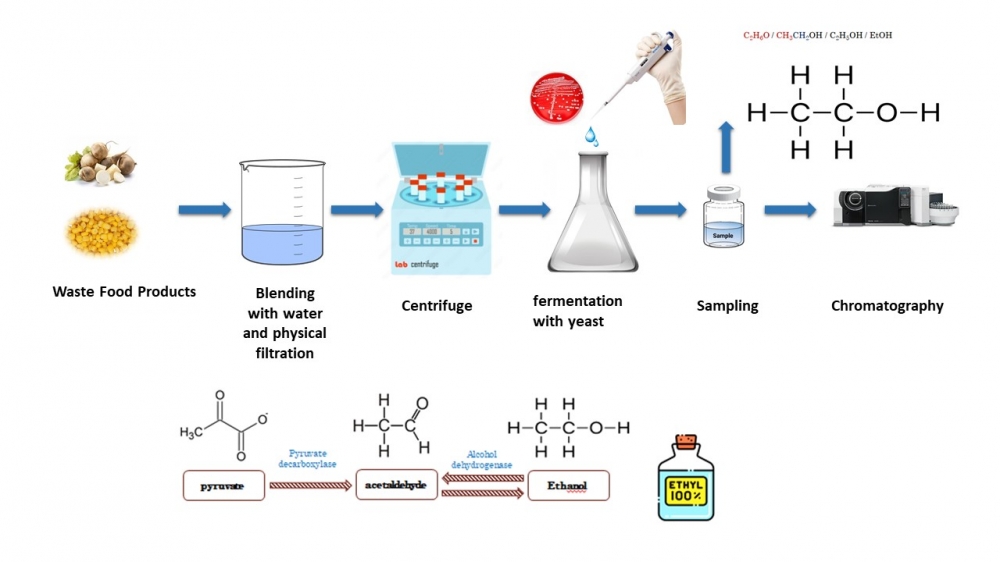
Ethanol is commonly used as an industrial raw material in various fields such as food, medicine, and pharmacy [1]. Chemically, ethanol and bioethanol are the same molecules. The term bioethanol is used in the literature to indicate ethanol obtained biologically from biomass, as opposed to synthetically from fossil fuels [2]. Ethanol is a colorless, highly flammable liquid fuel that mixes well with water and gasoline [3]. Bioethanol can be used as a pure gasoline substitute or mixed with gasoline. It has been reported that many microorganisms, including bacteria, yeasts, and filamentous fungi, can ferment lignocellulosic hydrolysates to produce ethanol. Among them, E. coli, Zymomonas mobilis, S. cerevisiae, and Pichia stipitis are the most relevant ones for lignocellulosic ethanol bioprocesses. These microorganisms have different natural properties that can be considered as advantageous or disadvantageous in ethanol production processes from lignocellulosic biomass [4]. Saccharomyces cerevisiae is the most preferred producer of bioethanol, as it can work in a wide pH range and is resistant to mutation. Since agricultural and industrial wastes reduce the cost of raw material in fermentation processes, many studies have focused on using these substrates as potential for bioethanol production. Like in most biotechnological processes, researchers have investigated ethanol production using various regional agricultural products and waste to reduce product costs and also to produce high-value-added products from waste. This presentation will explore resarch focused on obtaining high-value ethanol from various wastes.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3084 Keywords Bioethanol boethanol production food waste Saccharomyces cerevisiae DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.65) Developmenet of Aromatic Components – Rich Extract Specially for Chocolate Products from Hazelnut Grows Giresun, Türkiye with Supercritical CO2 Extraction
Türkiye is the largest producer and exporter country of various types of hazelnuts in the world, contributing to approximately 70% of the total world production. Among the 18 hazelnut varieties grown in Türkiye; these hazelnuts are classified as premium quality due to its high oil content, unique taste, and aroma [1] Different aroma extraction methods were used successfully in the seeds [2]. Taste and aroma of hazelnut extracts are caused by their taste-active components (free amino and phenolic acids, sugars, organic acids, and condensed tannins ) and aroma-active components (ketones, aldehydes, pyrazines, alcohols, aromatic hydrocarbons, furans, pyrroles, terpenes, and acids) [1]. Filbertone and pyrazines are components of extracts that causes the characteristic odor of roasted hazelnuts [3]. Hazelnut provides a distinctive and unique flavour as a food ingredient. In this study, it was aimed to examine the chemical content of extracts obtained by supercritical CO2 extraction that carried out under different conditions by using GC-MS and to compare these extracts with each other as sensory. Analytical and sensory evaluation of the obtained roasted hazelnut extracts was achieved by an evaluation team consisting of flavorists. When aromatic component profiles were analyzed by GC-MS and taste and odor profiles were compared in the supercritical CO2 extraction studies, the best results were achieved at temperature 40 oC, pressure 150 bar and extraction time 150 minutes.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3085 Keywords Rosted Hazelnut supercritical CO2 extraction flavour GC-MS DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.66) Determination of Thymoquinone Substance In Trace Amounts In Black Cumin Oil And In A Flavor Using High Performance Liquid Chromatography
Antioxidants play an active role to extend the shelf life of food products. Although they are used in trace amounts, there are many substances used as antioxidants in the literature. Many substances such as Ascorbic Acid, Alpha-Tocopherol and Thymoquinone are used as natural antioxidants. Thymoquinone, which has a higher antioxidant capacity than these substances used, is determined with the help of High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). [1–3] In this study, a High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) method specific to the Thymoquinone substance found in Black Cumin Oil was developed and a recovery study was achieved with real samples. It is aimed to introduce a new method to the literature by optimizing system and method parameters such as flow rate, column temperature, injection volume and mobile phase using HPLC. As a result of the performance tests, limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) limits were obtained at very low levels (0.1 mg/L and 0.2 mg/L) in the working range of 0.01-2.0 mg/L. This method was applied to black cumin oil purchased from a manufacturer and a flavor sample that was prepared specifically for this study. Recovery results were calculated as 100.7 – 109.4%, with a relative standard deviation value of 0.4%.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3086 Keywords Thymoquinone Black Seed Oil Antioxidant Flavor HPLC DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.67) Evaluation of Time Dependent Oxidation of Some Berry Flavors with CUPRAC Method
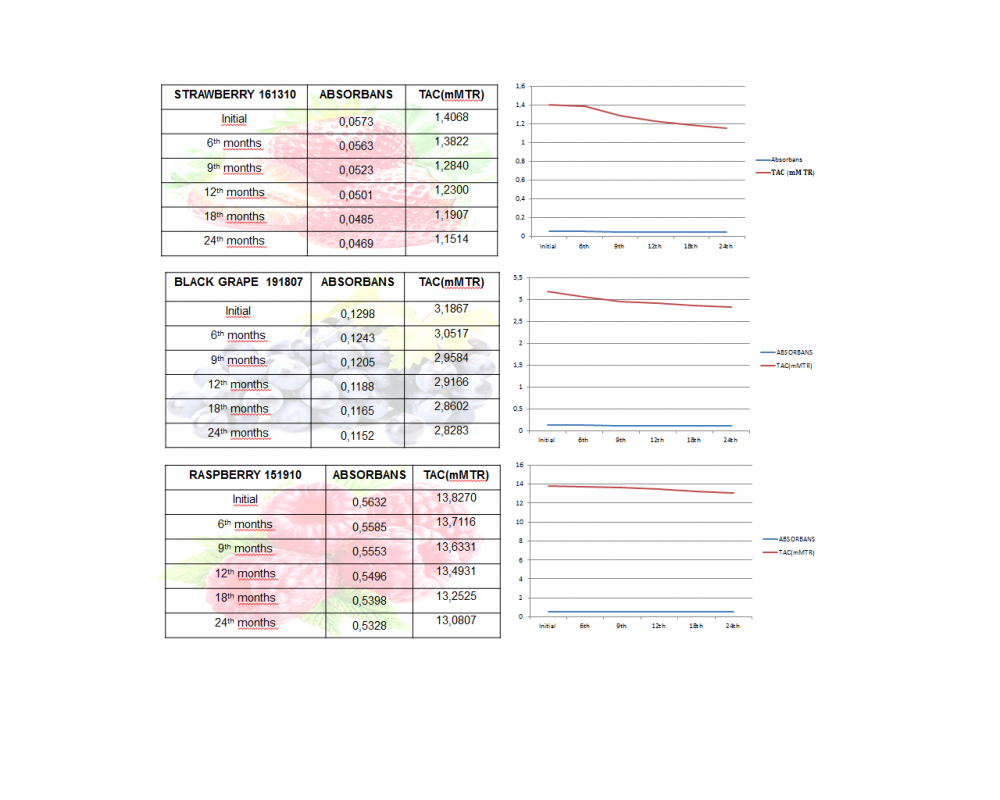
Flavors are components with smell and taste, which are formed by formulating chemical molecules that are more than one volatile or non-volatile. These include aldehydes, ketones, ethers, esters, etc. chemicals as main components. The purpose of this study is to examine the alteration of berry group flavors shelf lives due to oxidation using the CUPRAC method. In the Turkish Food Codex, flavors are defined as 'flavoring substances, flavor preparations, heat treatment flavors, incense flavors that are not intended for consumption, are used to give taste and/or scent, or are added to foods for modification purposes'. It is expressed as a product made or composed of flavor precursors or other flavors or mixtures thereof. In aromas, components with antioxidant capacity are used to preserve the odor and taste characteristics of the aroma in a more stable manner and to ensure that the odor and taste characteristics remain intact throughout the shelf life, depending on the type of the final product [1]. In this study, antioxidant-free flavors were selected and their antioxidant capacities were examined. Three berry flavoring groups named strawberry 161310, black grape 191807, raspberry 151910 were selected. Of these selected flavorings, 6-9-12-18 and 24. Months aging was performed using a microtest MIT-120 device under a light intensity of 6000 lux and 40 °C. The antioxidant capacities of the aged flavorings were determined by CUPRAC method. For the CUPRAC method, 10-2 M Cu2+, 1 M NH4Ac, 7,5×10-3 M neocuproin solutions were prepared with EtOH. 1 mL of each solution was taken, and 3 mL of the mixture was made and 1.1 mL of EtOH antioxidant mixture was added to this mixture. The resulting mixture is infused for 30 min. It was kept at room temperature and absorbance values were measured with UV-VIS spectrophotometer device at 450 nm [2]. The antioxidant capacities of the aromas determined by the CUPRAC method were examined with a UV-VIS device depending on the oxidation of the raw materials. Berry groups contain monoterpene and sesquiterpene volatile components such as limonene and linalool, which undergo oxidation. Terpenes, which are unsaturated hydrocarbons containing one or more C=C double bonds, are highly reactive with various oxidation products such as ozone, nitrate, and hydroxyl radicals. Terpenes have been recognized as important precursors of photochemical ozone formation [3]. As a result of the study, it was observed that the decrease in antioxidant capacities was not high in the berry groups, as seen in the graphs. It has been observed that terpene compounds in berry groups are not as easily oxidized as in citrus groups under the influence of gases in the air, temperature and light. Terpene compounds should not be exposed to factors that cause oxidation. Otherwise, oxidized taste profiles will occur, causing loss of taste and smell.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3090 Keywords Flavors Antioxidant UV-VIS CUPRAC DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.68) Cytotoxic Activity of Lactarius salmonicolor R.Heim&Leclair Apolar Extract Against Most Common Cancers and Determination of Cytotoxic Compounds Using GC-MS and Chemometric Techniques
Mushrooms have become increasingly important in human nutrition due to their nutritional, pharmacological, and organoleptic properties [1]. Edible mushrooms are rich in minerals and have high water, protein, fiber, and carbohydrate content as well as low fat/energy levels, making them an excellent food for low-calorie diets [1]. Therefore, mushrooms are valuable foods because of their content. People prefer wild edible mushrooms for their aroma content and valuable nutrients, including unsaturated fatty acids, fibers, carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins, and minerals [2,3]. Mushrooms are well-researched for their chemical composition and biological activities, including anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antiviral, antibacterial, antioxidant, anti-hypercholesterolemia, anti-hypertension, and immunomodulatory activities [1,4,5]. Fungi have attracted a great deal of attention in the last two decades, as many of them show cytotoxic activity and play an important role in the treatment of diseases such as cancer [5]. The aim of this study was to investigate the cytotoxic activity of petroleum ether extracts of Lactarius salmonicolor against colon (CaCo-2), lung (H1299), human breast (MCF-7) cancer cell lines, and kidney (HEK293) healthy cell lines by MTT assay and to determine cytotoxic ingredients using GC-MS and chemometrics. Subsequently, activity-guided fractionation was performed with the support of GC-MS elucidation. The percentage amounts of 36 common compounds elucidated from one extract, four fractions, eight sub-fractions, and their cytotoxic activity data against four cancer cell lines were subjected to Principal Component Analysis to reveal the cytotoxic compounds responsible for the total cytotoxic activity. The score and loading graphs of PCA monitored the cytotoxic compounds. In conclusion, the cytotoxic activity of the extract is due to the presence of azelaic acid, serine, sterols, and desmosterol, as well as the fatty acids, particularly long-chain fatty acids. In other words, the cytotoxic activity may be due to its polyunsaturated fatty acids and steroidal compounds.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3093 Keywords Lactarius salmonicolor edible mushroom cytotoxic activity GC-MS steroids principal component analysis (PCA). DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.69) The Bioflavonoid Fustin, Isolated from Cotinus coggygria Heartwood, Restores Intracellular Activity of Superoxide Dismutase in a Rat Model of Trinitrobenzensulfonic Acid-induced Colitis
The food chemistry analyses, and preclinical in vivo tests are powerful assessment tools for developing innovative functional food products and therapeutic agents from natural sources. The Eurasian Smoketree (Cotinus coggygria Scop.) is a popular medicinal plant in the Balkan and Anatolian traditional medicine. Due to its high content of flavonoids with well documented in vitro antioxidant activity, it has a significant therapeutic potential in combating chronic diseases. The bioflavonoid fustin, present at high concentration in C. coggygria heartwood, is poorly studied. The aim of the present study was to explore the antioxidant effects of the bioflavonoid fustin, isolated from C. coggygria heartwood, in a rat model of trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced colitis that mimics the signs and symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease. Fustin was isolated and purified from C. coggygria heartwood by silica gel column chromatography, reversed-phase semi-preparative high-performance liquid chromatography and by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Forty male Wistar rats (weight 150-250 g) were used, allocated to four groups (n=10): Control, TNBS, TNBS+F10 and TNBS+F20. Colitis was induced by rectal application of TNBS following the procedure described by Morris et al. [1]. Oral treatment by an orogastric cannula was initiated 24 hours after colitis induction and lasted for 8 days. Fustin, at doses of 10 mg/kg and 20 mg/kg, prepared at a volume of 10 ml/kg as a suspension in distilled water and Tween 80, was administered to groups TNBS+F10 and TNBS+F20, respectively. Groups Control and TNBS received the vehicle at a volume of 10 ml/kg. On the 10th day of the experiment, 24 hours after the last treatment, the animals were sacrificed under diethyl ether anesthesia. Colon tissue with weight of 1 g was mixed with 10 mL 50 mM Tris/HCL buffer (pH=7.4) and was homogenized for 3-4 min at 3500 rpm. The homogenate was centrifuged at 4°C and 3000 rpm for 15 min. The supernatant was collected, and the activity of the endogenous antioxidant enzyme superoxide dismutase (SOD) was measured by colorimetric assay using the Superoxide Dismutase Activity Kit (Product No. 19160, Sigma-Aldrich) and multi-mode microplate reader (Synergy 2, BioTek Instruments, USA). Data were analyzed by GraphPad Prism 6 using One-way ANOVA, followed by Dunnett's multiple comparisons test. SOD activity results are given as Mean of its inhibition activity (%) ± standard error of the mean (SEM). The results showed that SOD activity was significantly reduced (p<0.01) in the TNBS group (4.44±12.20%) compared to that of the Control group (62.64±7.45%). The activities of SOD in TNBS+F10 group (39.41±13.96%) and TNBS+F20 group (40.10±10.77%) were not significantly different from the control value. In conclusion, Fustin treatment restored the colon activity of SOD in the experimental TNBS-induced colitis. This antioxidant effect of fustin might be a result of its ability to increase the intracellular antioxidant defense most probably by gene expression regulation.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3097 Keywords Fustin antioxidant defense superoxide dismutase trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid colitis DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.70) A Candy from Orange Peels Using Osmotic Dehydration
When considering the most studied topics in the field of food today, it can be observed that studies have increased in two main categories. One of them is the suitable process of by-products that are suitable for consumption but cannot be evaluated in terms of content, the other is the applications and processes to extend the shelf life of foods. Osmotic dehydration, the immersion of fruits in high concentration solutions to remove water, is a process that results in water loss. The balance of soluble solids transferred to fruits with the removed water is a preferred method for extending the shelf life of fruits, allowing the development of natural taste and the preservation of color, and providing protection in terms of microbiology. In recent times, studies have been carried out on the drying of fruits, vegetables, etc. foods with the osmotic dehydration method to increase shelf life. The essence of this method is the preservation of the freshness of fruits and vegetables by immersing cellular materials containing water in an osmotic solution. This results in the development of intermediate moisture products with lower water activity obtained by osmotic gain and water loss, which also supports improvements in taste profile. Chemical, physical, and biological activities that damage foods are significantly reduced during the process; thus, the shelf life of food products is extended. Osmotic dehydration is influenced by various factors such as osmotic agent, time and temperature, soluble solid concentration, solution/sample ratio, agitation, and material geometry. When evaluating food industry wastes, it is anticipated that the most waste occurs in fruit processing. Turkey is one of the rare countries where different varieties of fruits can be grown thanks to its fertile soils, vast agricultural areas, and favorable seasonal conditions. According to the Agricultural Economy and Policy Development Institute, oranges are the most grown and processed fruit. While 92 million tons of citrus fruits were produced worldwide in the 2019/20 production season, orange accounts for 50% of total citrus fruit production. In the 2020/21 production season, 9,500 tons of orange juice were produced from the oranges grown in Turkey. However, the peels were evaluated as having low added value. In this study, the drying process was carried out using the osmotic dehydration method on orange peels to obtain confections. Two different processes were studied, and the first process was carried out with partial revisions to the method applied in the literature [5]. In the second process, an acidity removal process was applied for better taste and texture results due to the bitterness of the orange. According to the results obtained, while no significant difference was observed in color, appearance, brix, and process time, when the taste parameter was evaluated, the process made by removing bitterness was deemed consumable by the panelists. As a result of the study, a solution of 1/2 sugar, 8-10 hours of time, and temperatures of 50-60°C were found to be suitable; especially, it was determined that the pre-treatment of removing bitterness should be performed. As a result of this study, the by-product of the process was transformed into a value-added product.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3098 Keywords Orange peel osmotic dehydration infusion drying DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.71) Development of Sausage Formulation and Optimization of Process Parameters Compared to Cellulose Casing, Utilizing High Moisture Barrier Polyamide Casing as an Alternative
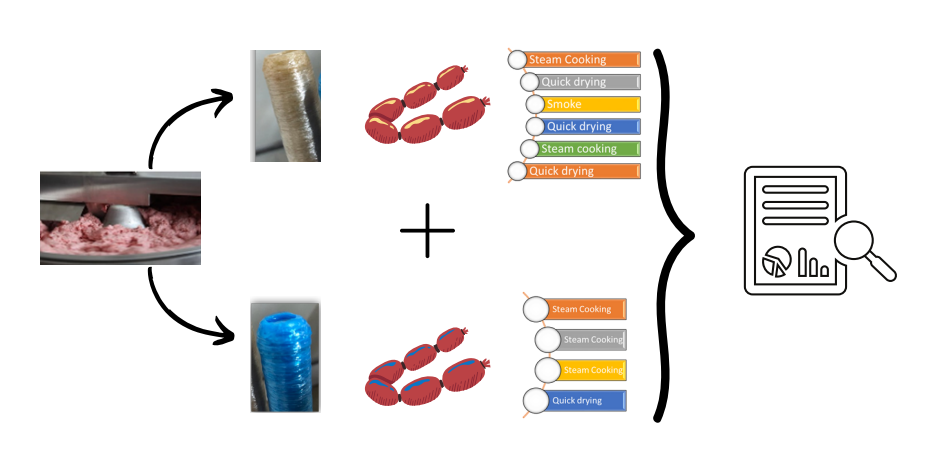
Nowadays, resource efficiency is critical for sustainability. This study investigates the use of high moisture barrier plastic casing as an alternative to traditional cellulose casing in sausage production, based on various innovative initiatives for sausage production by many casing suppliers. The plastic casing significantly reduces water loss during processing, leading to positive environmental and economic impacts. Various parameters including texture, shelf life, color analysis, and casing durability were examined. Results show no significant differences in chemical composition between products with plastic casing and those with traditional casing. However, texture analysis revealed differences, particularly in adhesiveness and springiness. Significant color variations were also observed. The study anticipates substantial water savings and energy conservation through the use of plastic casing, with a projected reduction in water consumption of 3,680 tons per month and energy savings of 1.36 kWh/ton through oven program optimization. This study demonstrates that the high moisture barrier polyamide casing can be used as an alternative.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3100 Keywords Cellulose Casing moisture barrier polyamide Casing Sausage formulation plastic Casing process parameters DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.72) The Impact of Coating Materials Obtained from Alternative Starch Sources on the Quality of Processed Chicken Meat Products
When preparing coated mixtures, the production involves coating, frying, and cooking stages. During these stages, deep frying in oil is a fundamental process that affects the surface parameters of the coated product. Deep frying in oil above the boiling point of water (150-160°C) is maintained for approximately 25-30 seconds, resulting in rapid evaporation of water due to the formation of a crust on the product surface, hindering the escape of steam. Accumulated intense steam creates cracks in the crust, allowing steam to escape, along with oil absorption. Gelatinization of starch components occurs during this process. Starch consists of intertwined amylose and amylopectin. These spiral shapes, with hydrophobic interiors and hydrophilic exteriors, facilitate the formation of complexes of lipids with hydrophobic cavities. Particularly, the use of starches with high amylopectin content has been observed to enhance crispiness in coated products. While high-amylose corn starch contains 85% amylose, the amylopectin content in waxy corn is 99%. This study examines the product texture properties, lipid peroxidation value (TBARS), oil absorption rates during frying, and sensory analysis values of commonly used starch types in the industry (waxy corn, modified corn, modified tapioca, modified wheat, and modified potato starches). Significant differences were observed in texture, oil absorption during frying, and sensory analysis results (appearance, color, texture, crispiness, greasiness, flavor, overall acceptance) (p=0.05) among the starch types, whereas no significant difference was observed in peroxidation values. According to the data obtained from the texture analyzer, products made using modified corn and waxy corn starches exhibited better crispiness, brittleness, hardness, and chewiness parameters compared to other starch types. In sensory analysis results, various parameters were found to be weaker in starches other than waxy corn starch. When comparing oil absorption rates during deep frying, modified tapioca absorbed the most oil, while waxy corn absorbed the least, with no significant difference observed among other starch types (p=0.05). Based on this study, it is anticipated that modified corn and waxy corn starches may provide advantages over other evaluated starch types in terms of both structural and oil absorption properties. This presumption could be attributed to the high amylopectin content, although it requires support from microscale analyses.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3102 Keywords Starch deep Frying coating poultry further process meize DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.73) Different Salt Concentrations and Ascorbic Acid Effect on Germination of Blue Skullcap (Scutellaria lateriflora) Plant
One of the most important stress factors affecting agricultural production in the world and in our country is soil salinity. This effect has constantly increased today, causing a decrease in efficiency and quality in many products. The main reason that triggers this situation is unconscious irrigation and evaporation [1]. Under salt stress, ascorbic acid plays an important role in growth regulation and plant metabolism, increasing the accessibility of water and nutrients [2]. Application of non-enzymatic antioxidant molecules such as ascorbic acid is considered an alternative way to reduce the negative effects of salt stress on plants [3]. In this research, it is aimed to determine the effect of ascorbic acid (AsA) application on germination and some physiological parameters of blue skullcap (Scutellaria lateriflora L.) seeds applied with different salt (NaCl) concentrations. This salts and AsA concentrations are taken as 0, 50, 100 and 150 mM. Analytical grade NaCl is used to create salt stress. Before germination, the seeds are subjected to surface sterilization in 5 % sodium hypochlorite solution for 10 minutes [4]. Surface sterilized seeds are kept in AsA solutions of different concentrations for priming for 12 hours [5] and then they are dried on drying papers at room conditions for 24 hours until they return to their previous moisture content. 20 seeds are placed in petri dishes containing double-layer filter paper and soak with 10 ml of solution from each of the different salt concentrations separately. In this research, germination rate (%), germination time (days), root length (cm) and stem length (cm) criteria are examined. As a result of this research, it is determined that increasing salt concentrations have a negative effect on germination. With the application of 100 mM AsA, the highest germination rate is found to be 91 %, germination time is 5.89 days, root length is 1.7 cm and stem length is 2.4 cm. It has been determined that AsA application at optimum level can have a positive effect on the germination of the blue skullcap plant in saline conditions.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3111 Keywords Scutellaria lateriflora ascorbic acid (AsA) NaCl DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.74) Cell-Based Crustacean Meat: Commercial Species, Cell Isolation Methods, and Culture Conditions
Cellular agriculture, defined as the production of agricultural products from cell cultures rather than whole plants or animals, is gaining traction as a solution to public health, environmental and animal welfare concerns associated with traditional animal agriculture. In this context, the possibility of producing seafood from fish cell cultures emerges as a promising way to overcome similar challenges in aquaculture. This review focuses on the specific area of cell-based crustacean meat by examining the selection of commercial species, techniques for isolating cells, and optimal conditions for cell culture. In light of growing concerns about sustainability in aquaculture, cellular agriculture is emerging as a potential solution. The review addresses advances and challenges in the field of cultured seafood, with a strong focus on crustacean cell culture, and also interests include various methods for isolating cells, optimizing culture conditions, formulating growth media, and implementing sustainable practices. The review highlights the importance of further research and innovation in crustacean cell culture. It is emphasized that for successful commercialization, it is necessary to develop suitable cell lines, improve growth conditions and ensure consumer acceptance. Overall, this review highlights the critical role of developing the field of cultured crustacean meat to promote sustainable seafood production.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3113 Keywords Cellular aquaculture cultivated seafood crustacean cell culture DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.75) Cellular Seafood: Current Challenges to Overcome in The Development of Cellular Seafood
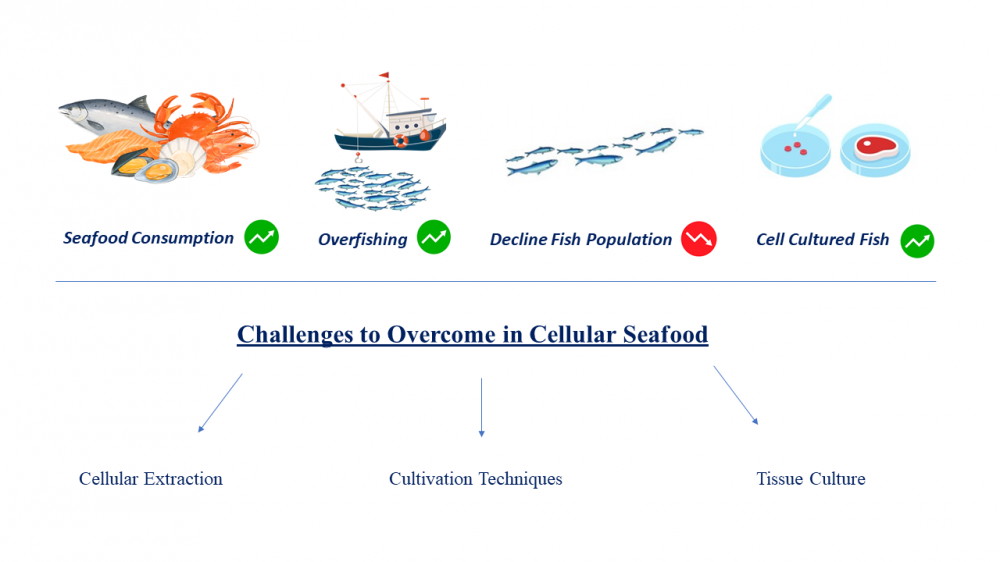
Worldwide, seafood accounts for nearly 20% of annual animal protein consumption, and its production is critical to ensure global food and nutrition security. The increase in seafood demand has resulted in overfishing and caused a decrease in aquatic species. Aquaculture or fish farming, includes breeding, growing, and harvesting fish and aquatic products in a controlled environment; It is the first solution to overfishing. To supply sufficient seafood for the growing demand, the alternative seafood industry provides promising opportunities. Cell-based seafood refers to seafood that is produced using cell and tissue culture without sacrificing the animal. This method, called cellular agriculture, has been adopted from regenerative medicine that uses advanced cellular extraction and cultivation techniques of fish cells and tissue culture. To serve as a credible alternative to traditional seafood, cellular seafood should be efficiently produced and should mimic meat in all of its physical sensations, such as visual appearance, smell, texture and of course, taste. The efficient culture of cells used for production of cellular seafood primarily depends on stem cells, cell culture conditions including incubation temperature and medium composition. Many of these variables are known and optimized for each production line, but their interactions are numerous and need to be optimized. Overall, this review underscores the importance of further research in cell culture to advance the field of cultured seafood and promote sustainable seafood production.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3114 Keywords Cellular seafood stem cells seafood alternatives cell culture DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.76) Medicinal Use and Chemical Composition of Scutellaria baicalensis Species
This work deals with the medicinal use and chemical composition of the Scutellaria genus. The Scutellaria genus, which belongs to the Lamiaceae family, is represented by approximately 360 species. In Turkey, the Scutellaria genus includes 15 species belonging to 4 sections and a total of 21 subspecies of these species [1,2]. Scutellaria baicalensis, known also as Huang-Qin is a traditional Chinese plant used in medicine for at least 2000 years. The plant is widely distributed in Japan, Korea, Mongolia and Russia, and is listed in Chinese Pharmacopoeia, European Pharmacopoeia and British Pharmacopoeia [3]. Medicinal plants in the Scutellaria genus are used in the treatment of various diseases such as gastrointestinal diseases (dysentery, hemorrhoids, stomach pain, constipation), liver and bile diseases (jaundice, hepatitis), neurological diseases (including epilepsy, spasm, insomnia, hysteria). It is also stated in the literature that it is also used in respiratory diseases (colds, respiratory tract infections), infectious diseases (carbuncles, furunculosis) and traumatic injuries It has been stated that some species of Scutellaria have a long history as traditional and herbal medicine to treat many diseases such as cancer, liver and stomach disorders, respiratory, neurological, cardiovascular diseases and infection [4]. It has been stated that S. baicalensis has a very good antioxidant activity thanks to its rich flavonoid content [5]. Some of the diterpenes in the Scutellaria genus are scutesiprine and barbatin A-E, and their compounds have been stated to have anticancer effects [6,7]. The main bioactive compounds of S. baicalensis are flavonoids. The total flavonoid content in plant roots varies between 15-20 %. Flavonoids are 12-16 % baikalin, baikalayin, norvoginin, oroxylin A, β-sitosterol and 3-4 % vogonocyte [8].
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3115 Keywords Scutellaria baicalensis medicinal uses DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.77) From Child Development to Country Development with Food

One of the main factors affecting the development level of countries is having well-educated individuals. The growth, development, health and productivity of well-educated individuals depend on adequate and balanced nutrition. Adequate and balanced nutrition; It is the intake of all the nutrients that the body needs for the development, renewal and functioning of tissues in sufficient and necessary proportions and their appropriate use in the body. Adequate and balanced nutrition not only meets human physiological, psychological and sociological needs, but also contributes to physical and cognitive development [1, 2]. The most important feature that distinguishes humans from other living creatures is their ability to use their brain in cognitive events. The brain, which begins to develop from the womb, undergoes a development process depending on internal and external factors. One of the most important factors in this process is healthy and quality nutrition. Nutrition is extremely important in a child's mental and cognitive development as well as physical development. The brain, one of our most important organs for cognitive development, completes two-thirds of its development in childhood between the ages of 0-6. The experiences gained during this period are the starting point of human development and determine the way the brain works. Cognitive thought; It includes the development of functions such as thinking, memory, learning, perception and attention. Cognitive development is also a determinant of success in childhood and later years. Studies have proven that cognitive development depends on adequate and regular nutrition as well as genetics [3, 4]. With this development starting from early childhood, depending on adequate and regular nutrition, the contribution of well-educated individuals to the development of the country will undoubtedly increase.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3116 Keywords Child Development country Development cognitive thought DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.78) Developing an Emulsifier/Stabilizer Blend for UHT Pudding Production by Using Encapsulation Technique
Given today's lifestyle, economic system, and technological and social structure, processed food products are frequently consumed, making the use of food additives necessary. Stabilizers and emulsifiers are used in food production to create the desired structure, and maintain or improve a certain structure, providing many benefits in food production and attracting more attention from producers. With the increasing consumption of ready-to-eat dairy desserts in recent years, this research aims to achieve a stable and high-quality final product in the industrial-scale production of pudding products. In the first stage of the study, the correct ratio of stabilizer and emulsifier mixture was determined to obtain a blend that would provide maximum efficiency and benefit. Particle size, zeta potential, and viscosity control analysis were conducted to stabilize the gums at the created recipes. This allowed the determination of the product's quality characteristics. In addition, a final product was produced and sensory evaluations were conducted with the target market's product. After the most suitable recipe content was determined as Xanthan gum, carrageenan, and monodiglycerides as fatty acids, in the second stage, Microfluidizer and ultrasound methods were tried for the homogeneous mixture of stabilizer-emulsifiers before encapsulation. After observing the adverse effects of high pressure on the product texture, different pressure applications were applied with the homogenizer, and the optimum pressure for reaching the target product was determined to be 30 mPa. In the encapsulation stage, the homogenized mixture was fed to the spray dryer, and drying parameters were determined. The optimum drying parameters were found to be an inlet temperature of 184 °C, outlet temperature of 75 °C, and product feeding temperature of 40 °C. The encapsulated product was then processed into the final product using a pilot UHT pudding application, and the quality parameters defined in the project were evaluated. It was observed that the encapsulated product yielded similar results to the target product.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3118 Keywords Stabilizer emulsifier encapsulation pudding homogenization DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.79) Acetone Extract of Tricholoma scalpturatum (Fr.) Quél Induced Apoptosis in Colon (Caco-2) Cancer Cell Lines
Numerous investigations have reported that mushrooms possess anticancer activities. For several decades, mushrooms have been approved as food additives against cancer particularly in Japan and China [1]. Since cancer incidence increases yearly, researchers have increased searching for effective anticancer compounds from mushrooms. This research explores the cytotoxic potential and apoptosis mechanisms of the acetone extract of edible Tricholoma scalpturatum (Fr.) Quél. mushroom against colorectal cancer (Caco-2) cell lines [2,3]. The MTT 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) assay was employed to assess the cytotoxic activity to find the effective concentration (EC50) value. The apoptotic effect was evaluated through three methodologies: image cytometry using the Annexin V-FITC/PI apoptosis detection kit, Western Blot analysis targeting apoptosis-associated proteins, and Real-Time PCR (qPCR) to determine mRNA levels of apoptosis-related genes. The extract from T. scalpturatum exhibited a dose-dependent suppression of Caco-2 cell lines proliferation, with an EC50 value of 46.86±2.01 µg/mL. The image cytometry results showed that Tricholoma scalpturatum acetone extract stimulated 6.75-fold apoptotic cells compared to the control group. According to the real-time PCR analysis, the acetone extract increased the expression level of the BAX gene 2.71-fold while it decreased the expression of the BCL-2 gene 1.90-fold (p<0.05) compared to the control group. Moreover, the extract also notably increased mRNA expressions of Caspase 3, 8, and 9 (5.46, 4.46, and 3.01-fold, respectively). Results were normalized using GAPDH (glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase). In addition, the anti-apoptotic BCL-2 protein level was significantly decreased. However, BAX, Caspase 3, 8, and 9 protein levels were significantly induced as a result of extract treatment. Apoptosis involves both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways regulated by various genes. Since the acetone extract appears to induce apoptosis by affecting both pathways, isolation of bioactive compounds should be performed as further investigations.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3129 Keywords Tricholoma scalpturatum apoptosis cytotoxicity colon cancer (Caco-2) cell lines DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.80) Food Irradiation for Food Safety and Its Legislation in Turkey
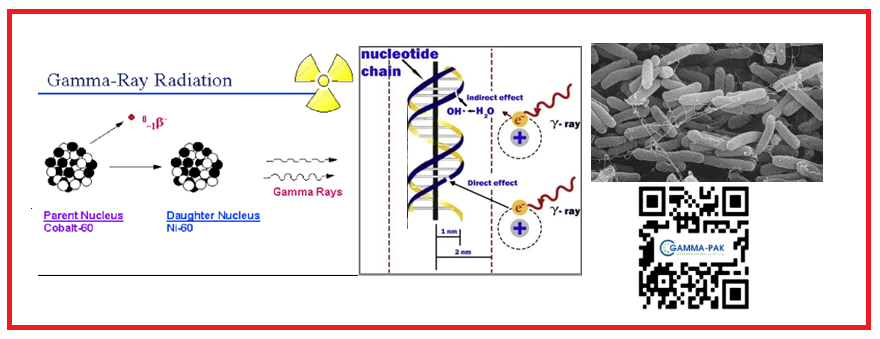
Food irradiation is the processing of food products by ionizing radiation in order to improve the microbial safety and quality of many foods. The World Health Organization recommends food irradiation as one of the most important methods to fight the increasing trend in the incidence of foodborne diseases. Food irradiation starts in the 1920's but is used effectively after the 1980's. Today in the world over 70 countries use this technology for food preservation: Disinfestations and disinfection. Turkey's Food Irradiation Regulation was published in 1999 [1]. Some of the provisions of the Regulation were revised in 2019 in accordance with the regulation of the European Union. This regulation is based on 7 food groups and the maximum overall average absorbed dose is accepted as 10 kGy. These food groups are:1. bulbs, roots and tuber, 2. fresh fruits and vegetables, 3. cereals, nuts, oil seeds, pulses, dried vegetables and fruits, 4. raw or processed fish and frog legs, 5. poultry meat, and red meat (fresh or frozen), 6. dry vegetables, spices, herbs, condiments and herbal teas, 7. dry food of animal origin [2]. When food is irradiated; DNA of parasites, insects, and disease-causing microorganisms such as E. coli, Campylobacter, and Salmonella breaks the bonds in molecules, that is, creates DNA damage. After DNA damage occurs, living things cannot repair the broken bonds, die or cannot reproduce. Thus, consumers are protected from foodborne diseases and the shelf life of foods is extended [3]. Thayer and Boyd [4] studied the irradiation resistance of S.typhimurium in mechanically deboned chicken meat. They observed that the number of viable cells per gram of meat was reduced by 2.8-5.1 log10 CFU/g at 0 °C when doses of 1.5-3.0 kGy were applied. Thayer et al. [5] reported that chicken wings inoculated with 103 or 104 CFU/g of S.typhimurium and then irradiated at 2.7 kGy contained no detectable viable cells. At a dose of 1.8 kGy, there was an estimated 19% survival rate. Narvaiz, et al. [6] studied the effects of gamma irradiation at 20 °C on inactivation of microflora in egg powder. A dose of 2.0 kGy inactivated Salmonella (positive in 25 g of non-irradiated powder) [7]. For this reason, the biggest advantage of the technology is that although microorganisms and insects become resistant to chemicals, they cannot become resistant to irradiation [8].
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3028 Keywords Ionizing radiation gamma irradiation food irradiation DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.81) Determination of Sugar in Honey Samples Using NMR Spectroscopy and Chemometric Methods
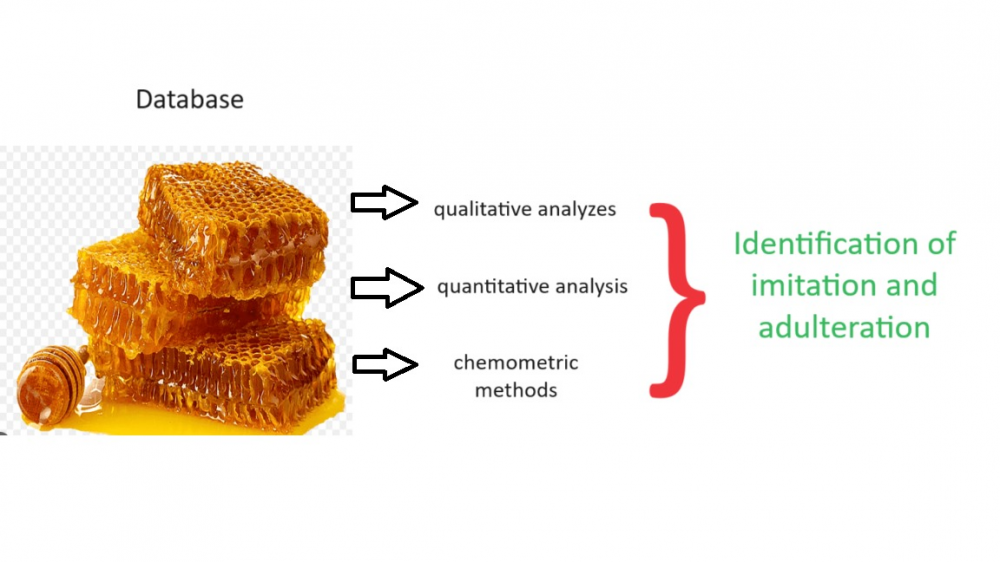
Honey is a complex food that is produced by the processing of plant or animal secretions by bees in their metabolism and contains an average of 200 different biomarkers. It is well known that this food consists of approximately 80% sugar components, depending on its botanical origin. Due to the high economic value of the commercial honey, the amount of honey is increased by adulterating it in different ways, and some samples are fake honey that is not produced naturally and is produced only from various sugar syrups. In order to determine the adulterants in honey the following techniques are currently used: water-insoluble solids, pollen number and type examination, 13C/12C isotope examination, and C4 sugar determination. However, there is a need to develop these techniques or introduce new innovations to be sure from the adulteration [1]. Recently, the presence of adulterated sugar in honey has become detectable by 1 H-NMR (Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) spectroscopy by using the honey profiling method [2] developed by Bruker Corporation in studies carried out to determine adulteration elements in honey. The method allows a comprehensive holistic evaluation of honey samples by using qualitative-quantitative and chemometric analysis methods by using its database created using approximately 28,500 reference honey samples. The method determines suitability by comparing sugar composition, acid composition, and markers of fermentation products with the quantitative values in the reference database of it, on the other hand, it also uses chemometric analysis methods on sugar groups. Thus, it can compare sample contents with the database. However, although the analysis method in question works with a high accuracy rate depending on its own database, it has not yet been revealed how successful it is in representing honey contents produced in narrower locations or different flora. In this study on the creation of an NMR library in which honey produced in Türkiye is also represented are reported.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3154 Keywords NMR adulteration honey chemometry DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.82) Production of Food Industrial Enzymes from Recombinant Microorganisms
Enzymes are widely used in food processing and the production of food ingredients. Early efforts to extract enzymes from culturable microorganisms, plants, and mammalian tissues were generally not well adapted to the conditions used in modern food production methods. The use of recombinant DNA technology has made it possible to produce new enzymes suitable for specific food processing conditions. Such enzymes can be discovered by screening microorganisms sampled from various environments or can be developed by modification of known enzymes using modern methods of protein engineering or molecular evolution. As a result, several important food-processing enzymes, such as amylases and lipases, have become available with properties adapted to specific food applications. Another important achievement is the improvement of microbial production strains. For example, several microbial strains recently developed for enzyme production have been engineered to increase enzyme yield by deleting natural genes encoding extracellular proteases. Thanks to recombinant DNA technology, it is now possible to produce highly efficient enzymes suitable for specific food processing conditions. By applying genetic engineering tools, the desired enzyme gene is cloned and expressed on a large scale in the host microorganism. Several genetically modified microbial strains have been developed for enzyme production, which promotes increased enzyme yield as well as elimination of secondary metabolite production. This talk will cover the basic strategies of cloning and expression of recombinant food processing enzymes in Pichia pastoris. It also includes the general structure and characteristics of Pichia host strains and the associated advantages and disadvantages of their use.
DOI http://doi.org/10.25135/rfac.2024.3rd.3132 Keywords Recombinant enzymes Pichia pastoris food enzymes DETAILS PDF OF ARTICLE © 2024 ACG Publications. All rights reserved.